
Orginally Written by Aditya Shastri
Updated on Aug 12, 2025
Share on:
About Visa
Visa was founded in 1958 by Dee Hock as BankAmericard, with the goal of providing a universal credit card for consumers. Its unique selling proposition lies in its secure, global payment network, which connects banks, merchants, and cardholders worldwide.
As of 2023, Visa processes over 160 billion transactions annually, with an annual revenue of over $28 billion, and is present in more than 200 countries and territories. Visa is known for its constant innovation in payment technologies and its role in simplifying global commerce. Customer experience is centred around convenience, security, and speed, offering seamless digital payments across all platforms.
Visa’s secret to success is its powerful and scalable payment network that enables frictionless transactions for consumers and businesses alike.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Founded | 1958 |
| Founder | Dee Hock |
| Headquarters | Foster City, California, USA |
| Industry | Financial Services, Payments |
| Revenue (2023) | $28.6 Billion |
| Presence | 200+ countries |
| Employees | 20,000+ |
| Popular for | Secure Payment Solutions, Credit Cards |


Learn Digital Marketing for FREE


How does Visa make money?
1. Revenue Stream Breakdown:
- Transaction Fees: Visa earns a significant portion of its revenue from processing transactions between cardholders, merchants, and financial institutions
- Service Fees: Visa generates income from offering services to banks, including fraud prevention, data analytics, and credit card processing
2. Revenue Contribution:
- Transaction Fees: 60% of Visa’s total revenue comes from transaction fees, with each transaction fee depending on the amount processed
- Service Fees: 40% of revenue comes from service fees charged to financial institutions and merchants for value-added services
3. Pricing Strategy:
Visa follows a value-based pricing model, focusing on providing high-value services such as security, fraud prevention, and digital payment innovations, which justify its premium pricing.
Read the marketing strategy of Puma, which highlights the importance of partnerships and digital engagement, strategies that Visa also utilises to drive brand awareness and loyalty.
Visa Business Model Canvas
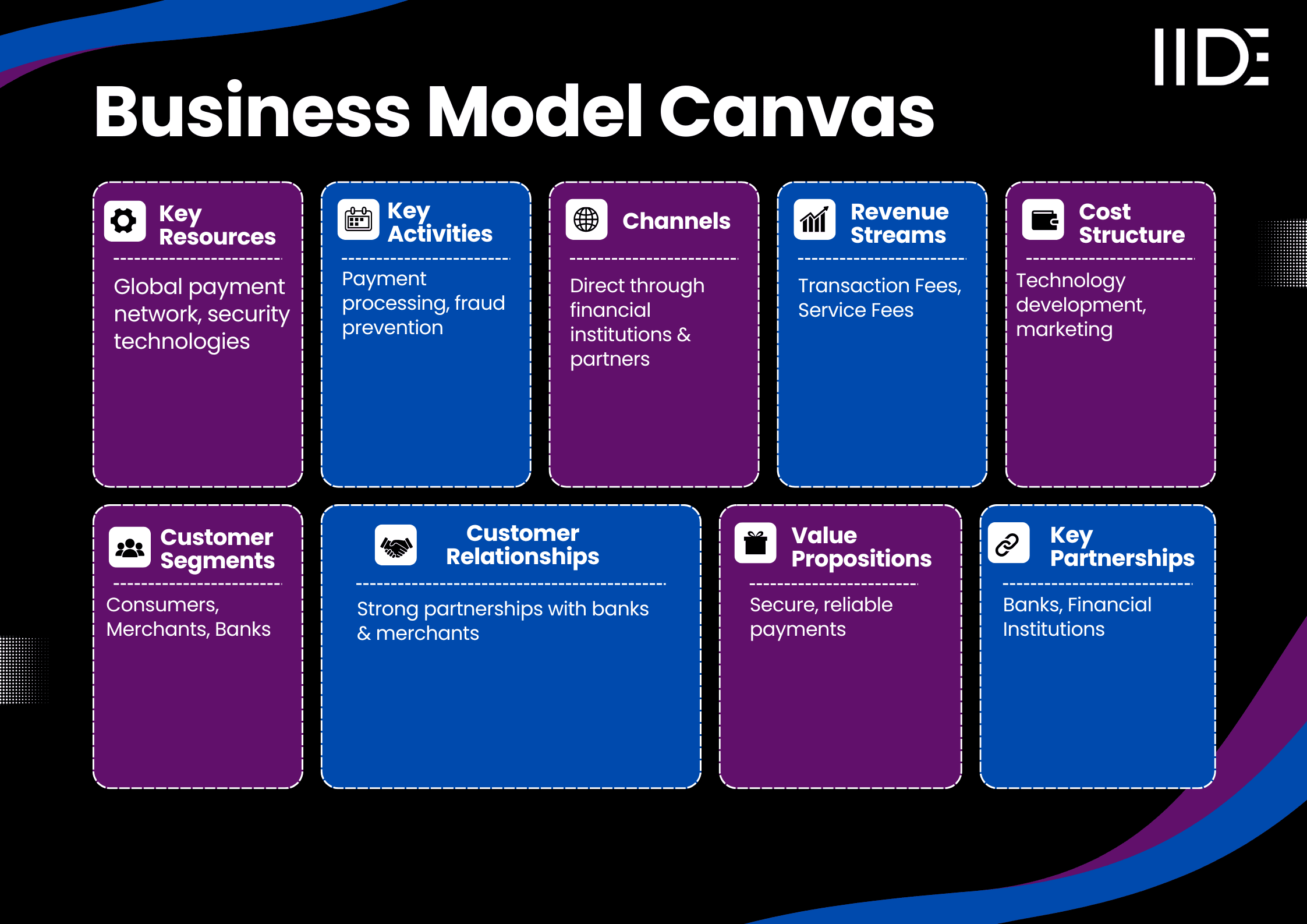
Visa Value Proposition
Visa’s value lies in its secure, global payment network that enables seamless and fast transactions for consumers and businesses worldwide. It addresses key pain points by offering speed, security, and convenience in financial transactions, providing a trusted alternative to cash.
The emotional benefits for users include peace of mind, knowing their transactions are safe and processed efficiently. Functional benefits include faster payments, wider merchant acceptance, and support for digital and contactless payments.
Visa’s competitive advantage lies in its large-scale network and constant innovation, ensuring its leadership in the payments industry.
Visa Revenue Model
Visa’s revenue model primarily comes from transaction fees, which account for 60% of its total income, with each transaction processed generating a fee. The remaining 40% comes from service fees, where Visa charges banks and merchants for value-added services such as fraud protection and data analysis.
Visa’s constant innovation in digital payment solutions drives additional revenue streams, allowing it to maintain strong market positioning.
