
Orginally Written by Aditya Shastri
Updated on Feb 12, 2026
Share on:
KFC’s business model revolves around its iconic fried chicken, franchise operations, and convenience. This strategy allows them to offer delicious meals globally while maintaining operational efficiency.
KFC achieves this by optimizing its supply chain and expanding its global reach through franchising. The brand’s widespread presence drives continuous revenue growth and market dominance.
In this blog, we decode KFC's revenue model and strategy, shedding light on how it has achieved global success.
About KFC
KFC (Kentucky Fried Chicken) was founded in 1952 by Colonel Harland Sanders in Louisville, Kentucky, with the goal of offering high-quality, delicious fried chicken. Known for its secret blend of 11 herbs and spices, KFC quickly became a global phenomenon.
Today, KFC operates over 24,000 outlets in more than 145 countries, generating an estimated revenue of $30 billion in 2024. Its key selling point lies in the unique recipe and focus on offering delicious and affordable meals. KFC’s franchise model allows rapid expansion while maintaining product consistency worldwide.
The company’s ethos revolves around providing high-quality, tasty meals that customers can rely on. Customers enjoy fast, friendly service in a family-friendly environment, with a menu designed for convenience and affordability.
KFC’s secret to success is its ability to combine a unique product offering with an efficient, scalable business model that has sustained global growth for decades.
Summary Table
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Founded | 1952 |
| Founder | Colonel Harland Sanders |
| Headquarters | Louisville, Kentucky, USA |
| Industry | Fast Food, Quick-Service Restaurant (QSR) |
| Revenue (2024) | $30 Billion (estimated) |
| Presence | 24,000+ outlets in 145+ countries |
| Employees | 800,000+ globally |
| Popular For | Original Recipe Fried Chicken |
How Does KFC Make Money?
Revenue Stream Breakdown:
KFC generates revenue through product sales, franchise royalties, and home delivery services. The core revenue is from fried chicken, sandwiches, and sides, with additional income from franchises and delivery.
Revenue Contribution:
Product Sales: 70-75%
Franchise Revenue: 20-25%
Services (Delivery, Catering): Small portion
Pricing Strategy:
Value-Based Pricing: Offering affordable meals with premium options like family buckets.
KFC Value Proposition
- KFC's value proposition is built on offering high-quality fried chicken made from a secret blend of 11 herbs and spices, setting it apart from its competitors.
- This unique recipe keeps customers returning for the distinctive taste and quality. KFC’s diverse menu caters to all customer needs, offering affordable individual meals as well as family-sized servings.
- The company’s global presence allows it to maintain consistency in product quality across its outlets, ensuring that every meal meets the same high standards, whether in the US or international markets.
- Emotionally, KFC’s brand connects with customers by offering a nostalgic, family-friendly dining experience. The company creates a sense of comfort with every meal, reinforcing brand loyalty.
- KFC’s competitive advantage lies in its proprietary recipe, scalability through franchising, and its ability to deliver consistent quality across global locations, making it difficult for competitors to replicate at such a scale.
KFC Revenue Model
- KFC generates revenue from product sales, primarily fried chicken, sandwiches, and sides, which account for 70-75% of total revenue.
- Franchise royalties and fees contribute 20-25%, with additional revenue from services such as home delivery and catering.
- The company’s franchise model enables rapid global expansion while maintaining consistency, ensuring a steady income flow from both product sales and franchise operations.
KFC Cost Structure
- Major Expenses: KFC’s primary expenses include food sourcing, manufacturing, logistics, and marketing.
- Cost-Saving Strategies: KFC leverages economies of scale, bulk purchasing, and supply chain optimization to reduce costs. The brand also invests in automation for food preparation to increase efficiency.
- Maintaining Healthy Margins: KFC maintains healthy margins by focusing on its franchise-driven revenue model, allowing it to scale efficiently while keeping operational costs low.
KFC Customer Segment
- KFC serves a wide range of customers, from fast-food enthusiasts to families seeking affordable meals.
- It operates a hybrid B2C and B2B model, offering meals directly to consumers through its outlets and home delivery, while providing franchise opportunities globally.
- Customers are drawn to KFC for its affordable pricing, quick service, and iconic menu items like fried chicken, appealing to both convenience seekers and those desiring a family-friendly dining experience.
