Orginally Written by Aditya Shastri
Updated on Jan 21, 2026
Share on:
Before diving into the article, I would like to inform you that the research and initial analysis for this piece were conducted by Akansha Jain. She is a current student in IIDE's PG in Digital Marketing, June Batch 2025.
If you found this helpful, feel free to reach out to Akansha Jain and send a quick note of appreciation for his fantastic research. She will appreciate the kudos!
About Future Retail

(Source: Sugar Mint)
Future Retail Limited, founded in 2007 as the flagship of Kishore Biyani's Future Group, revolutionized Indian organized retail through its Big Bazaar hypermarket chain and "Rewrite Rules, Retain Values" philosophy.
By 2026, the company exists only in liquidation, with the Mumbai NCLT ordering asset dissolution after ₹28,452 crore in admitted liabilities.
SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats-a framework that reveals how a market leader can collapse through strategic misalignment.
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Official Company Name | Future Retail Limited |
| Founded Year | 2007 (as Future Retail Ltd) |
| Website URL | Under maintenance / Not operational |
| Industries Served | Organised Retail, Supermarkets, Hypermarkets, Fashion Retail |
| Geographic Areas Served | India (Nationwide network) |
| Revenue (Latest) | ₹6,261.04 crore (FY2021) |
| Net Income (Latest) | -₹3,180.03 crore (FY2021) |
| Employees | ~29,000 (pre-liquidation) |
| Main Competitors | Avenue Supermarts (DMart), Reliance Retail, Trent (Westside), Aditya Birla Fashion & Retail |
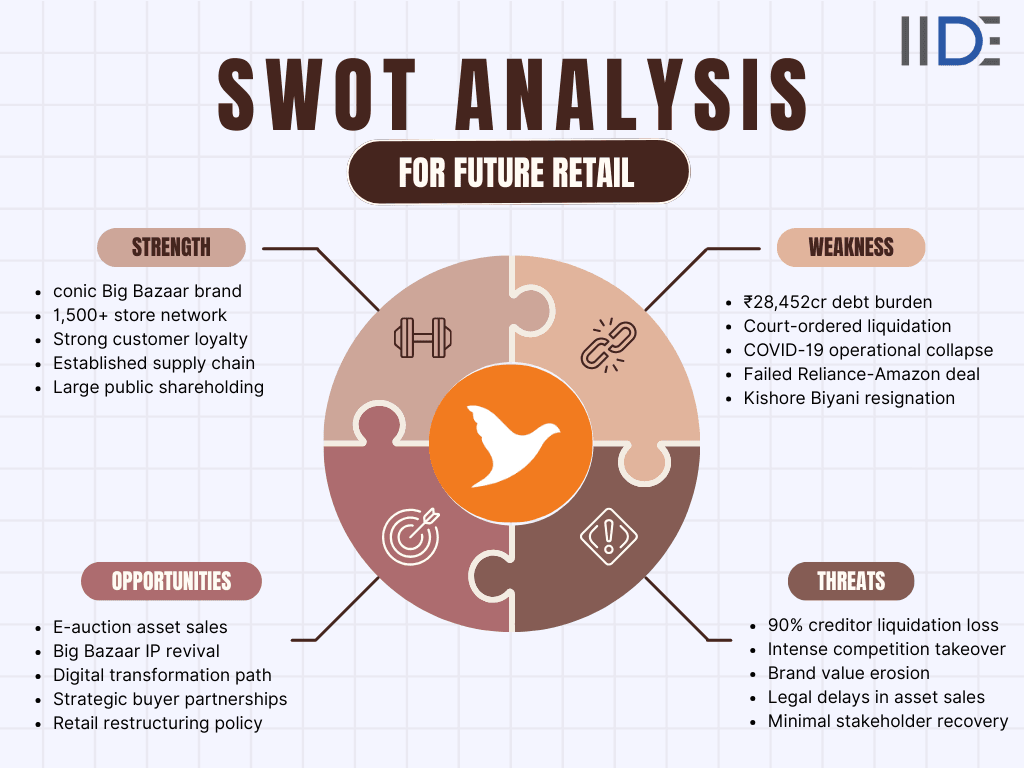
What Does SWOT Stand For in Future Retail's Case?
SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. In this article, we will dive deep into each of these aspects to uncover how Future Retail navigated the competitive retail industry and ultimately faced liquidation in 2026.
Why SWOT Analysis Matters for Future Retail in 2026?
-
Market Competition: Strong players like DMart, Reliance, and Trent absorbed Future Retail’s stores and customers during insolvency, exposing the weakness of traditional hypermarket models.
-
Customer Shift: Consumers moved toward digital, quick commerce, and omnichannel shopping, making Future Retail’s physical-store-heavy strategy outdated.
-
Technology Failure: Lack of digital integration, data analytics, and automation put the company far behind tech-driven competitors.
-
Economic Pressure: Inflation and reduced discretionary spending pushed value-seeking customers toward cheaper, integrated retail ecosystems.
-
Regulatory Role: IBC and NCLT liquidation processes determined asset outcomes and finalized the company’s shutdown.
-
Ethical Impact: Poor financial governance led to massive job losses and supplier distress, highlighting the human cost of corporate mismanagement.


