
Orginally Written by Aditya Shastri
Updated on Dec 12, 2025
Share on:
Qantas, Australia’s flagship airline, is a standout name in 2025’s aviation landscape. Whydoes Qantas continue to capture attention this year? With a remarkable rebound from pandemic lows, the airline is not only showing strong profits but also reshaping its market position through innovative strategies and fleet expansion. Are there growing challenges ahead?
Absolutely, from reputational risks to fierce competition, making this analysis is crucial. Readers will gain valuable insights into Qantas’ evolving strategies and market dynamics, providing lessons that can be applied across business and aviation sectors. This blog offers a glimpse into Qantas’ strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, without revealing all inviting readers to explore the complex forces shaping its future.
Before diving into the article, it's worth mentioning that the research and initial analysis forthis piece were conducted by Jaineel Chauhan, a current student of IIDE’s Online Digital Marketing Course, May 2025 Batch 2. If this content was helpful, feel free to reach out to Jaineel Chauhan with a quick note ofappreciation for his fantastic research - he will truly value the kudos!
About Qantas
Founded in 1920 in the Queensland outback, Qantas began as Queensland and NorthernTerritory Aerial Services Limited. It is now Australia’s largest and one of the world’s oldest continuously operating airlines, maintaining a vital role in domestic, international, cargo, and loyalty services in 2024-25.Qantas’ legacy is deeply tied to its slogan, “The Spirit of Australia,” which captures itsnational pride and long-standing heritage.
From its humble beginnings starting scheduled flights in 1922 and pioneering services like the Royal Flying Doctor Service to becoming aglobal aviation leader, Qantas continues to adapt and reinvent itself. In recent years, Qantas has invested heavily in fleet renewal and enhanced services,rebounding strongly after pandemic challenges.
In fiscal year 2025, it posted an Underlying Profit Before Tax of AUD 2.39 billion and a Statutory Profit After Tax of AUD 1.61 billion, highlighting robust financial health. What does SWOT mean for Qantas? This analysis will explore its Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats key facets that shape how the airline competes and evolves inan ever-changing market.
Key Highlights of Qantas
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Founded | 1920, Queensland, Australia |
| Original Name |
Queensland and Northern Territory Aerial Services Limited |
| Headquarters | Mascot, New South Wales |
| Business Scope |
Domestic & International Flights, Cargo, Loyalty Programs |
| FY25 Financials |
Underlying Profit Before Tax: AUD 2.39 billion Statutory Profit After Tax: AUD 1.61 billion |
| Brand Slogan |
"The Spirit of Australia" - Symbolizes national pride & legacy |
Why SWOT Analysis Matters Now?
The aviation industry in 2025 is marked by intense dynamics that directly impact Qantas’ performance and strategic positioning. Fuel price volatility, shifting customer demand, and rising operational costs challenge airlines globally, requiring nimble responses to changing market realities.
Post-pandemic recovery remains a critical phase as carriers race to regain lost traffic and rebuild margins. For Qantas, competition intensifies from low-cost carriers like Jetstar and Virgin Australia, as well as ultra long-haul models and strategic alliances reshaping network strategies.
Customer preferences are evolving, with increasing demand for seamless digital experiences, sustainability, and personalized services. Qantas is adapting by investing in fleet modernization, service upgrades, and loyalty program enhancements to meet these expectations.
Technology plays a vital role, driving innovation and operational efficiency with initiatives such as automation, improved booking platforms, and fuel-efficient aircraft adoption. However, economic headwinds, including rising fuel costs and inflation, continue to pressure margins, requiring careful cost management.
Additionally, regulatory and environmental factors impose new challenges. Emission reduction targets, carbon offset mandates, and sustainable aviation fuels (SAF) are no longer optional but critical to maintaining compliance and brand reputation.
This SWOT analysis uncovers how Qantas can leverage its strengths, address internal weaknesses, capitalize on emerging opportunities, and defend against threats in today’s competitive and complex aviation market.


