
Orginally Written by Aditya Shastri
Updated on Feb 10, 2026
Share on:
Costco's business model is built on membership‑only wholesale retail with cost‑leadership and treasure‑hunt merchandising. This strategy allows them to offer everyday low prices and high perceived value while maintaining healthy margins via membership revenue and streamlined operations. Costco achieves this by leveraging bulk buying, limited SKUs, and global scale. It uses economies of scale, lean operational costs, and strong membership loyalty.
But what’s the secret behind its market dominance and customer retention? Costco’s loyal membership base and global scale drive consistent growth. In this blog, we decode Costco's revenue model and strategy, shedding light on how it has achieved global leadership and member‑led profitability.
Want next‑level takeaways? Keep scrolling!
About Costco

Founded in 1983 by James Sinegal and Jeff Brotman, Costco was born out of a vision to offer wholesale goods at unbeatable prices to members. Its unique USP: a membership‑only warehouse model combining low prices, limited SKUs, and treasure‑hunt shopping. As of fiscal year 2025, Costco reported net sales of $269.91 billion with net income of $8.10 billion.
With 890 warehouses globally and over 140 million members, Costco enjoys widespread scale and strong customer loyalty.
Its core ethos is value first, evidenced by capped markups (no more than 14-15%) and no advertising spend, aligning with its philosophy of member savings over margins.
Customer experience is characterised by straightforward pricing, efficient stores, and a rotating selection of high‑value products. Members appreciate transparency, quality (especially Kirkland Signature), and low cost. The secret to Costco’s success? A tight‐margin, high‑volume model supported by predictable membership income and operational discipline.
Summary Table
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Founded | 1983 |
| Founder | James Sinegal & Jeff Brotman |
| Headquarters | Issaquah, Washington, USA |
| Industry | Membership warehouse retail |
| Revenue (2023) | $242.29 billion |
| Revenue (2024) | $249.6 billion |
| Presence | 890 warehouses; 91% renewals; 140M members |
| Employees | 333,000 globally |
| Popular for | Low prices, Kirkland brand, bulk offerings |


