
Orginally Written by Aditya Shastri
Updated on Dec 11, 2025
Share on:
Zomato's business model is built on a customer-centric approach, leveraging technology to connect users with restaurants and delivery partners. This strategy allows them to offer convenient food delivery services while maintaining healthy profit margins.
Zomato achieves this by optimizing its supply chain, expanding its service offerings, and continuously innovating its platform. It uses technology and partnerships to streamline operations. But what’s the secret behind its global reach and strong brand loyalty? Zomato's rapid market expansion and customer base drive consistent growth.
In this blog, we decode Zomato’s revenue model and strategy, shedding light on how it has achieved market leadership.
About Zomato

Founded in 2008 by Deepinder Goyal and Pankaj Chaddah, Zomato started as a restaurant discovery platform and has since evolved into a global food delivery service. Headquartered in Gurugram, Haryana, India, Zomato operates in over 800 cities across India and several international markets, making it one of the largest food-tech companies globally.
The company's mission is to "power India's changing lifestyles" by providing better food for more people and making instant commerce indistinguishable from magic. As of FY24, Zomato reported a Gross Order Value (GOV) of INR 47,918 crore, and an adjusted revenue of INR 13,545 crore, marking a 48% and 56% year-over-year growth, respectively. It achieved profitability with an adjusted EBITDA of INR 372 crore and a Profit After Tax (PAT) of INR 1,155 crore.
Zomato's philosophy centers on customer obsession, operational excellence, and technological innovation. The company prioritizes seamless user experiences, efficient delivery, and sustainable practices. Zomato's secret to success lies in its adaptability, focus on innovation, and constant evolution in service offerings.
Summary Table
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Founded | 2008 |
| Founder | Deepinder Goyal, Pankaj Chaddah |
| Headquarters | Gurugram, Haryana, India |
| Industry | Online Food Delivery & Restaurant Discovery |
| Revenue (FY24) | INR 13,545 crore |
| Presence | Over 800 cities in India, international markets |
| Employees | 4,440 (as of 2024) |
| Popular For | Food delivery, restaurant discovery, quick commerce |