Visa Cost Structure
Visa’s major expenses include:
- Technology Development: Significant investments in cybersecurity, blockchain, and payment technologies
- Marketing & Branding: Visa spends on advertising and maintaining its global brand presence
- Operations: Costs associated with maintaining its global payment network and support services
To maintain strong margins, Visa leverages its economies of scale and low operational costs due to its network-based model.
Visa Customer Segment
Visa operates on a B2B and B2C model, serving both businesses (merchants, financial institutions) and individual consumers who use Visa-branded payment products. Core customers include middle to high-income individuals and businesses looking for secure and efficient ways to process payments.
Visa also appeals to tech-savvy, digital-first users who prefer contactless or online payment solutions.
Distribution Channels of Visa
- Banks and Financial Institutions: Visa’s primary channel for reaching consumers is through banks, which issue Visa cards to their customers
- Online Platforms: Visa has integrated its payment solutions into online platforms, allowing consumers to use their cards for e-commerce transactions
- Merchants: Visa’s payment network enables merchants to accept Visa cards, both in physical stores and online
Visa Key Partnerships
Visa collaborates with:
- Financial Institutions: Banks and credit unions issue Visa cards and provide Visa’s services to customers
- Merchants: Retailers and online platforms that accept Visa payments
- Tech Partners: Companies focused on cybersecurity and payment technologies to enhance Visa’s offerings
These partnerships enable Visa to maintain its large-scale payment network and support continuous growth.
Nykaa's marketing strategy reveals the power of customer-centric approaches, which can resonate with Visa's focus on user experience and financial inclusion.
SWOT Analysis of Visa
| Strengths | Weaknesses | Opportunities | Threats |
|---|---|---|---|
| Global network | Dependence on banks | Expansion in digital payments | Competition from fintech startups |
| Strong brand | Vulnerability to fraud | Fintech innovation | Regulatory challenges |
| Established market presence | High transaction fees | Mobile and digital wallet adoption | Cybersecurity threats |
Visa Competitor Comparison
| Parameter | Visa | MasterCard | American Express |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pricing | Premium | Premium | High fees |
| Customer Experience | Secure, efficient | Seamless, efficient | Exclusive, high-touch |
| Channel Strategy | Extensive partner network | Extensive partner network | Direct to consumers |
| Market Focus | Global payments | Global payments | Premium consumers |
| Innovation | Payment tech, security | Payment tech, security | Customer loyalty programs |
Key Takeaways for Students / Marketers
- Scalability: Visa’s payment network is highly scalable, allowing it to cater to both large businesses and individual consumers
- Replication for Small Businesses: Focusing on partnerships and providing value-added services is key to expanding a business model in a network-driven industry
- Strategic Thinking: Visa’s long-term success stems from its ability to innovate, adapt to changing payment technologies, and build strong global relationships
Want to Know Why 2,50,000+ Students Trust Us?
Dive into the numbers that make us the #1 choice for career success