Learn Digital Marketing for FREE


How does Costco Make Money?
Revenue Stream Breakdown:
Membership Fees (Gold Star & Executive): Recurring income from over 140 million members, contributing more than 65% of operating income in 2024.
Product Sales: Bulk goods and general merchandise, including food, fresh produce, electronics, apparel, and more, account for ~95% of Costco's revenue.
Private Label (Kirkland Signature): Kirkland Signature, Costco’s private label, makes up 33% of total sales, generating around $86 billion in 2024.
Service Revenue: Ancillary services such as pharmacy, travel, optical, and gold bullion contribute a smaller portion of revenue. These services serve as traffic drivers with minimal markup.
Revenue Contribution:
- Membership Fees: Account for approximately 65% of operating income.
- Product Sales (Bulk and Kirkland): Contribute around 95% of net sales.
- Services & Others: The remainder of revenue is from various ancillary services.
Pricing Strategy:
- Costco employs a low-cost pricing model, with product markups capped at ~14% over cost and ~15% for private label products.
- This pricing strategy positions Costco as a value leader, attracting price-conscious customers and enabling high transaction volumes, with membership fees playing a crucial role in maintaining profitability and supporting its business model.
While many retailers struggle to balance scale with speed, our deep dive into the marketing strategy of Walmart reveals how the giant uses 'Everyday Low Prices' and AI-driven logistics to maintain its $600 billion-plus dominance.
Costco Business Model Canvas
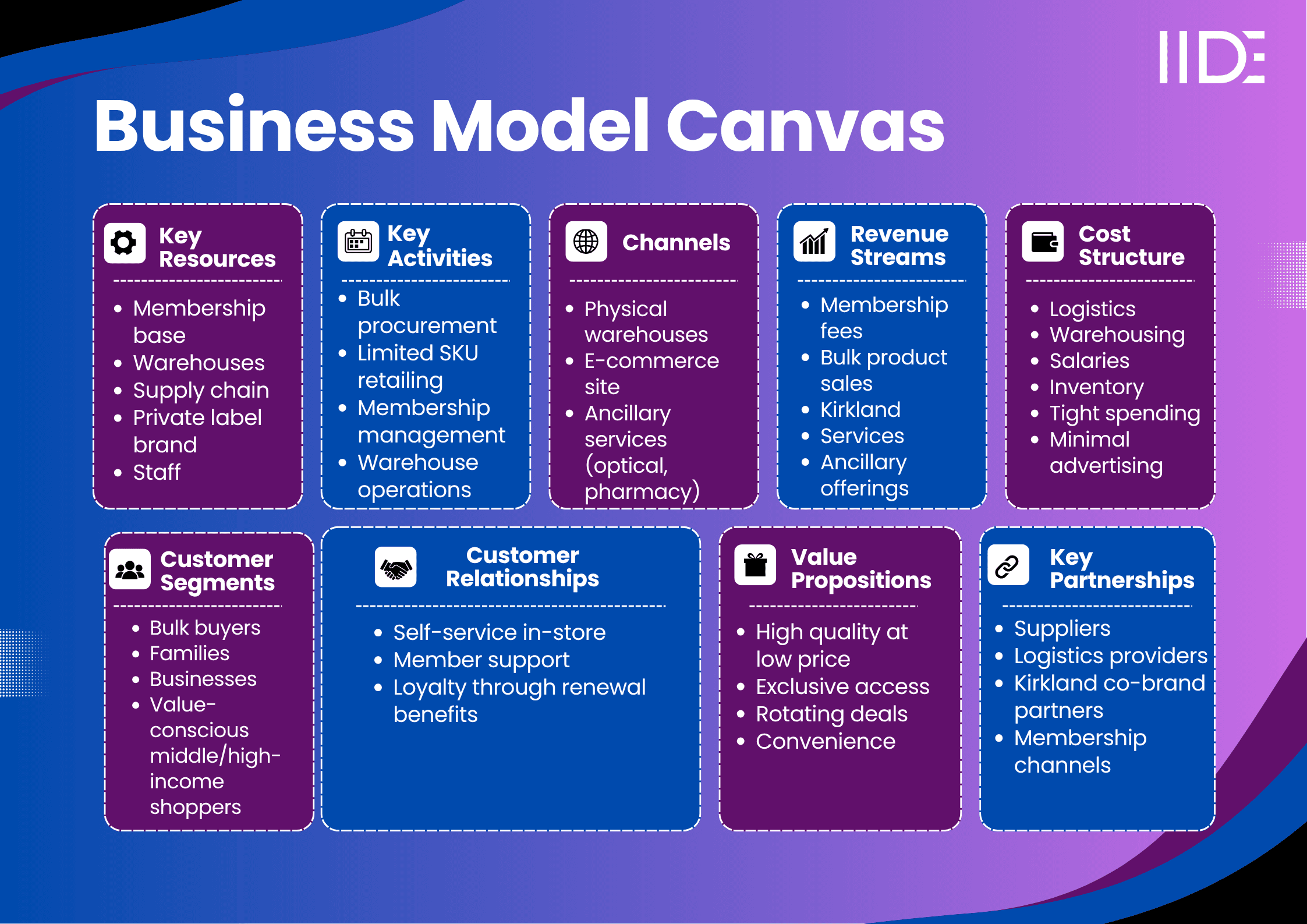
Costco Value Proposition
- Costco’s unique value stems from its membership‑only warehouse club model, which guarantees access to bulk goods at exceptionally low prices per unit.
- This model addresses key customer pain points: affordability and convenience, enabling busy families, small businesses, and value‑driven shoppers to access bulk essentials and high‑quality goods in one stop.
- Emotionally, members enjoy a sense of exclusivity and smart‑shopping pride, buoyed by consistent quality and savings.
- Functionally, Costco delivers speedy checkout, efficient warehouse layouts, and rotating “treasure hunt” merchandise that sparks delight.
- The Kirkland Signature private label ensures trusted quality at lower cost, enhancing confidence.
- Competitively, the firm’s capped markups, zero-advertising policy, and disciplined supplier negotiation create a moat that others cannot easily replicate.
- This enables Costco to sustain low prices while fueling high volume and robust membership loyalty, and keeps competitors at bay.
Costco's Revenue Model
- Costco’s primary revenue streams consist of membership fees (~65% of operating profit) and bulk product sales (95% of net sales), including its high‑margin private label Kirkland Signature (~1/3rd of total sales).
- Ancillary services like pharmacy, travel, gold bars, and optical contribute modestly.
- Most revenue (~70-75%) comes through U.S. warehouses, with the rest from international and Canadian operations.
- This hybrid revenue mix, underpinned by membership income and cost‑efficiency, drives consistent profitability and global expansion.
Costco's Cost Structure
- Major expenses include logistics, inventory procurement, warehouse operating costs, wages, and utilities.
- Costco cuts costs through minimal advertising, high employee productivity, and centralised procurement.
- Bulk purchasing and limited SKU offerings reduce inventory complexity.
- The use of private label (Kirkland) enhances margin control. Outsourcing replenishment and automation improves efficiency.
- These tactics help keep overhead below ~10% of revenue, preserving narrow margins (~2–3%) and supporting high-volume profitability.
Costco's Customer Segment
- Costco operates primarily on a B2C membership model targeting middle‑ to high‑income families, small businesses, and bulk shoppers typically aged 25-50 and value-conscious.
- Customers across urban and suburban markets around the world buy in large quantities for personal or small business use.
- The model appeals to price-sensitive, loyal consumers who value quality, bulk savings, and an efficient shopping experience.
- High renewal rates (>90%) reflect strong trust, while the Executive tier drives 73% of total sales.
Costco's Distribution Channels
- Costco operates physical warehouses (≈890 globally, with ~614 in the U.S.) and a growing e‑commerce platform (~16% of net sales).
- It employs an omnichannel strategy, blending in‑warehouse pickup with online ordering.
- Additional touchpoints include services like pharmacy, travel, optical, and loyalty offers.
- Innovations include membership scanners at entry, click-and-collect options, and in-store early-hours access for Executive members, enhancing flow and customer experience.
Costco's Key Partnerships
- Costco partners with major suppliers, Kirkland co‑brand manufacturers, logistics and distribution providers, and technology vendors for membership systems and POS.
- It collaborates with local suppliers in international markets for fresh and regional goods.
- Key tech partnerships support e‑commerce and scanning systems.
- Through these partnerships, Costco ensures reliable supply, cost negotiation leverage, consistent quality, and operational efficiency.
- Additionally, co-branding Kirkland products with trusted labels such as Chinet and Starbucks adds credibility and scale.
SWOT Analysis Of Costco
| Strengths | Weaknesses | Opportunities | Threats |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low Prices | Membership barrier | International growth | Competitor clubs |
| High Renewal | Limited variety | E‑commerce expansion | Inflation pressure |
| Operational Efficiency | Low margin | Ancillary service growth | Regulatory risk |
Looking for a deeper look at the grocery giant's internal strengths and external threats? Read our full SWOT analysis of Kroger for an updated 2026 perspective.
Competitor Comparison Of Costco
| Brand | Pricing | Customer Experience | Channels | Market Focus | Innovation | Loyalty |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Costco | Ultra‑low | Efficient, value‑rich | Warehouses + online | Global bulk shoppers | Private label, scanners | High (>90%) |
| Sam's Club | Low | Familiar, tiered | Mixed club & retail | U.S. & Mexico | Online integration | Moderate |
| BJ’s | Competitive | Regional focus | East Coast warehouses | U.S. Northeast | Digital coupons | Mid-tier |
Want to Know Why 5,00,000+ Students Trust Us?
Dive into the numbers that make us the #1 choice for career success

