
Orginally Written by Aditya Shastri
Updated on Feb 17, 2026
Share on:
Honda is the world's largest motorcycle manufacturer and Japan's second-largest automaker, operating across automobiles, motorcycles, and power products in over 150 countries. Yet in 2026 it faces a pivotal moment: EV losses, US tariff pressure, and a collapsed Nissan merger have shaken its outlook.
This Honda SWOT Analysis gives entrepreneurs and business students the strategic clarity they need to understand exactly where Honda stands today.
About Honda Company
Founded in October 1946 by Soichiro Honda, Honda Motor Co., Ltd. is a global mobility giant with JPY 21.69 trillion in fiscal year 2025 revenues. Its slogan, "The Power of Dreams," reflects an engineering culture that built the world's best-selling motor vehicle, the Super Cub, and pioneered Japan's first luxury car brand, Acura.
In 2026, the swot analysis of honda is one of the most strategically relevant automotive case studies for business learners. SWOT: Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats.

In 2025, Honda pivots to hybrid leadership amid a shifting EV market. This SWOT analysis explores how Honda leverages its core strengths to tackle emerging challenges and why it matters in today’s business landscape.
Honda Company Overview 2026
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Official Company Name | Honda Motor Co., Ltd. |
| Founded Year | October 1946 |
| Headquarters | Minato, Tokyo, Japan |
| Website | https://global.honda global |
| Industry | Automotive, Motorcycles, Power Products |
| Key Geographies Served | North America, Asia Pacific, Europe, Middle East, Africa |
| Products | Automobiles, Motorcycles, Power Equipment, Marine, Aerospace (HondaJet) |
| Revenue (FY2025, ended March) | ¥21 trillion (approx. USD $143bn, 6.2% YoY growth) |
| Operating Profit (FY2025) | ¥1.2 trillion (down 12% YoY) |
| Net Income (FY2025) | ¥35 billion (down 24% YoY) |
| Employees (FY2025) | 194,173 globally |
| Stock Exchange | Tokyo Stock Exchange (TSE), New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) |
| Main Competitors | Toyota, Nissan, Hyundai-Kia, Ford, General Motors, BMW |


Learn Digital Marketing for FREE


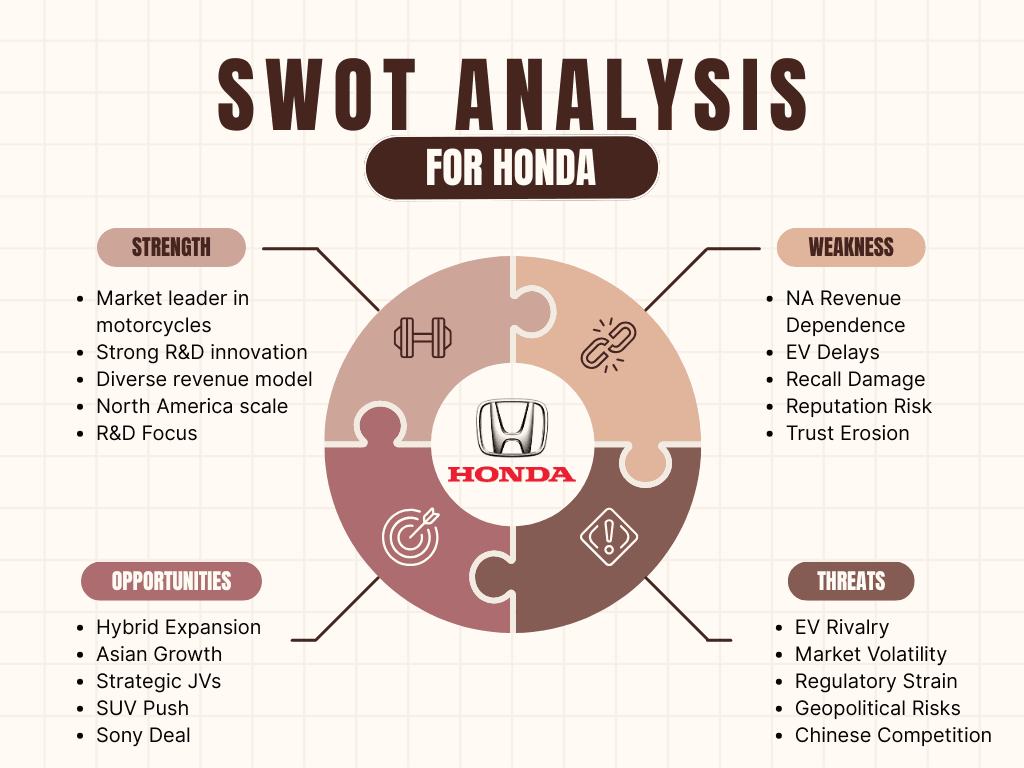
SWOT Analysis of Honda 2026
In 2026, Honda sits at a critical inflection point in its 80-year history. The company's Honda SWOT Analysis reveals a business with extraordinary foundational strengths, including world motorcycle leadership, proven hybrid engineering, and a loyal global customer base.