Learn Digital Marketing for FREE


SWOT Analysis of Qantas
Here is a concise yet comprehensive overview of Qantas’ key strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in 2025, aligned with the latest industry insights:
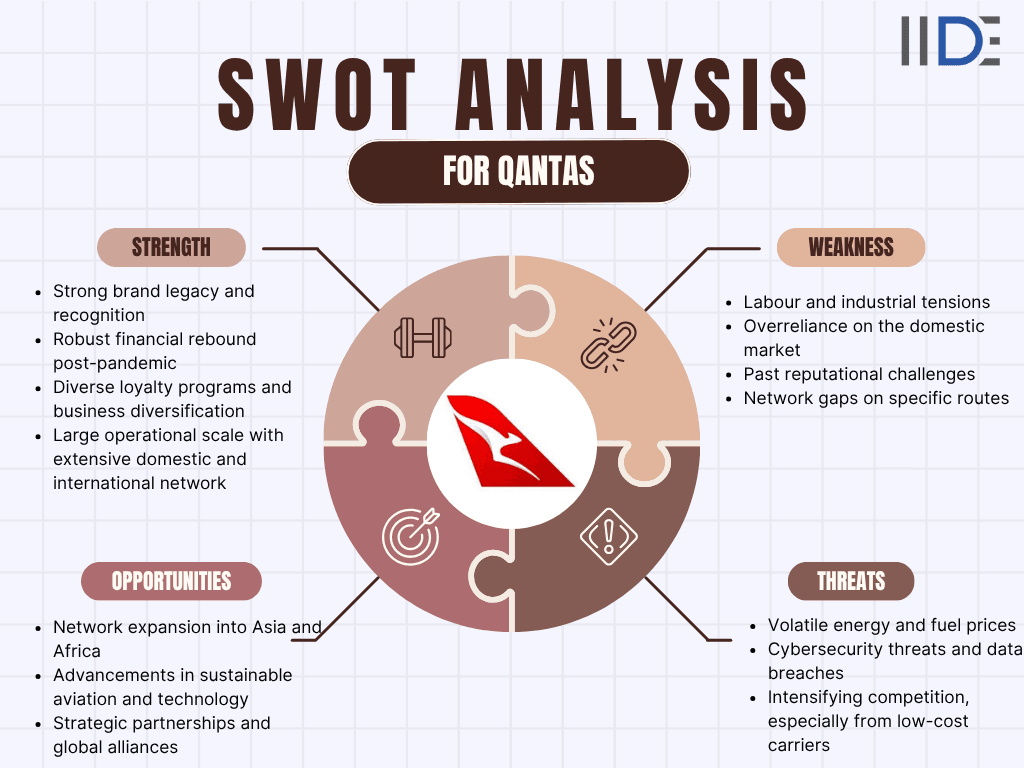
1. Strengths of Qantas
Dominating the Aviation Industry in 2025 Qantas stands as a powerful player in the aviation sector in 2025, underpinned by solid financial performance, a strong brand, and strategic diversification. Here’s a detailed look at its core strengths driving success and resilience:
- Strong Financial Recovery & Profitability: In the fiscal year ending June 2025, Qantas achieved an Underlying Profit Before Taxof AUD 2.39 billion, signifying a roughly 15% growth from the previous year. Statutory Profit After Tax hit AUD 1.61 billion, enabling Qantas to resume dividend payouts for the first time in years. This financial robustness underlines operational resilience and capacity for further strategic investments.
- Legacy Brand & National Identity: As Australia’s flag carrier, Qantas holds a prestigious brand known for trust, safety, and reliability. This legacy strengthens its marketing appeal and customer loyalty indomestic markets, especially among those valuing a dependable airline with a rich heritage.
- Diversified Business Model & Loyalty Segment: The Qantas Frequent Flyer program delivers steady revenue, buffering fluctuationsin passenger volumes. The dual-brand strategy with full-service Qantas and the budget Jetstar caters to varied market segments effectively. Cargo and logistics operations add further revenue diversification, supporting stability during market downturns.
- Operational Scale & Network Reach: Qantas commands a significant presence domestically and internationally, including routes across Asia, North America, Europe, and the Pacific. Projects like Project Sunrise are paving the way for ultra-long-haul flight expansions. In FY25, available seat kilometres (ASKs) grew by about 6%, reflecting network growth and capacity enhancements.
- Cost Management & Efficiency Gains: Focused efforts to streamline costs and boost operational efficiency have paid off, especially through Jetstar’s use of newer aircraft and increased ancillary revenues. Favorable foreign exchange movements and fuel cost management also contributed positively, enhancing profitability and competitiveness.
2. Weaknesses of Qantas
While Qantas remains a dominant player in aviation, it faces significant internal and external weaknesses that could impact its growth and market position if not addressed. Understanding these vulnerabilities is critical in assessing the airline's future prospects:
- Labor Relations & Industrial Tensions: Qantas has a longstanding history of contentious negotiations with unions and staff. During the pandemic, controversial outsourcing and layoffs led to a record-breaking AUD 90 million fine in 2025 for illegally outsourcing 1,800 ground staff. These labor disputes threaten operational stability, risk service disruptions, and have caused reputational damage. The airline’s aggressive legal approach has further strained employee relations.
- Reputational & Legal Challenges: Qantas’ reputation has suffered due to mass dismissals, ticket cancellations during COVID, and a major cyber-attack exposing up to 6 million customer records. In October 2025, the airline was also targeted in ransomware demands. These incidents erode customer trust, invite regulatory scrutiny, and further pressure brand image.