MBA - Level
Best For
Fresh Graduates
Mode of Learning
On Campus (Mumbai & Delhi)
Starts from
Mar 23, 2026
Duration
11 Months
Live & Online
Best For
Working Professionals
Mode of Learning
Online
Starts from
Mar 6, 2026
Duration
4-6 Months

Online
Best For
AI Enthusiasts
Mode of Learning
Online
Duration
5 Months

Offline
Best For
12th Passouts
Mode of Learning
On Campus (Mumbai)
Duration
3 Years
Recent Post
Visa makes money through transaction fees, cross-border fees, and licensing fees from financial institutions.
Mastercard, American Express, Discover, UnionPay, and PayPal are Visa’s main competitors.
Visa employs advanced fraud detection systems and tokenisation technology to secure transactions.
VisaNet is Visa’s proprietary global processing network that enables rapid and secure transaction processing.
Visa focuses on financial inclusion, education, and sustainability in its CSR initiatives.
Visa uses traditional and digital marketing, sponsorships, and partnerships to promote its brand and drive adoption.
Visa has introduced innovations like Visa Token Service and contactless payments to enhance payment security and convenience.
Aditya Shastri leads the Business Development segment at IIDE and is a seasoned Content Marketing expert. With over a decade of experience, Aditya has trained more than 20,000 students and professionals in digital marketing, collaborating with prestigious institutions and corporations such as Jet Airways, Godrej Professionals, Pfizer, Mahindra Group, Publicis Worldwide, and many others. His ability to simplify complex marketing concepts, combined with his engaging teaching style, has earned him widespread admiration from students and professionals alike.
Aditya has spearheaded IIDE’s B2B growth, forging partnerships with over 40 higher education institutions across India to upskill students in digital marketing and business skills. As a visiting faculty member at top institutions like IIT Bhilai, Mithibai College, Amity University, and SRCC, he continues to influence the next generation of marketers.
Apart from his marketing expertise, Aditya is also a spiritual speaker, often traveling internationally to share insights on spirituality. His unique blend of digital marketing proficiency and spiritual wisdom makes him a highly respected figure in both fields.