Yet it simultaneously faces one of its most challenging operational periods: a automotive business operating loss driven by USD 1.7bn in EV restructuring charges, US tariff impacts of 310 billion yen, a semiconductor shortage that cut 110,000 vehicles from its sales forecast, and an abandoned merger with Nissan.
The four quadrants below map this strategic landscape with precision.

Honda's Strengths: The Brand's Superpowers in 2026
Understanding Honda strengths and weaknesses requires starting with a genuinely impressive set of structural advantages that have been built over eight decades of engineering-led growth.
1. World's Largest Motorcycle Manufacturer
Honda has been the world's largest motorcycle manufacturer since 1959, and in May 2025 it reached a historic cumulative production milestone of 500 million motorcycles. Its motorcycle division posted record-breaking results in the nine months ending December 2025, generating strong operating profit that helped offset automotive losses. The Honda Super Cub alone is the most produced motor vehicle in history, with tens of millions of units sold across Asia, Africa, and Latin America. This motorcycle dominance provides revenue diversification and emerging market penetration that rival automakers cannot replicate.
2. Hybrid Engineering Leadership and Intellectual Property
Honda's two-motor hybrid system is one of the most refined powertrain technologies in the automotive industry, a genuine competitive differentiator as the global market transitions away from pure internal combustion engines. In its 2025 business briefing, Honda confirmed it would accelerate a new generation of hybrid models from 2027 onward, with a target of 2.2 million hybrid vehicle sales by 2030.
This positions Honda well in markets where EV infrastructure is insufficient and where consumer demand for fuel-efficient vehicles is growing, particularly in Southeast Asia, India, and parts of Europe.
As noted in the SWOT Analysis of Toyota, hybrid leadership is the defining competitive battleground for Japanese automakers in this decade.
3. Global Scale and Manufacturing Diversification
Honda operates manufacturing plants in more than 30 countries and, critically, produces over 60% of the vehicles it sells in the US domestically.
In 2024, 99.6% of Honda and Acura automobiles sold in the US were produced in North America, a localisation strategy that materially reduces tariff exposure compared with automakers that rely heavily on Japanese imports.
This manufacturing footprint, built over four decades in North America, is a strategic asset that cannot be replicated quickly, as illustrated in the SWOT Analysis of BMW, where geographic manufacturing strategy plays an equally critical role in margin management.
4. Brand Trust, Reliability Reputation and Customer Loyalty
Honda consistently ranks among the most reliable automotive brands in global consumer surveys. Models such as the Civic, Accord, CR-V, and HR-V maintain strong residual values and repeat-purchase rates across North America, Asia, and Europe.
This reliability reputation drives lower customer acquisition costs and stronger dealer network economics, particularly in the used vehicle market where Honda vehicles command consistent premiums. The Honda Accord has been produced continuously since 1976, a 50-year production run that few automotive nameplates in the world can match.
5. Product Diversification Across Mobility Categories
Unlike most automotive competitors, Honda generates revenue across automobiles, motorcycles, power equipment, marine engines, and aerospace through HondaJet. This diversification provides financial resilience when any single segment faces headwinds, as demonstrated in fiscal year 2025 and 2026 when record motorcycle profits partially offset automotive losses.
Honda is also the world's largest manufacturer of internal combustion engines by volume, producing more than 14 million engines annually across all categories, giving it unique economies of scale in powertrain development.
6. Research, Development and Innovation Culture
Honda's engineering DNA, captured in the "Power of Dreams" philosophy, has produced consistent technological firsts including the ASIMO humanoid robot, the HondaJet with its unique over-wing engine mount design, and the CR-V e:FCEV hydrogen fuel-cell plug-in hybrid launched in 2024.
In January 2025, Honda signed an agreement with Renesas Electronics to develop a next-generation high-performance system-on-chip for software-defined vehicles, positioning it at the frontier of automotive technology convergence.
Honda's Weaknesses: The Struggles in 2026
Any honest examination of Honda strengths and weaknesses must confront a difficult financial reality in 2025 and 2026. Honda's weaknesses are not superficial; several are structural and demand strategic resolve to address.