Marketing strategy of Jollibee reveals how local adaptation and emotional branding strengthen fast-food business models in global markets.
Distribution Channels of KFC
KFC uses a mix of physical stores and digital tools to make sure customers can get their chicken quickly and easily, no matter where they are.
1. Physical Stores
KFC has over 24,000 locations in 145 countries. These are divided into different types:
- Dine-in Restaurants: These are the classic big stores where families sit down to eat. They are now being updated with digital screens for faster ordering.
- Drive-Thru and Express: These are smaller shops found near highways or gas stations. They focus on serving people who are in a hurry or traveling.
- Smart Pick-up Stores: In 2026, many stores now have automated lockers. You scan a code on your phone, and a locker opens with your hot food inside.
2. KFC’s Own Digital Apps
KFC wants customers to buy directly from them to save on fees.
- The KFC App: This is the most popular way to order. It remembers your favorite meals and gives you points or rewards every time you buy.
- Official Website: This is used for bigger orders, like office parties or family gatherings, and allows people to pay online before they arrive.
3. Omnichannel
KFC connects its apps and its stores so they work together perfectly:
- Order and Collect: You can start your order on the bus and finish it at the store. The kitchen knows exactly when you arrive so your chicken is still crunchy and hot.
- Digital Kiosks: Inside the stores, large touchscreens let you customize your meal without waiting in a long line at the counter.
4. Outside Delivery Partners
To reach even more people, KFC works with other famous delivery companies:
- Delivery Apps: They partner with apps like Uber Eats and DoorDash. This helps them deliver to areas where they don't have their own delivery drivers.
- Delivery-Only Kitchens: In some crowded cities, KFC has kitchens that have no tables or chairs. These locations only cook food for delivery apps to get meals to customers faster.
KFC Key Partnerships
KFC partners with food suppliers, logistics providers, and tech companies like Grubhub and DoorDash for delivery services.
Additionally, KFC collaborates with sustainability organizations to ensure eco-friendly practices.
Its franchise model allows rapid expansion, while strategic partnerships with tech companies enable enhanced customer experiences through digital platforms.
These partnerships contribute to operational efficiency, market expansion, and sustainability within the business.
Marketing strategy of Dunkin Donuts showcases how consistent menu offerings and franchising support rapid international growth.
SWOT Analysis of KFC
