
Orginally Written by Aditya Shastri
Updated on Feb 12, 2026
Share on:
Nike's business model is built on innovation, strong branding, and customer engagement. This strategy allows them to offer high-quality athletic gear while maintaining strong profit margins and market dominance.
Nike achieves this by optimising its supply chain, leveraging global distribution networks, and focusing on cutting-edge technologies. The secret to its success lies in continuous product innovation and strategic marketing.
About Nike
Nike, founded in 1964 by Bill Bowerman and Phil Knight, is a leader in athletic apparel and footwear. The company revolutionised sportswear by combining innovation, style, and functionality. With annual revenue exceeding $50 billion in 2023 and operations in over 190 countries, Nike dominates the sportswear market.
Its core philosophy centres around performance, innovation, and sustainability. Nike focuses heavily on customer experience, offering personalised products, leveraging digital technologies like Nike Training Club, and offering exclusive membership benefits.
The brand is known for its iconic Just Do It slogan and its partnerships with top athletes and teams. Nike's secret to success is its ability to continuously innovate while fostering brand loyalty through effective marketing and global outreach.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Founded | 1964 |
| Founder | Bill Bowerman, Phil Knight |
| Headquarters | Beaverton, Oregon, USA |
| Industry | Sportswear & Footwear |
| Revenue (2023) | $50 billion |
| Presence | 190+ countries |
| Employees | 79,100 (2023) |
| Popular for | Athletic footwear, apparel, innovation |