1. Automotive Operating Loss Driven by EV Restructuring
Honda's automobile business recorded a cumulative operating loss of 166.4 billion yen in the nine months to December 2025, with one-time EV-related expenses alone totalling 267.1 billion yen. This follows a pattern shared with Ford (USD 20bn in EV losses), General Motors (USD 6bn), and Stellantis (USD 26bn), but the scale of Honda's restructuring relative to its overall profitability is particularly acute.
The company cut its 2030 global EV sales target from 30% to 20% in 2025, and then postponed its planned four-factory EV and battery complex in Ontario, Canada, by at least two years. This delayed EV rollout creates a vulnerability gap as Chinese manufacturers accelerate their global EV push.
2. Heavy Dependence on the North American Market
North America accounts for more than 40% of Honda's global vehicle sales and an even higher proportion of its automotive profits. While its localised production offers some tariff insulation, 15% US tariffs on Japanese vehicle imports and an increasingly protectionist trade environment create material financial exposure.
Honda's full-year operating profit forecast for fiscal 2026 was cut to 550 billion yen, partly because it could only mitigate tariff impacts from an initial 450 billion yen to 310 billion yen.
Over-reliance on a single market, regardless of domestic production levels, remains a concentration risk that the SWOT Analysis of Mercedes-Benz shows is a common vulnerability for premium-volume manufacturers with uneven global footprints.
3. Semiconductor Supply Chain Vulnerability
In late 2025, the Dutch government's takeover of semiconductor manufacturer Nexperia triggered Chinese government export restrictions, halting production at Honda's joint-venture plants in China and temporarily closing facilities in Japan.
The resulting semiconductor shortage forced Honda to cut its full-year vehicle sales forecast by 110,000 units from 3.62 million to 3.34 million, and reduce its operating profit outlook by a further 150 billion yen.
This episode exposed the depth of Honda's dependency on specific semiconductor suppliers and the geopolitical fragility of its supply chain.
4. Failed Nissan Merger and Strategic Uncertainty
In December 2024, Honda announced a proposed merger with Nissan that would have created the world's third-largest automaker. By February 2025, both companies announced that merger talks had collapsed after Honda proposed that Nissan become a subsidiary, a structure Nissan rejected.
The collapse left Honda without the scale consolidation it had sought, while also consuming management bandwidth and creating investor uncertainty about the company's long-term strategic direction.
This episode, combined with the EV strategy reversals, signals a period of strategic instability that could affect supplier confidence and talent retention.
5. China Market Share Erosion
Honda's joint ventures in China, historically a significant profit contributor, are under severe pressure from domestic Chinese automakers led by BYD, which now outsell all foreign brands in China's EV segment.
Honda's China sales have declined materially as consumers shift toward locally produced electric vehicles that offer competitive technology at lower price points.
Unlike Toyota, which has deeper manufacturing partnerships and a broader product range in China, Honda's China exposure is concentrated in a shrinking segment of the market.
6. EV Brand Perception Lag
While Honda has credible hybrid technology, its pure EV brand perception lags significantly behind Tesla, BYD, Hyundai, and even domestic rival Toyota in global consumer surveys. The Honda 0 Prototype concept, intended to anchor a new EV identity, has not generated the commercial momentum or cultural resonance needed to compete with brands that have built dedicated EV ecosystems and over-the-air software capabilities.
This perception gap is harder to close than a product gap, because it requires sustained marketing investment alongside engineering credibility.
Honda's Opportunities: Future Moves for the Brand
The SWOT Analysis of Honda identifies several structurally compelling growth vectors that align well with Honda's existing capabilities and geographic positioning. In the SWOT Honda literature, India expansion and hybrid technology consistently emerge as the two clearest near-term catalysts for sustained profitability.
1. Hybrid Vehicle Boom as the Transition Pathway
With EV adoption slowing in key markets due to reduced government incentives and infrastructure constraints, hybrid vehicles are experiencing a significant demand resurgence across North America, Europe, and Asia. Honda's next-generation hybrid systems, due for expanded rollout from 2027 with a 2.2 million unit annual sales target, position it to capitalise precisely on this trend. The company's HEV technology is mature, cost-competitive, and trusted by consumers, making hybrids a near-term volume and margin opportunity that few competitors are as well-placed to capture.
2. India and Southeast Asia Motorcycle and Automobile Expansion
India is already Honda's largest motorcycle market by volume, and the company is investing significantly to expand capacity. In May 2025, Honda began constructing a fourth manufacturing line at its fourth Indian plant in Gujarat, with annual capacity of 650,000 units when operational in 2027. Southeast Asia's rapidly growing middle class, rising incomes, and strong preference for two-wheelers and fuel-efficient compact cars create a long runway for both motorcycle and automobile volume growth that is largely insulated from the geopolitical and EV headwinds affecting Honda's developed-market business.
