
Orginally Written by Aditya Shastri
Updated on Dec 12, 2025
Share on:
About Amazon
Amazon was founded in 1994 by Jeff Bezos as an online bookseller in Bellevue, Washington. Its founding idea - “customer-obsessed convenience at scale” led Amazon to expand into nearly every product category and build the world’s leading e‑commerce platform.
In full-year 2024, Amazon generated approximately US $638 billion in net sales and net income of roughly US $59.2 billion, nearly doubling its 2023 profit. Its cloud arm, AWS, pulled in $107.6 billion in revenue and $39.8 billion in operating income, making it the dominant profit source. The company employs about 1.56 million people globally, with over 300 million active customers, and continues expanding its footprint across North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific.
Amazon revolves around core values of customer obsession, innovation, and long-term thinking. It emphasises fast delivery, deep product selection, low prices, and data-informed personalisation. Its success stems from marrying retail volume with a high-margin digital services business, fuelled by its global logistics network and technology infrastructure.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Founded | 1994 |
| Founder | Jeff Bezos |
| Headquarters | Seattle, Washington, USA |
| Industry | E‑commerce, Cloud Services, Digital Advertising |
| Revenue (2024) | US$638 billion |
| Presence | Global ~200 countries; ~300M active users |
| Employees | ~1.56 million (2024) |
| Popular for | Fast delivery, retail scale, AWS cloud dominance |