Learn Digital Marketing for FREE


How does Nike make money?
1. Revenue Stream Breakdown:
- Product Sales: Nike generates the bulk of its revenue through direct sales of shoes, apparel, and equipment (70%)
- Nike Memberships & Subscriptions: Subscriptions, including services like Nike Training Club, contribute to 10% of revenue
- Licensing & Partnerships: Deals with retailers and athletes provide additional income
- Advertising Revenue: Nike also generates income from sponsorships and advertisements
2. Revenue Contribution:
Product Sales (70%), Memberships & Subscriptions (10%), Licensing & Partnerships (15%), Advertising Revenue (5%).
3. Pricing Strategy:
Nike uses a premium pricing model, which allows it to target high-income consumers and athletes while maintaining market positioning as a premium brand.
Nike’s marketing strategy has been pivotal in shaping its dominant position in the sportswear market through influential campaigns and sponsorships. Tap on the link to learn more.
Nike's Business Model Canvas
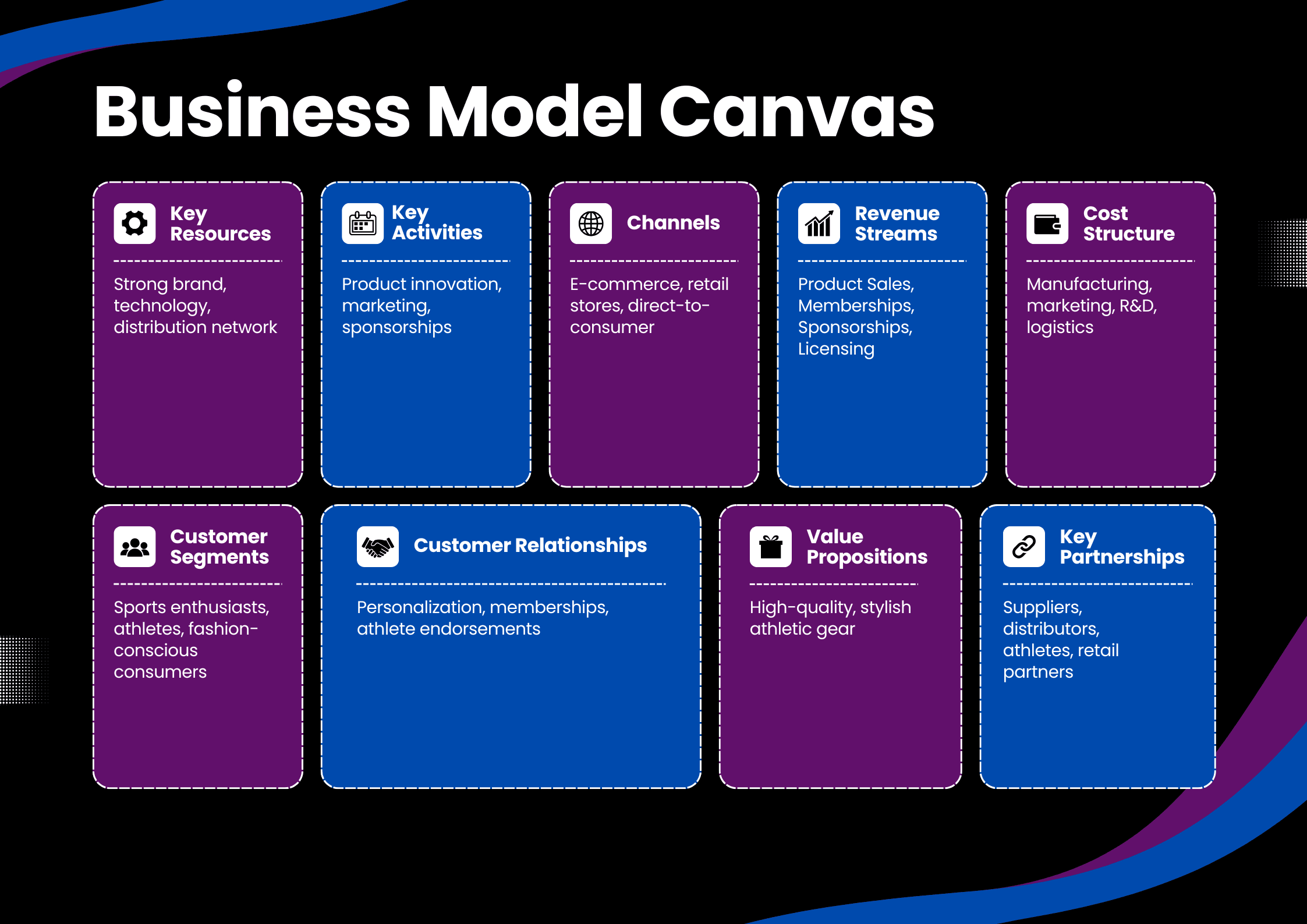
Nike's Value Proposition
- Nike’s value proposition centres on delivering high-performance athletic products that combine style, innovation, and sustainability.
- Unlike other sportswear brands, Nike uses cutting-edge technology in product design, ensuring that athletes achieve peak performance while maintaining comfort.
- The brand’s emotional appeal lies in empowering customers to reach their full potential, symbolised by its iconic "Just Do It" slogan.
- Functionally, Nike provides durable, long-lasting products that optimise performance, while also delivering value through personalised experiences like the Nike Training Club app.
- Nike differentiates itself by offering exclusive access to limited-edition products and athlete-driven endorsements.
- Whether it's delivering the latest sneaker technology or sustainability-focused designs, Nike continuously adapts to consumer needs, positioning itself as a global leader in both product excellence and customer loyalty.
Nike's Revenue Model
- Nike primarily generates revenue from product sales, including footwear, apparel, and equipment, accounting for 70% of total income.
- Memberships and subscriptions (Nike Plus, Nike Training Club) contribute 10%, while licensing and partnerships generate an additional 15%.
- Finally, advertising and sponsorships contribute 5%. The brand maintains a strong online presence, with a growing portion of revenue derived from eCommerce channels, supplemented by physical retail stores.
Nike's Cost Structure
- Nike’s major expenses include logistics, manufacturing, marketing, and research and development (R&D).
- The company saves costs through automation, outsourcing manufacturing, and leveraging economies of scale.
- Nike invests heavily in brand promotion and digital innovation while keeping operating margins strong through efficient supply chain management and bulk production.
- Its cost-saving strategies help balance its premium pricing strategy.
Nike's Customer Segment
- Nike operates primarily in a B2C model, catering to young, active, and health-conscious individuals.
- The target demographics include 18-34-year-olds, both men and women, globally, with an income level from middle to high-income.
- Customers are often athletes, fitness enthusiasts, and fashion-forward individuals looking for performance and style.
- Nike also appeals to early adopters and millennials, who value innovation and sustainability in their products.
Distribution Channels of Nike
1. Physical Retail Presence
Nike maintains a strong physical footprint through a mix of owned and partner-operated locations:
- Flagship Stores: These high-profile locations serve as major brand hubs in key global markets, offering the full Nike experience.
- Franchise Networks: Nike utilizes a network of franchises to bolster its presence and reach across different regions efficiently.
2. Digital and Online Platforms
The brand has built a powerful online ecosystem to drive global accessibility:
- E-Commerce Website: A primary digital storefront where customers can browse and purchase products directly.
- Mobile Apps: Nike uses dedicated apps to facilitate shopping and deepen brand loyalty.
- Third-Party Platforms: To maximize reach, Nike integrates with major online marketplaces like Amazon to meet customers where they already shop.
3. Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Strategy
Nike focuses heavily on selling directly to the end user:
- Direct Sales Channels: By prioritizing its own stores and digital platforms, Nike maintains better control over the brand experience and customer data.
- Engagement Tools: The brand uses innovative technology, such as AR (Augmented Reality) apps, to make the shopping process more interactive, personalized, and seamless.
4. Omnichannel Integration
- Nike employs an omnichannel strategy, which means it bridges the gap between the physical and digital worlds.
- This integration ensures that whether a customer is shopping on their phone or standing in a flagship store, the experience is unified and consistent.
Nike's Key Partnerships
Nike’s partnership strategy focuses on four key areas to drive innovation and global reach:
- Athlete and Team Collaborations: Nike partners with top-tier athletes and sports teams to enhance its market reach and drive product innovation through high-profile endorsements and professional feedback.
- Retail and Technology Partnerships: The brand collaborates with retailers and technology partners to improve global distribution and gain access to cutting-edge technologies, ensuring a seamless experience for customers.
- Manufacturing and Supply Chain: Nike works closely with key suppliers, particularly manufacturing partners in Asia, to produce its goods efficiently and maintain a strong, reliable supply chain.
- Sustainability and NGO Alliances: Nike maintains strong partnerships with NGOs and sustainability-focused organizations. these collaborations are essential for reducing the brand's environmental footprint and supporting its long-term sustainability initiatives.
Interested in similar reads? Consider a SWOT analysis of Nike which will help to understand the company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in the competitive sportswear industry.
SWOT Analysis of Nike
| Strengths | Weaknesses | Opportunities | Threats |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strong brand equity | High manufacturing costs | Expanding digital presence | Rising competition |
| Product innovation | Reliance on external suppliers | Global market expansion | Changing consumer preferences |
| Athlete endorsements | Vulnerability to counterfeits | Eco-friendly innovation | Economic downturns |
Key Takeaways for Students/Marketers & Conclusion
- Nike’s scalable business model relies heavily on strong branding and continuous product innovation
- Smaller businesses can replicate Nike’s customer-centric approach by focusing on personalised experiences and innovation
- Nike's mindset revolves around creating emotional connections with customers while maintaining premium product quality and leveraging data-driven insights
Nike’s business model thrives on its global presence, innovation, and ability to adapt to consumer demands. As the market evolves, Nike’s continuous focus on technology and sustainability positions it for future success, with an ability to adapt to emerging trends and maintain its market leadership.
Want to Know Why 2,50,000+ Students Trust Us?
Dive into the numbers that make us the #1 choice for career success