- Overreliance on Domestic Market: A significant portion of Qantas’ revenue depends on the Australian domestic market, leaving it vulnerable to national economic fluctuations, travel restrictions, and local disruptions. By contrast, its international segments which tend to be more volatileand competitive have seen setbacks, including the suspension of Sydney-Shanghai flights due to weak demand.
- Route & Network Gaps: Qantas’ global reach, though expansive, lags behind some larger competitors in frequency and presence on key international routes, particularly in parts of Asia and Africa. Post-COVID recovery has been uneven across markets, weakening the business case for certain long-haul operations.
- Exposure to External Costs: The airline remains exposed to structural risks from fluctuating fuel prices, carboncredit costs, and currency exchange rates. Pending fleet renewal means some legacyaircraft still carry higher maintenance and operational costs, impacting costefficiency.
Unlock the secrets behind IndiGo's sky-high success with our latest SWOT analysis of IndiGo Airlines where market leadership meets cost-efficiency and bold expansion plans, but fierce competition and limited premium services keep the race exciting.
3. Opportunities for Qantas
Qantas is strategically positioned to leverage several emerging opportunities in 2025, driven by global travel trends, technological advancements, and market expansions. Here’s a detailed overview of how the airline can capitalize on these trends:
- Expansion into High-Growth Regions: Qantas is actively launching new routes to key destinations such as Perth Aucklandand Perth-Johannesburg, set to commence in December 2025. These routes opennew gateways for customer access and tap into the increasing demand for international travel, particularly in the Asia-Pacific, Africa, and emerging marketslike India. Additionally, the reopening of China routes possibly re-entering when demand recovers is a significant growth avenue as the Chinese market slowly recovers from pandemic impacts.
- Sustainable Aviation & Innovation: Growing pressure for greener operations including mandates for sustainable aviation fuels (SAF), carbon offsets, and eco-friendly aircraft presents a chance for Qantas to differentiate itself. Leading in sustainability can attract environmentally conscious travelers, including Gen Z consumers, who prioritize eco-friendly brands. Investing in next-generation aircraft and offsetting emissions positions Qantas as a pioneer in Australian aviation’s green future.
- Strengthening Cargo & Logistics Services: The global supply chain pressures and booming e-commerce sector continue to boost demand for air cargo. Qantas can expand its cargo operations, integrating airand ground logistics partnerships to create new revenue streams while supporting the digital economy and international trade.
- Digital & Technology Upgrades: Cutting-edge investments in AI, predictive maintenance, data analytics, and customer personalization can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer loyalty. Furthermore, strengthening cybersecurity safeguards will restore trust and protect customer data against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats.
- Strategic Partnerships & Alliance Expansion: Collaborations with global airlines and emerging-market carriers through code shares and joint ventures enable Qantas to extend its reach without heavy capital expenditure. Such alliances also provide access to underserved markets and enhance competitiveness in an era of rapid industry consolidation.
- Ancillary & Non-Flight Revenue Growth: Expanding ancillary services like premium seat upgrades, travel packages, subscriptions, and loyalty program monetization including fintech partnerships andco-branded deals can significantly boost revenue. These services align with therising demand for personalized, premium travel experiences by affluent and younger travelers alike.
4. Threats to Qantas
Qantas faces a range of significant threats that could impact its market share, operational stability, and consumer trust in 2025. These challenges stem from volatile costs, fierce competition, cybersecurity vulnerabilities, and regulatory pressures, all of which require strategic mitigation to maintain industry leadership.
- Fuel, Energy & Macro Cost Shocks: Fluctuating fuel prices and rising carbon credit costs pose a persistent risk tomargins. Inflationary pressures affecting salaries, leasing fees, and ground operations add to the cost burdens that could erode profitability if not efficiently managed.
- Intensifying Competition: The rise of low-cost carriers domestically and internationally threatens to undercut Qantas on pricing, especially in cost-sensitive market segments. Additionally, global mega-alliances and ultra-low-cost entrants challenge Qantas’ premium services, forcing constant innovation and competitive pricing.
- Cybersecurity & Data Risks: Qantas has been a prime target for cyberattacks, including a major data breach inJuly 2025 affecting up to 6 million customers via a third-party call center platform. In October 2025, the airline also faced a ransomware attack targeting its booking systems. These breaches highlight ongoing vulnerability that risks regulatory penalties, reputational harm, and operational disruption.
- Regulatory, Legal & Labor Risks: Past outsourcing practices and industrial relations disputes have led to costly fines, including a recent AUD 90 million penalty in 2025. Ongoing compliance, litigation costs, and evolving aviation regulations especially environmental mandates exertcontinued operational and financial pressure.
- Demand Volatility & External Shocks: Economic downturns, geopolitical tensions, and health crises continue to cause unpredictable travel demand swings. The uneven recovery of international markets, notably between Australia and China, creates revenue instability and operational uncertainty.