Learn Digital Marketing for FREE


Summary Table – SWOT of Future Retail
IIDE Student Takeaway, Recommendations & Conclusion
Future Retail's transformation from market pioneer to a liquidation case study highlights critical strategic tensions between aggressive expansion, debt-fueled growth, and effective legal risk management.
The brand's competitive strengths-iconic Big Bazaar recognition, nationwide infrastructure, and customer loyalty-proved insufficient against cascading weaknesses of unsustainable leverage, operational rigidity, and a catastrophic legal dispute that blocked the Reliance lifeline.
The core strategic dilemma facing the brand in 2026 is whether any residual value can be salvaged through asset sales before brand equity fully evaporates, or whether the Big Bazaar name will permanently symbolise corporate failure in Indian business curricula.
Recommendations
-
Maximise Asset Value Through Accelerated Digital Auctions: The liquidator must implement transparent, technology-driven e-auction platforms with global bidder outreach, compressing the liquidation timeline to prevent further brand deterioration and maximise creditor recovery before market conditions worsen.
-
Monetise Intellectual Property Separately: The Big Bazaar trademark and customer data should be carved out as distinct assets, marketed to e-commerce or quick-commerce players who can reboot the brand digitally without assuming physical store liabilities, creating value where none currently exists.
-
Implement Employee Transition Support Programs: Given the 29,000-strong workforce impact, creditors should mandate that winning bidders absorb maximum employee reallocation, while the government provides skill retraining incentives, transforming a corporate failure into a workforce development opportunity.
-
Establish Corporate Governance Benchmarks for Retail Expansion: Indian regulators must use Future Retail's collapse to mandate stricter debt-to-equity thresholds and shareholder agreement disclosures, preventing future conglomerates from replicating the debt-legal trap that ensnared Kishore Biyani's empire.
Beyond 2026, Future Retail's legacy will likely bifurcate-its physical assets dissolved through liquidation while the Big Bazaar brand potentially resurfaces under new ownership as a digital-native value retail platform.
The company's trajectory serves as a stark reminder that retail dominance built on physical scale and debt leverage cannot survive without digital agility, legal due diligence, and capital discipline.
For India's entrepreneurial ecosystem, Future Retail's most valuable remaining asset is the cautionary tale it provides: innovation without financial sustainability and contractual clarity ultimately destroys shareholder value, making it essential reading for every business student planning to disrupt traditional retail.
Want to Know Why 2,50,000+ Students Trust Us?
Dive into the numbers that make us the #1 choice for career success

MBA - Level
Post Graduate in Digital Marketing & Strategy
Best For
Fresh Graduates
Mode of Learning
On Campus (Mumbai & Delhi)
Starts from
Mar 23, 2026
Duration
11 Months
Live & Online
Advanced Online Digital Marketing Course
Best For
Working Professionals
Mode of Learning
Online
Starts from
Mar 23, 2026
Duration
4-6 Months

Online
Professional Certification in AI Strategy
Best For
AI Enthusiasts
Mode of Learning
Online
Duration
5 Months

Offline
Undergraduate Program in Digital Business & Entrepreneurship
Best For
12th Passouts
Mode of Learning
On Campus (Mumbai)
Duration
3 Years
Recent Post
Future Retail failed due to unsustainable ₹28,452 crore debt, COVID-19 operational collapse, and strategic blunders. The Reliance deal block by Amazon's arbitration prevented debt reduction. Overdependence on large-format stores, high pricing vs DMart, and weak digital transformation accelerated the downfall. Leadership vacuum after Biyani's resignation sealed the fate.
Future Retail collapsed into liquidation after admitting ₹28,452 crore in debt. NCLT ordered liquidation in July 2024 when the 330-day CIRP period expired without resolution. The crisis began with the COVID-19 shutdowns. A failed ₹24,713 crore Reliance deal blocked by Amazon sealed its fate. Most 1,500+ stores are now shuttered.
Full revival is virtually impossible under liquidation. However, the Big Bazaar brand IP could be acquired and rebooted as a digital-native platform. Physical assets are being dissolved through e-auctions. Original shareholders face a complete loss. Strategic buyers might leverage brand recognition, but the company as structured is finished.
No active owner exists. Kishore Biyani resigned as executive chairman in January 2023. The company is administered by an NCLT-appointed liquidator. The 76%+ public shareholding remains technically intact but worthless. The Biyani family lost control when NCLT admitted the company for insolvency in 2022. Ownership now rests with the liquidation estate.
No, trading remains suspended. Shares were delisted after NCLT's July 2024 liquidation order. Market value collapsed to ₹123.64 crore against ₹28,452 crore debt. Delisted shares cannot trade on exchanges. Shareholders face a near-total value wipeout as creditors have priority. Any recovery depends on liquidation proceeds, but equity holders will receive zero.
Aggressive debt-fueled expansion created unsustainable leverage. Overdependence on mall-based large formats proved fatal during COVID-19. High pricing lost to DMart's cost leadership. The Reliance deal structure allowed Amazon to block acquisition through arbitration. Weak corporate governance, financial indiscipline, and leadership instability sealed the company's fate.
Aditya Shastri leads the Business Development segment at IIDE and is a seasoned Content Marketing expert. With over a decade of experience, Aditya has trained more than 20,000 students and professionals in digital marketing, collaborating with prestigious institutions and corporations such as Jet Airways, Godrej Professionals, Pfizer, Mahindra Group, Publicis Worldwide, and many others. His ability to simplify complex marketing concepts, combined with his engaging teaching style, has earned him widespread admiration from students and professionals alike.
Aditya has spearheaded IIDE’s B2B growth, forging partnerships with over 40 higher education institutions across India to upskill students in digital marketing and business skills. As a visiting faculty member at top institutions like IIT Bhilai, Mithibai College, Amity University, and SRCC, he continues to influence the next generation of marketers.
Apart from his marketing expertise, Aditya is also a spiritual speaker, often traveling internationally to share insights on spirituality. His unique blend of digital marketing proficiency and spiritual wisdom makes him a highly respected figure in both fields.