| Strengths | Weaknesses | Opportunities | Threats |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strong global brand | High dependence on franchise model | Expansion in emerging markets | Intense competition |
| Iconic recipe | Price sensitivity | Digital innovation | Economic downturns |
| Loyal customer base | Supply chain complexities | Sustainability efforts | Changing consumer preferences |
KFC Competitor Comparison
| Brand | Pricing | Customer Experience | Channel Strategy | Market Focus | Innovation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| McDonald's | Affordable | Fast, consistent service | Strong global footprint | Mass market | Limited tech |
| Popeyes | Mid-range | Quality-focused | Growing online presence | Fast-food lovers | Product innovation |
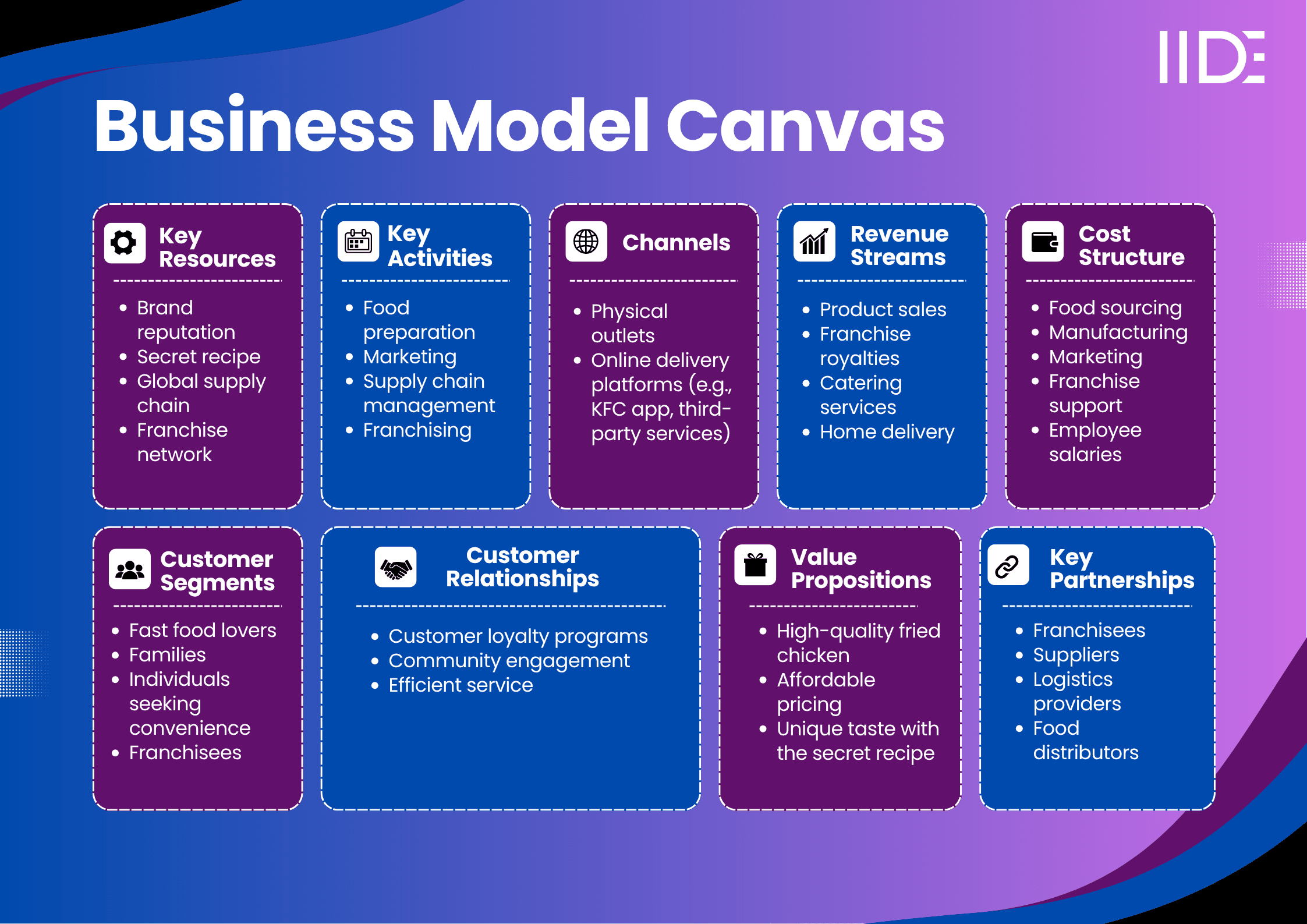
KFC Business Model Canvas
Explore how the marketing strategy of Amul turned a local dairy cooperative into an iconic household name by mastering the art of topical storytelling and the power of an umbrella brand.


Learn Digital Marketing for FREE


What’s New With KFC?
- In 2026, KFC is undergoing a major brand transformation focused on extreme affordability and advanced technology to stay ahead of rising competition.
- A core part of their strategy this year is the global push for $5 Comfort Bowls and the revival of $10 Tuesdays, specifically designed to capture value-seeking diners facing higher living costs.
- Beyond the menu, the brand has introduced its Saucy restaurant concept in urban centers, which features a younger, bolder design with self-service kiosks and DJ-led events to attract Gen Z.
- On the technology front, KFC is now heavily integrated with AI-driven systems through its parent company’s digital platform.
- This includes voice-based AI ordering at drive-thrus to reduce wait times and a revamped loyalty app that uses past order history to send personalized deals.
- Sustainability has also become a visible reality rather than just a goal, with the full rollout of 100% home-compostable packaging and the expansion of eco-friendly flagship stores.
- Even their marketing has taken a playful turn with limited-edition lifestyle merchandise, like the sold-out Bowl-o-Tie, proving that the brand is effectively blending its historical nostalgia with a futuristic, digital-first business model.
Business model of Zomato presents a tech-driven food service approach, offering an interesting contrast to KFC's traditional dine-in and QSR franchise structure.
Key Takeaways for Students/Marketers & Conclusion
Scalable Model
- KFC uses a franchise-first approach to enter new markets quickly without bearing the full financial risk of opening every location.
- By partnering with local business owners, the brand can adapt its store sizes - ranging from large family restaurants to tiny express pods in gas stations, ensuring it fits into any neighborhood.