3. Hydrogen Fuel Cell Technology Commercialisation
Honda is one of the few automakers with commercially deployed hydrogen fuel-cell vehicle technology, having launched the CR-V e:FCEV in the US and Japan in 2024. As hydrogen infrastructure investment accelerates in Europe, Japan, South Korea, and parts of North America, Honda's head start in this technology could prove significant, particularly in commercial vehicle and fleet applications where battery EVs face range and charging-time limitations.
The partnership with the United Nations Road Safety Fund announced in February 2025, combined with ongoing fuel-cell R&D, signals that Honda views hydrogen as a genuine long-term platform rather than a speculative side project.
4. Software-Defined Vehicle and AI Integration
Honda's January 2025 agreement with Renesas Electronics to develop a next-generation system-on-chip for software-defined vehicles, and its November 2025 collaboration with Mythic to develop energy-efficient analogue AI chips for vehicles, position it at the emerging frontier of intelligent mobility.
As vehicles increasingly compete on software capability, over-the-air updates, and advanced driver-assistance systems, Honda's engineering partnerships and in-house ADAS development programme could become meaningful differentiators, particularly in premium and fleet segments where technology leadership drives purchase decisions.
5. Brazil and Latin America Market Development
In October 2025, Honda's subsidiary in Brazil announced an investment of approximately 6 billion reais over four years from 2026 to 2029 in its Manaus plant to meet rising motorcycle demand. Latin America's growing middle class, urbanisation, and preference for affordable two-wheelers and compact vehicles align well with Honda's product strengths.
Brazil in particular offers a large domestic market and export hub for the broader regional opportunity.
Honda's Threats: Challenges in a Competitive Arena
The Honda SWOT framework cannot be complete without a candid assessment of the external forces that could materially impair Honda's competitive position through 2026 and beyond.
1. BYD and Chinese EV Manufacturers
BYD surpassed Volkswagen as the world's best-selling car brand by volume in major markets in 2024 and continues to expand aggressively in Southeast Asia, Europe, and Latin America, all markets where Honda has historically been strong.
Chinese EV brands offer technology-rich products at price points that are structurally difficult for Japanese manufacturers to match given their higher-cost domestic supply chains. This competitive threat is not a future risk; it is already eroding Honda's China volumes and threatening its Southeast Asian market position.
2. US Trade Tariffs and Geopolitical Instability
The 25% tariffs on imported cars and the 15% tariff on Japanese vehicle imports imposed by the US administration represent a material and sustained structural cost for Honda.
Despite localising over 60% of its US-bound vehicles, the residual tariff impact of 310 billion yen in fiscal 2026 (after mitigation) represents a profit headwind that is difficult to offset without price increases that risk volume loss. Further escalation in US-China or US-Japan trade tensions could worsen this exposure materially.
3. Toyota Dominance and Intensifying Rivalry
Toyota remains substantially larger than Honda in both revenue and global vehicle sales, and its early investment in hybrid technology has given it a broader HEV product range, deeper dealer networks, and stronger consumer trust in the efficiency vehicle segment where Honda is also competing.
As the SWOT Analysis of Tesla demonstrates, market leaders in the transition period tend to compound their advantages through scale, and Honda faces the challenge of competing with Toyota's established hybrid dominance while simultaneously rebuilding its EV strategy.
4. Semiconductor and Supply Chain Geopolitical Risk
The Nexperia crisis of late 2025 demonstrated that Honda's production system remains vulnerable to geopolitical disruptions in the global semiconductor supply chain. As US-China tensions persist and export controls on advanced semiconductors become more common, any automaker with significant exposure to affected suppliers faces ongoing production volatility.
Honda's CFO acknowledged in Q3 2025 that the company was working to diversify semiconductor sourcing, but structural diversification takes years to execute.
5. Accelerating Regulatory and Emissions Standards
Tightening emissions regulations across the European Union, California, and other jurisdictions continue to raise the cost and complexity of powertrain compliance for manufacturers that have not yet fully transitioned their fleets to zero-emission vehicles.
Honda's revised EV target of 20% global sales by 2030 (down from 30%) creates a potential compliance risk if regulatory timelines tighten or if fuel-cell vehicles do not achieve the commercial scale needed to offset internal combustion engine phase-out requirements.