Learn Digital Marketing for FREE


How Does Zomato Make Money?
Revenue Stream Breakdown
Food Delivery Services: Zomato generates a major portion of its revenue from food delivery services, where it facilitates the delivery of meals from restaurants to customers.
Restaurant Listings & Advertising: Zomato earns fees from restaurants for premium listings and advertisements on its platform.
Subscription Services: Zomato Pro, a subscription-based program, offers benefits like discounts and exclusive offers, which is another important revenue stream.
Quick Commerce (Blinkit): Blinkit, Zomato's quick commerce platform, generates revenue from delivering groceries and essentials.
Event Ticketing (District): The District platform generates revenue from selling tickets for events and experiences.
Revenue Contribution
Food Delivery Services: Approximately 60% of Zomato’s total revenue comes from food delivery services.
Restaurant Listings & Advertising: Around 20% of total revenue.
Subscription Services: Roughly 10% of the total revenue.
Quick Commerce (Blinkit): About 5% of total revenue.
Event Ticketing (District): Approximately 5% of total revenue.
Pricing Strategy
- Zomato follows a value-based pricing strategy.
- Its food delivery services are priced competitively, with premium pricing for subscription services like Zomato Pro.
- The company also utilises dynamic pricing for event tickets and quick commerce deliveries to maximise revenue.
The marketing strategy of HelloFresh reveals how food-tech brands leverage subscriptions and content to build loyal user bases.
Zomato Business Model Canvas
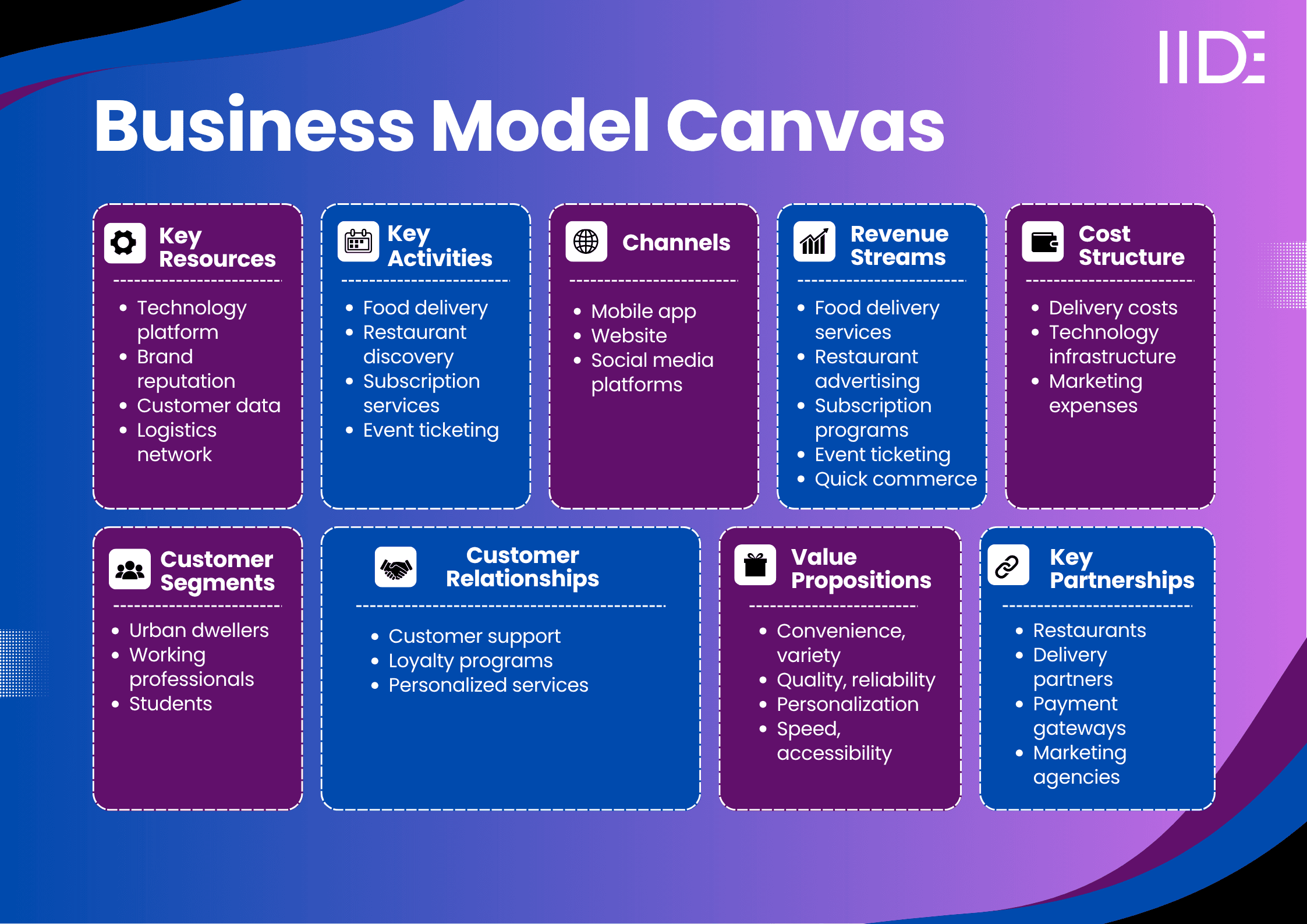
Zomato Value Proposition
Zomato's unique value proposition lies in its ability to connect customers with a vast network of restaurants and food delivery services, addressing key customer needs like convenience, affordability, and variety. Unlike many competitors, Zomato offers personalized recommendations based on user preferences, creating a more tailored experience.
Emotionally, Zomato appeals to customers by providing a sense of reliability and trust, as it consistently delivers high-quality service. Users feel confident in their choice, knowing they will receive a timely and satisfying experience every time they order food.
Functionally, Zomato simplifies the process of ordering food and discovering new dining options, saving time and effort for its users. The company's quick commerce platform further enhances convenience by offering grocery delivery, making Zomato a one-stop shop for all food and lifestyle needs.
Zomato's competitive advantage comes from its extensive restaurant network, innovative use of technology, and its ability to adapt to changing market demands, which competitors struggle to replicate.
Zomato Revenue Model
Zomato's revenue model is multifaceted, with the largest revenue streams coming from food delivery services, restaurant advertising, and subscription programs like Zomato Pro.
The company also earns income from its quick commerce service (Blinkit) and event ticketing platform (District).
Zomato’s ability to diversify its income sources across food services and lifestyle offerings has enabled it to maintain robust revenue growth, with substantial contributions from its digital and subscription-based services.
Marketing strategy of Maggi illustrates how household food brands use emotional appeal and familiarity, offering context to Zomato’s local partnerships.
Zomato Cost Structure
Major Expenses
- Logistics and Delivery Costs: A significant portion of Zomato's expenses is allocated to logistics and delivery operations, including payments to delivery partners.
- Technology and Platform Maintenance: Costs related to maintaining and improving the digital platform that powers Zomato’s services.
- Marketing and Advertising: Zomato invests heavily in advertising and promotional campaigns to attract new users and restaurants.
- Employee Salaries and Benefits: The cost of running Zomato’s operations globally, including a diverse workforce.
Cost-Saving Strategies
- Automation: Zomato uses automated systems to optimize delivery routes, reducing operational costs.
- Outsourcing: By outsourcing certain operational processes, Zomato cuts down on in-house costs and boosts efficiency.
- Economies of Scale: Leveraging its vast order volumes, Zomato negotiates better deals with suppliers, reducing costs per unit.
Maintaining Healthy Margins
Zomato keeps its margins healthy by focusing on high-margin services like subscription programs and improving operational efficiencies via technology.
Zomato Customer Segment
Zomato operates on a Business-to-Consumer (B2C) model, primarily targeting urban dwellers aged 18-45, with a focus on working professionals, students, and tech-savvy individuals.
Its customers seek convenience, quality, and variety in food delivery services, which is why they choose Zomato over competitors.
Customers are attracted to Zomato for its personalized experience, reliable service, and time-saving features, making it the go-to platform for food delivery.
Zomato Distribution Channels
Physical Retail:
- Zomato does not operate physical stores but partners with local restaurants to offer food delivery services.
Online Channels:
- Zomato operates through its mobile app and website, providing users with a platform to explore restaurants, place orders, and discover food options.
- Additionally, it collaborates with third-party platforms like Swiggy and Amazon to expand reach.
Omnichannel or Digital-First:
- Zomato follows a digital-first approach, focusing on its eCommerce platforms to provide a seamless experience for users.
Additional Touchpoints:
- Zomato offers personalized recommendations through its app and engages customers through loyalty programs and email marketing.
Innovations in Distribution:
- Zomato integrates real-time tracking and AI-based suggestions, along with partnerships with delivery platforms, to enhance the customer experience.
Zomato Key Partnerships
Zomato has formed key partnerships with restaurants, delivery service providers, and tech companies.
It collaborates with restaurants for premium listings, payment gateways for secure transactions, and logistics partners for efficient delivery.
Zomato also works with sustainability-focused organizations to promote eco-friendly initiatives.
These partnerships are vital to ensuring Zomato's business runs smoothly, helping the company scale its services while maintaining quality and efficiency.
Zomato SWOT Analysis
| Strengths | Weaknesses | Opportunities | Threats |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brand loyalty, large user base | High operational costs | Expanding international markets | Intense competition |
| Strong technological infrastructure | Dependence on third-party logistics | Quick commerce expansion | Regulatory challenges |
| Diversified revenue streams | Customer retention challenges | Sustainability initiatives | Rising fuel prices |
Zomato Competitor Comparison
| Brand | Pricing | Customer Experience | Channel Strategy | Market Focus | Innovation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zomato | Competitive | User-friendly, fast delivery | Digital-first, omnichannel | B2C, urban markets | Personalization, AI |
| Swiggy | Competitive | Excellent customer support | Mobile-first | B2C, urban markets | Hyperlocal delivery |
| Uber Eats | Premium | Reliable, quick deliveries | Digital-first, partnership-based | B2C, urban markets | AI-powered logistics |
What’s New with Zomato?
Zomato continues to innovate with AI-powered personalized recommendation engines, enhancing the user experience.
The company is also focusing on sustainability, implementing initiatives to reduce packaging waste and promote eco-friendly materials.
Additionally, Zomato explores automation and blockchain technologies to improve logistics, streamline operations, and further enhance service efficiency.
Key Takeaways for Students / Marketers & Conclusion
Scalability: Zomato’s tech-driven infrastructure and diversified revenue streams make its business model highly scalable across global markets.
Replication by Small Businesses: Local food businesses can replicate Zomato’s focus on partnerships and quick commerce to enhance customer experience.
Strategic Mindset: Zomato’s adaptability, innovation, and customer-centric approach ensure long-term success in a competitive market.
Zomato digital marketing strategy dives into how content, social media, and hyperlocal campaigns drive its customer engagement.
Conclusion:
Zomato’s business model thrives on innovation, operational efficiency, and customer obsession.
With its focus on technology and diverse revenue streams, Zomato is poised for continued growth.
Will Zomato’s model continue to revolutionise the online food delivery industry?
Want to Know Why 5,00,000+ Students Trust Us?
Dive into the numbers that make us the #1 choice for career success