MBA - Level
Best For
Fresh Graduates
Mode of Learning
On Campus (Mumbai & Delhi)
Starts from
Mar 23, 2026
Duration
11 Months
Live & Online
Best For
Working Professionals
Mode of Learning
Online
Starts from
Mar 6, 2026
Duration
4-6 Months

Online
Best For
AI Enthusiasts
Mode of Learning
Online
Duration
5 Months

Offline
Best For
12th Passouts
Mode of Learning
On Campus (Mumbai)
Duration
3 Years
Recent Post
You May Also Like
Nike’s main products include athletic footwear, apparel, and equipment for various sports and activities.
Nike’s top competitors include Adidas, Puma, Under Armour, New Balance, and Reebok.
Nike uses advanced materials, wearable tech, and digital platforms to enhance product performance and customer experience.
Nike holds approximately 27.4% of the global sportswear market.
Nike’s CSR initiatives focus on sustainability, community support, and diversity and inclusion through programmes like Move to Zero and the Nike Community Impact Fund.
Nike markets its products through inspirational storytelling, athlete endorsements, digital marketing, and social media engagement.
Aditya Shastri leads the Business Development segment at IIDE and is a seasoned Content Marketing expert. With over a decade of experience, Aditya has trained more than 20,000 students and professionals in digital marketing, collaborating with prestigious institutions and corporations such as Jet Airways, Godrej Professionals, Pfizer, Mahindra Group, Publicis Worldwide, and many others. His ability to simplify complex marketing concepts, combined with his engaging teaching style, has earned him widespread admiration from students and professionals alike.
Aditya has spearheaded IIDE’s B2B growth, forging partnerships with over 40 higher education institutions across India to upskill students in digital marketing and business skills. As a visiting faculty member at top institutions like IIT Bhilai, Mithibai College, Amity University, and SRCC, he continues to influence the next generation of marketers.
Apart from his marketing expertise, Aditya is also a spiritual speaker, often traveling internationally to share insights on spirituality. His unique blend of digital marketing proficiency and spiritual wisdom makes him a highly respected figure in both fields.