MBA - Level
Best For
Fresh Graduates
Mode of Learning
On Campus (Mumbai & Delhi)
Starts from
Mar 23, 2026
Duration
11 Months
Live & Online
Best For
Working Professionals
Mode of Learning
Online
Starts from
Mar 6, 2026
Duration
4-6 Months

Online
Best For
AI Enthusiasts
Mode of Learning
Online
Duration
5 Months

Offline
Best For
12th Passouts
Mode of Learning
On Campus (Mumbai)
Duration
3 Years
Recent Post
Interesting Reads
Yes, you can use the Digital Membership Card via the Costco app, but you must still scan it at the new entry membership scanners.
Yes, Costco offers a 100% risk-free satisfaction guarantee and will refund your membership fee in full at any time if you are dissatisfied.
No, Costco does not offer one-day passes. However, non-members can shop if they have a Costco Shop Card (gift card) provided by a member.
Cardholders earn 4% back on gas and EV charging (on the first $7,000/year), 3% on travel and restaurants, and 2% on all Costco purchases.
Yes, members have access to Costco Optical, Hearing Aid Centers, and Pharmacies, often including virtual primary care visits for as low as $29 via partners like Sesame.
Aditya Shastri leads the Business Development segment at IIDE and is a seasoned Content Marketing expert. With over a decade of experience, Aditya has trained more than 20,000 students and professionals in digital marketing, collaborating with prestigious institutions and corporations such as Jet Airways, Godrej Professionals, Pfizer, Mahindra Group, Publicis Worldwide, and many others. His ability to simplify complex marketing concepts, combined with his engaging teaching style, has earned him widespread admiration from students and professionals alike.
Aditya has spearheaded IIDE’s B2B growth, forging partnerships with over 40 higher education institutions across India to upskill students in digital marketing and business skills. As a visiting faculty member at top institutions like IIT Bhilai, Mithibai College, Amity University, and SRCC, he continues to influence the next generation of marketers.
Apart from his marketing expertise, Aditya is also a spiritual speaker, often traveling internationally to share insights on spirituality. His unique blend of digital marketing proficiency and spiritual wisdom makes him a highly respected figure in both fields.