MBA - Level
Best For
Fresh Graduates
Mode of Learning
On Campus (Mumbai & Delhi)
Starts from
Mar 23, 2026
Duration
11 Months
Live & Online
Best For
Working Professionals
Mode of Learning
Online
Starts from
Mar 23, 2026
Duration
4-6 Months

Online
Best For
AI Enthusiasts
Mode of Learning
Online
Duration
5 Months

Offline
Best For
12th Passouts
Mode of Learning
On Campus (Mumbai)
Duration
3 Years
Recent Post
Aditya Shastri leads the Business Development segment at IIDE and is a seasoned Content Marketing expert. With over a decade of experience, Aditya has trained more than 20,000 students and professionals in digital marketing, collaborating with prestigious institutions and corporations such as Jet Airways, Godrej Professionals, Pfizer, Mahindra Group, Publicis Worldwide, and many others. His ability to simplify complex marketing concepts, combined with his engaging teaching style, has earned him widespread admiration from students and professionals alike.
Aditya has spearheaded IIDE’s B2B growth, forging partnerships with over 40 higher education institutions across India to upskill students in digital marketing and business skills. As a visiting faculty member at top institutions like IIT Bhilai, Mithibai College, Amity University, and SRCC, he continues to influence the next generation of marketers.
Apart from his marketing expertise, Aditya is also a spiritual speaker, often traveling internationally to share insights on spirituality. His unique blend of digital marketing proficiency and spiritual wisdom makes him a highly respected figure in both fields.