IIDE Student Takeaway, Recommendations & Conclusion
Recap & Biggest Insights
Qantas’ standout strength in 2025 is its robust financial recovery, enabling strategic investments after years of downturn. Its iconic brand and diversified operations provide structural resilience. However, pressing vulnerabilities, notably in reputation, labor relations, and cybersecurity, pose significant risks. The biggest threat remains are putational or data breach crisis that could severely damage customer trust.
Strategic Recommendations
- Proactive Cybersecurity & Data Governance: Invest heavily in threat detection,incident response, and third-party security audits. Publicly commit to customer dataprotection transparency and rapid recovery support.
- Labor Engagement & Trust Building: Engage unions early, align incentives withperformance, and foster a positive workplace culture to reduce conflicts and legalrisks.
- Sustainable Leadership & ESG Differentiation: Set ambitious emission targets, scalesustainable fuel use, and brand sustainability as a market differentiator - not justcompliance.
- Route & Network Strategy Focus: Prioritize reopening or launching routes in high-growth under-served regions like India, Southeast Asia, and Africa, mitigating riskthrough partnerships.
- Digital & Ancillary Revenue Growth: Leverage AI and analytics to personalizeofferings, upsell ancillary services, and expand subscription models. Strengthencargo and logistics synergy for new revenue streams.
Conclusion & Future Outlook
If Qantas effectively manages reputational risks and scales in emerging markets with asustainability focus, it could solidify and extend its Asia-Pacific leadership. The airline’s future hinges on balancing innovation and resilience against legacy challenges and an evolving, competitive landscape.
Want to Know Why 2,50,000+ Students Trust Us?
Dive into the numbers that make us the #1 choice for career success

MBA - Level
Best For
Fresh Graduates
Mode of Learning
On Campus (Mumbai & Delhi)
Starts from
Mar 23, 2026
Duration
11 Months
Live & Online
Best For
Working Professionals
Mode of Learning
Online
Starts from
Mar 6, 2026
Duration
4-6 Months

Online
Best For
AI Enthusiasts
Mode of Learning
Online
Duration
5 Months

Offline
Best For
12th Passouts
Mode of Learning
On Campus (Mumbai)
Duration
3 Years
Recent Post
Qantas addresses operational challenges such as delays or cancellations through timely notifications, flexible rebooking options, and efficient customer communications. The company emphasizes customer care by prioritizing transparency and support during disruptions, both in-person and through digital channels, to reduce inconvenience for its passengers.
In 2025, Qantas introduced changes to its Frequent Flyer program, including increased availability of premium cabin and partner airline reward seats, lower Economy reward fares within Australia, and the ability to earn more points per flight. These changes are part of continuous efforts to enhance member benefits and stay competitive in customer loyalty.
Qantas invests in extensive crew training, modernizes its fleet, and regularly upgrades its onboard and airport experiences to ensure safety and high-quality service. Regular audits, adherence to global standards, and responsiveness to customer feedback form the backbone of Qantas’s approach to passenger wellbeing.
Ongoing investment in premium lounges, improved boarding, refreshed in-flight services, and wide-ranging global connectivity set Qantas apart. The airline’s commitment to continuous innovation ensures an upgraded journey for both leisure and business travelers.
Qantas allows passengers to cancel eligible bookings within 24 hours of ticketing without any cancellation fee. This policy applies mainly to bookings made directly with Qantas, often requiring the flight to be at least seven days away. It provides travelers with flexibility and peace of mind shortly after booking.
Qantas provides dedicated customer service contact points for baggage assistance and lost property both in Australia and at major international airports. The airline processes claims and offers reimbursement for essential items when baggage is delayed or lost, emphasizing efficient customer care in baggage handling.
Qantas’s Conditions of Carriage outline crucial aspects of travel including baggage limits, check-in, flight schedules, delays, cancellations, and passenger conduct. The airline maintains strict safety protocols and operational policies aligned with regulatory requirements to ensure safety and comfort for all passengers.
Aditya Shastri leads the Business Development segment at IIDE and is a seasoned Content Marketing expert. With over a decade of experience, Aditya has trained more than 20,000 students and professionals in digital marketing, collaborating with prestigious institutions and corporations such as Jet Airways, Godrej Professionals, Pfizer, Mahindra Group, Publicis Worldwide, and many others. His ability to simplify complex marketing concepts, combined with his engaging teaching style, has earned him widespread admiration from students and professionals alike.
Aditya has spearheaded IIDE’s B2B growth, forging partnerships with over 40 higher education institutions across India to upskill students in digital marketing and business skills. As a visiting faculty member at top institutions like IIT Bhilai, Mithibai College, Amity University, and SRCC, he continues to influence the next generation of marketers.
Apart from his marketing expertise, Aditya is also a spiritual speaker, often traveling internationally to share insights on spirituality. His unique blend of digital marketing proficiency and spiritual wisdom makes him a highly respected figure in both fields.