
Orginally Written by Aditya Shastri
Updated on Aug 12, 2025
Share on:
About Uber
Uber was founded in 2009 by Garrett Camp and Travis Kalanick, with the vision of revolutionising the transportation industry through an on-demand ride-hailing service. It started as a way to make urban transportation more efficient and affordable. Uber's key proposition is making transportation simple and accessible via a mobile app, allowing anyone to book rides from nearby drivers.
As of 2025, Uber has expanded its offerings beyond ride-hailing, incorporating food delivery through Uber Eats, freight logistics through Uber Freight, and even autonomous vehicle research. The brand operates globally, with services in over 900 metropolitan areas in 69 countries.
In 2023, Uber reported a revenue of approximately $39 billion, with a workforce of over 30,000 employees worldwide. Uber is popular for its flexibility, competitive pricing, and disruptive influence on traditional taxi services.
Uber's ethos revolves around providing reliable and accessible services, driving innovation in mobility, and empowering drivers with the opportunity to earn independently.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Founded | 2009 |
| Founder | Garrett Camp, Travis Kalanick |
| Headquarters | San Francisco, California, USA |
| Industry | Ride-Hailing, Food Delivery, Logistics |
| Revenue (2023) | $39 Billion |
| Presence | 900+ Cities, 69+ Countries |
| Employees | 30,000+ |
| Popular For | Ride-Hailing, Uber Eats (Food Delivery), Uber Freight (Logistics), Innovation in Autonomous Vehicles |


Learn Digital Marketing for FREE


How Does Uber Make Money?
Revenue Stream Breakdown:
- Ride-Hailing: Uber’s largest revenue source comes from its ride-hailing services, which account for about 60% of its total revenue. Customers pay based on distance, time, and surge pricing
- Uber Eats: The food delivery service generates a significant share of Uber's income, contributing around 25%. Uber charges a service fee to restaurants and a delivery fee to customers
- Uber Freight: Uber's logistics division connects truckers with freight companies, generating 10% of its revenue. It charges brokers and carriers a fee for facilitating the transportation of goods