6. Changing Consumer Preferences Among Younger Buyers
Gen Z and Millennial consumers in key markets increasingly prioritise software experience, connected features, and sustainability credentials alongside traditional automotive values such as reliability and fuel efficiency. Honda's current lineup, strong on reliability but comparatively behind on in-car technology and software-defined features, risks appearing less relevant to these buyers as they enter peak car-purchasing years.
Brands such as Hyundai and Kia have been notably more aggressive in capturing younger consumers through design investment and technology positioning.
Summary Table: SWOT of Honda (Infographic-Ready)
IIDE Student Takeaway, Conclusion & Recommendations
For business students and aspiring strategists, this honda swot analysis reveals a company with real structural strengths navigating one of its most challenging strategic periods. World motorcycle leadership, proven hybrid engineering, a trusted global brand, and manufacturing localisation provide genuine resilience.
Yet the 267 billion yen EV write-down, a collapsed Nissan merger, a semiconductor crisis that cut 110,000 vehicles from forecast, and China market share losses are equally real and demand clear-headed responses.
The central tension in 2026 is clear: Honda must execute a credible EV and software-defined vehicle pivot without sacrificing the hybrid and motorcycle profitability that funds the transition, in an environment where tariffs, geopolitics, and Chinese competition are compressing the time and capital available.
Five actionable priorities:
- Accelerate next-generation hybrids as the near-term volume and margin engine, targeting the 2.2 million unit HEV annual sales goal through disciplined regional pricing from the 2027 model rollout.
- Reduce semiconductor concentration risk by diversifying supplier relationships and co-developing automotive-grade chips through the Renesas and Mythic partnerships.
- Invest in India and Southeast Asia capacity, leveraging motorcycle dominance as the entry point for deeper automotive penetration in the world's fastest-growing consumer markets.
- Build a credible EV identity around the Honda 0 platform with sustained marketing investment and clear software roadmaps that give younger buyers a compelling reason to engage with the brand.
- Formalise geopolitical scenario planning at board level, with pre-built responses to further tariff escalation, semiconductor export controls, and China volume deterioration.
Looking beyond 2026, the honda strengths and weaknesses framework points to a company with the engineering heritage and global footprint to remain a top-five mobility brand, provided it executes its hybrid, EV, and software-defined vehicle strategies with clarity and commercial discipline.
Want to Know Why 5,00,000+ Students Trust Us?
Dive into the numbers that make us the #1 choice for career success

MBA - Level
Best For
Fresh Graduates
Mode of Learning
On Campus (Mumbai & Delhi)
Starts from
Mar 23, 2026
Duration
11 Months
Live & Online
Best For
Working Professionals
Mode of Learning
Online
Starts from
Mar 6, 2026
Duration
4-6 Months

Online
Best For
AI Enthusiasts
Mode of Learning
Online
Duration
5 Months

Offline
Best For
12th Passouts
Mode of Learning
On Campus (Mumbai)
Duration
3 Years
Recent Post
Honda cars are known for their reliability, fuel efficiency, advanced safety features, and strong resale value. They also come with a smooth driving experience, excellent build quality, and innovative technologies.
Yes, most Honda dealerships accept trade-ins. You can visit a dealership to get an appraisal for your old vehicle, which can be applied as a down payment or toward the purchase of a new Honda car.
Yes, Honda provides car leasing options through Honda Financial Services. Leasing allows you to drive a new vehicle for a few years and then return it when the lease ends, with flexible terms available.
The price of Honda cars varies by model and trim level. The prices typically range from about ₹7 lakhs for a Honda Jazz to ₹40 lakhs or more for a high-end Honda CR-V or Accord. For exact prices, visit your nearest Honda dealership.
Aditya Shastri leads the Business Development segment at IIDE and is a seasoned Content Marketing expert. With over a decade of experience, Aditya has trained more than 20,000 students and professionals in digital marketing, collaborating with prestigious institutions and corporations such as Jet Airways, Godrej Professionals, Pfizer, Mahindra Group, Publicis Worldwide, and many others. His ability to simplify complex marketing concepts, combined with his engaging teaching style, has earned him widespread admiration from students and professionals alike.
Aditya has spearheaded IIDE’s B2B growth, forging partnerships with over 40 higher education institutions across India to upskill students in digital marketing and business skills. As a visiting faculty member at top institutions like IIT Bhilai, Mithibai College, Amity University, and SRCC, he continues to influence the next generation of marketers.
Apart from his marketing expertise, Aditya is also a spiritual speaker, often traveling internationally to share insights on spirituality. His unique blend of digital marketing proficiency and spiritual wisdom makes him a highly respected figure in both fields.