- To keep the experience the same worldwide, every franchisee must follow a strict 10-week training program and use centralized ingredient sourcing, ensuring the secret recipe tastes identical in London, Mumbai, or New York.
Innovation & Customer Focus
- The brand has shifted from being just a food outlet to a tech-driven service by investing heavily in the KFC app and a personalized loyalty program called the Colonel’s Club.
- In 2026, this includes using AI to suggest meals based on a user's past habits and implementing geofencing, which alerts the kitchen to start cooking only when a customer is physically close to the store for maximum freshness.
- Menu innovation also plays a huge role, as KFC constantly introduces plant-based options and local flavor twists to stay relevant to Gen Z and health-conscious diners.
Efficient Operations
- KFC lowers its expenses by using its massive size to buy chicken, oil, and packaging in bulk at much lower prices than smaller rivals.
- Modern stores now use AI software to predict exactly how many customers will visit each hour, which helps managers prepare the right amount of food and reduces expensive kitchen waste.
- Additionally, the introduction of voice-AI for drive-thru orders and automated lockers for pick-ups speeds up service and reduces the need for large numbers of staff, making the business more profitable.
KFC’s business model is built on product uniqueness, franchising, and customer-centric strategies. With its continued focus on digital innovation and global expansion, KFC is well-positioned for future growth. Will KFC's model continue to define the fast-food industry’s future?
Buyers Persona:

Fareena
Mumbai
Occupation: Student
Age: 18 years
Motivation
Interest & Hobbies
Pain Points
Social Media Presence
Want to Know Why 5,00,000+ Students Trust Us?
Dive into the numbers that make us the #1 choice for career success

MBA - Level
Best For
Fresh Graduates
Mode of Learning
On Campus (Mumbai & Delhi)
Starts from
Mar 23, 2026
Duration
11 Months
Live & Online
Best For
Working Professionals
Mode of Learning
Online
Starts from
Mar 6, 2026
Duration
4-6 Months

Online
Best For
AI Enthusiasts
Mode of Learning
Online
Duration
5 Months

Offline
Best For
12th Passouts
Mode of Learning
On Campus (Mumbai)
Duration
3 Years
Recent Post
You May Also Like
KFC India follows a "Farm-to-Bucket" model, sourcing only from reputed Indian suppliers like Venky's and Godrej, who follow strict international quality and safety standards.
No. KFC India uses only whole muscle chicken (real pieces of chicken) that are breaded and fried fresh in the store.
Yes, recognizing India's large veg population, KFC has a dedicated veg range including the Veg Zinger, Paneer Zinger, and Veg Strips, cooked in separate fryers to avoid cross-contamination.
In many Indian outlets, KFC guarantees that your takeaway order will be ready in 7 minutes, or you get a piece of Hot & Spicy chicken for free.
KFC uses Location-based Pricing. Prices in a premium airport outlet or a high-rent mall in Mumbai might be slightly higher than in a small-town high-street outlet.
As of 2026, KFC India has switched to 100% biodegradable wooden cutlery and paper-based straws and bowls to reduce plastic waste.
Yes, KFC has rolled out "KFC Green" in metro cities, offering plant-based protein that tastes like chicken for vegan and flexitarian customers.
KFC is owned by Yum! Brands, but in India, it is operated primarily by two large franchisees: Devyani International and Sapphire Foods.
Aditya Shastri leads the Business Development segment at IIDE and is a seasoned Content Marketing expert. With over a decade of experience, Aditya has trained more than 20,000 students and professionals in digital marketing, collaborating with prestigious institutions and corporations such as Jet Airways, Godrej Professionals, Pfizer, Mahindra Group, Publicis Worldwide, and many others. His ability to simplify complex marketing concepts, combined with his engaging teaching style, has earned him widespread admiration from students and professionals alike.
Aditya has spearheaded IIDE’s B2B growth, forging partnerships with over 40 higher education institutions across India to upskill students in digital marketing and business skills. As a visiting faculty member at top institutions like IIT Bhilai, Mithibai College, Amity University, and SRCC, he continues to influence the next generation of marketers.
Apart from his marketing expertise, Aditya is also a spiritual speaker, often traveling internationally to share insights on spirituality. His unique blend of digital marketing proficiency and spiritual wisdom makes him a highly respected figure in both fields.