Learn Digital Marketing for FREE


How does Amazon make money?
1. Revenue Stream Breakdown
- First‑party product sales (direct retail) account for about 38–40% of total net sales.
- Third‑party seller services (commissions, fulfilment, storage) contribute roughly 24–25%.
- AWS cloud services make up around 17%+ of net sales and drive the lion’s share of profit.
- Advertising operations generate close to 9% of revenue.
- Subscription services (Prime memberships, video/music streaming) represent about 7%.
- Physical stores and other revenue make up the remaining 3–5%.
2. Revenue Contribution
- Retail sales account for the highest volume but have slim margins.
- AWS contributes nearly 60% of Amazon’s operating profits, making it the powerhouse for profitability.
- Advertising margins are high and growing fast.
- Subscriptions provide reliable recurring cash flow that strengthens customer stickiness.
3. Pricing Strategy
Amazon employs low-cost pricing across its retail catalogue, reducing prices through scale and efficiency. AWS operates on a pay-per-usage model, tailored to enterprise needs. Subscription services like Prime are priced for perceived value - locked-in benefits justify membership fees. Advertising is priced on performance and targeting efficacy.
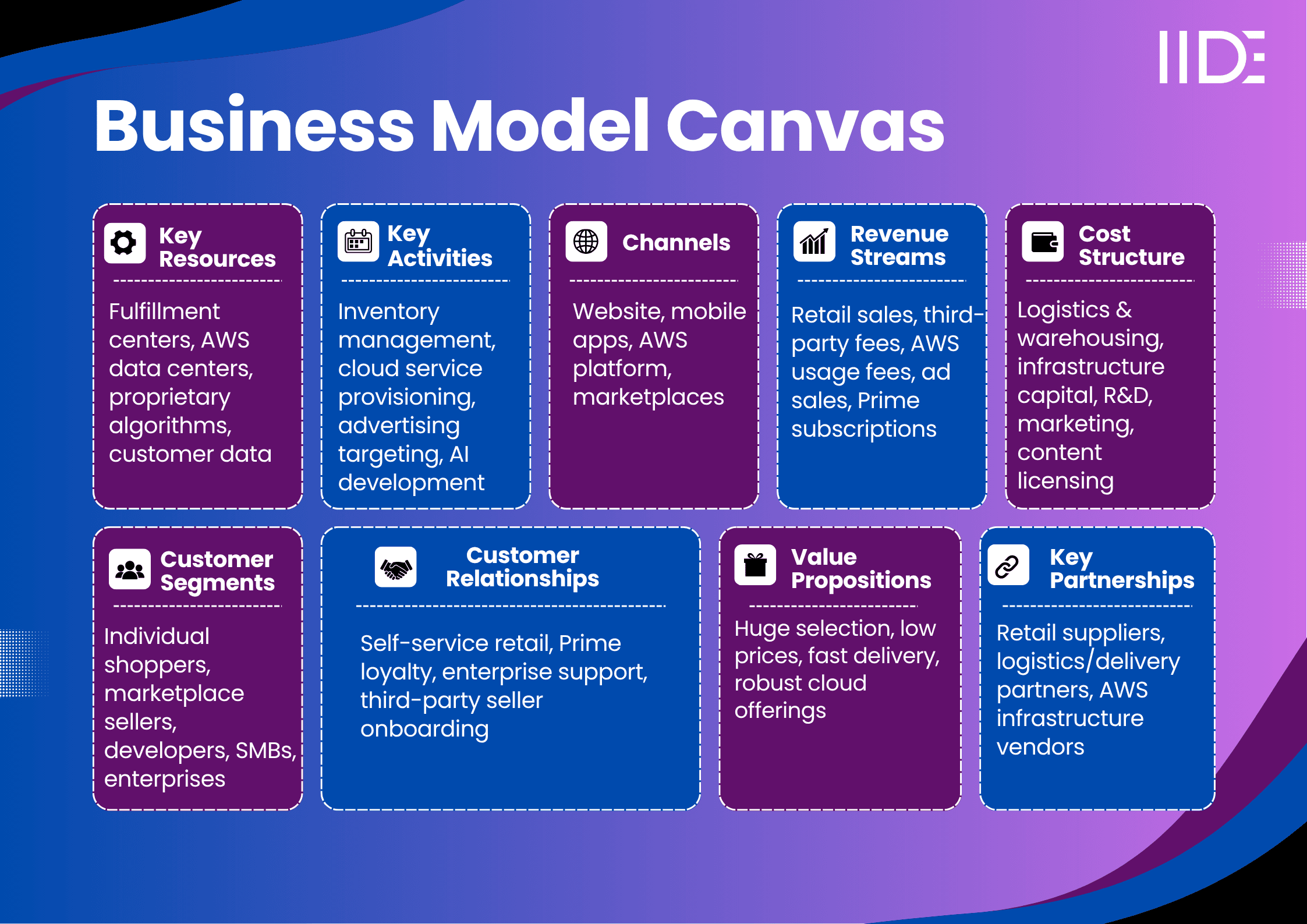
Amazon Business Model Canvas
Amazon Value Proposition
Amazon offers a massive product selection and convenience, backed by a logistics network that enables delivery at competitive prices. It solves key customer pain points: low prices for everyday goods, reliable fast delivery, one-stop shopping with easy returns, and personalised recommendations. For enterprises and developers, AWS delivers enterprise-grade cloud services on a flexible, usage-based model—eliminating infrastructure burdens while scaling quickly.
Emotionally, customers trust Amazon for its consistency, simplicity, and innovation. Shoppers feel confident using Amazon because they expect reliability, fast resolution, and a sense of being valued through Prime perks. AWS clients benefit emotionally from confidence in security, scalability, and global reach.
Functionally, Amazon cuts friction: one-click ordering, frictionless checkout, fast delivery, and rich digital services. AWS offers scalable computing, storage, and AI tools across the globe. Amazon’s edge lies in its unmatched logistics infrastructure, data intelligence platform, and ecosystem lock-in via Prime and marketplace services - a combination competitors find difficult to replicate.
Read the SWOT analysis of eBay, which sheds light on the dynamics of global e-commerce platforms, offering context that parallels Amazon’s competitive landscape.
Amazon Cost Structure
Amazon’s major cost drivers include global logistics and warehousing, cloud infrastructure investment, R&D in AI and digital, content acquisition and licensing, and marketing/selling expenses. Cost efficiencies come from automation (robotic fulfilment), bulk logistics operations, and negative working capital cycles. Technology investment and scale help maintain healthy margins even as Amazon reinvests heavily in AI and growth.
Amazon Customer Segment
Amazon serves a global B2C audience - mainly middle- to upper-income urban and suburban shoppers across age groups. It also targets businesses and developers via AWS for B2B and B2B2C services. Early adopters and tech-savvy consumers appreciate Amazon’s convenience, broad selection, and frictionless experience. Buyers choose Amazon for its price competitiveness, fast delivery, rich ecosystem, and trusted reliability, making it the default platform for everyday needs and enterprise infrastructure alike.
Distribution Channels
Amazon is primarily digital-first, reaching customers via its website and mobile app. It also uses third-party seller integrations to expand choice. Though Amazon operates physical stores (e.g., Amazon Fresh, Whole Foods), these are a small part of revenue. It follows an omnichannel approach - customers can shop online, pick up in-store, or order through Alexa and WhatsApp. Innovative tools include one-click ordering, app-based shopping, voice agents, and fast-delivery networks such as same-day or two-hour Prime options.
Key Partnerships
Amazon collaborates with manufacturers and suppliers, logistics and delivery partners, third-party sellers, and technology vendors for cloud infrastructure and AI tools. It partners with payment providers, media licensors (for Prime content), and sustainability organisations. It also invests in startups like AI firms. These alliances enhance its reach, supply chain efficiency, innovation pace, and global expansion, while reinforcing its customer-focused and tech-led ethos.
SWOT Analysis of Amazon
| Strengths | Weaknesses | Opportunities | Threats |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scale dominance | Narrow AWS margins | AI-powered growth | Rising cloud competition |
| Logistics network | Thin retail margins | New marketplaces also use AI | Tariffs and regulation |
| Platform ecosystem | High capex costs | Enterprise services growth | Macroeconomic pressures |
Competitor Comparison
| Brand | Pricing | Customer Experience | Channel Strategy | Market Focus | Innovation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | Low cost/value | Fast, personalised | Digital-first + formats | Global multi‑segment | AI, logistics |
| Walmart | Competitive | Physical & digital | Strong offline+online | Mass-market retail | Omnichannel pickup |
| Microsoft Azure | Usage-based | Enterprise-grade | B2B cloud-first | B2B services | AI cloud leadership |
| Google Cloud | Flexible | Developer-focused | Cloud platform | Cloud/AI heavy users | ML/AI tooling |
What’s New With Amazon?
Recently, Amazon has accelerated investment in AI infrastructure, developing agents like DeepFleet and platforms such as Strands and Bedrock AgentCore for scalable AI tools. Advertising and subscription segments are growing double-digits. Capital expenditures for 2025 are projected at $118 billion to support AI and cloud expansion. Sustainability remains a priority, with Amazon using renewable energy in data centres and exploring circular-economy packaging.
Key Takeaways for Students & Marketers
- Amazon’s model is highly scalable, blending low-cost retail with profitable digital services
- Even small businesses can replicate data-led customer focus and efficient fulfilment
- Diversified revenue streams - retail, subscriptions, ads, cloud - buffer volatility
- Strategic investment in infrastructure and AI enables long-term dominance
Examining the business model of Uber offers an interesting perspective on platform-based scalability and logistics efficiency, much like Amazon’s approach.
Want to Know Why 2,50,000+ Students Trust Us?
Dive into the numbers that make us the #1 choice for career success

MBA - Level
Best For
Fresh Graduates
Mode of Learning
On Campus (Mumbai & Delhi)
Starts from
Mar 23, 2026
Duration
11 Months
Live & Online
Best For
Working Professionals
Mode of Learning
Online
Starts from
Mar 6, 2026
Duration
4-6 Months

Online
Best For
AI Enthusiasts
Mode of Learning
Online
Duration
5 Months

Offline
Best For
12th Passouts
Mode of Learning
On Campus (Mumbai)
Duration
3 Years
Recent Post
Amazon makes money through product sales, AWS, Prime subscriptions, and advertising fees.
Amazon’s main products include consumer electronics, books, groceries, AWS, Prime Video, and Kindle.
Amazon’s top competitors include Walmart, Alibaba, eBay, Microsoft, and Google.
Amazon Prime is a subscription service offering benefits like free shipping, exclusive deals, and access to streaming services.
Amazon uses technology for logistics, AI, cloud computing, and customer service, enhancing efficiency and user experience.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a cloud computing platform providing scalable solutions to businesses and developers.
Amazon’s CSR initiatives focus on sustainability, renewable energy, community support, and employee welfare.
Amazon targets a broad audience through personalised marketing, Prime membership, and diverse product offerings.
Amazon holds approximately 39% of the US online retail market.
Aditya Shastri leads the Business Development segment at IIDE and is a seasoned Content Marketing expert. With over a decade of experience, Aditya has trained more than 20,000 students and professionals in digital marketing, collaborating with prestigious institutions and corporations such as Jet Airways, Godrej Professionals, Pfizer, Mahindra Group, Publicis Worldwide, and many others. His ability to simplify complex marketing concepts, combined with his engaging teaching style, has earned him widespread admiration from students and professionals alike.
Aditya has spearheaded IIDE’s B2B growth, forging partnerships with over 40 higher education institutions across India to upskill students in digital marketing and business skills. As a visiting faculty member at top institutions like IIT Bhilai, Mithibai College, Amity University, and SRCC, he continues to influence the next generation of marketers.
Apart from his marketing expertise, Aditya is also a spiritual speaker, often traveling internationally to share insights on spirituality. His unique blend of digital marketing proficiency and spiritual wisdom makes him a highly respected figure in both fields.