- Other Revenue Streams: Uber also earns from services like Uber for Business, vehicle leasing, and various tech innovations
Pricing Strategy:
Uber’s pricing strategy includes dynamic pricing, where rates are influenced by factors such as demand, weather, and traffic conditions. It employs a value-based pricing model in ride-hailing services, offering customers an efficient service at competitive prices. Uber Eats uses a commission-based structure from restaurants and customers to optimise revenue while maintaining flexibility.
FedEx’s SWOT analysis, although in logistics, highlights key insights into how global operational challenges are overcome, similar to the ride-sharing and delivery issues Uber faces.
Uber Business Model Canvas
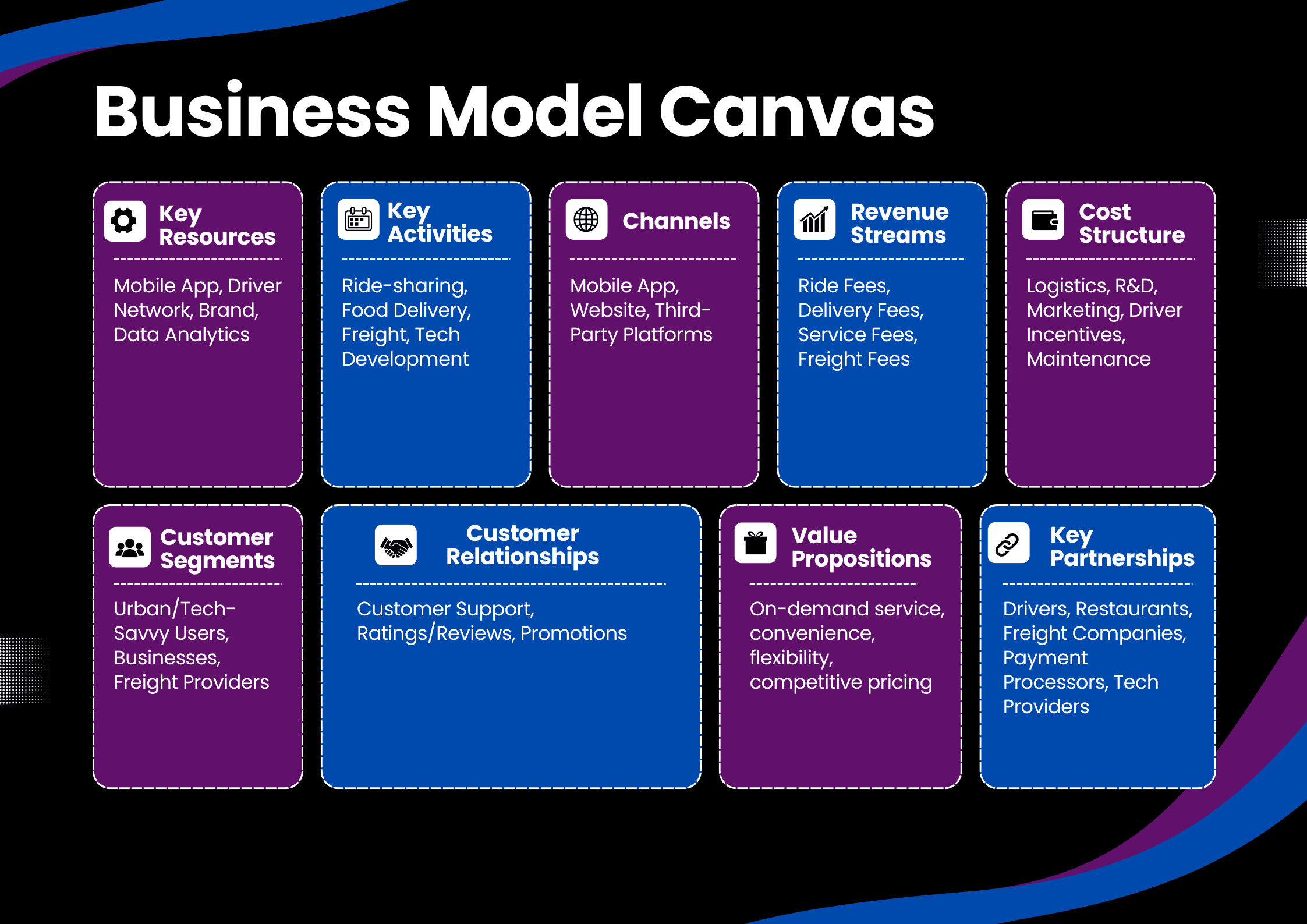
Uber’s Value Proposition
Uber’s value proposition centres around providing a seamless, on-demand, and accessible transportation service. Unlike traditional taxis, Uber offers flexible pricing through its mobile app, ensuring convenience and speed. It offers a high level of customer satisfaction through driver ratings and reviews, and ensures safety with real-time tracking.
The flexibility for both drivers and riders is a key differentiator, where drivers have the autonomy to choose their hours while customers benefit from a wide range of available rides. Additionally, Uber Eats capitalises on the growing demand for food delivery services, offering both businesses and customers an efficient platform. Uber’s integration of autonomous vehicles and innovative technology promises a future-proof service offering.
Uber Revenue Model
Uber’s revenue primarily comes from ride-hailing services, contributing approximately 60% of total income. Its second major source is Uber Eats, which accounts for about 25%. Uber Freight and other services like Uber for Business make up 15% of its overall revenue. Uber operates a commission-based model, taking a percentage of the total fare from drivers and from restaurant orders in the case of Uber Eats. In addition, Uber collects service fees from freight providers, making its model diversified and robust.
Uber Cost Structure
Uber’s main expenses are:
- Driver Incentives and Payments: Ensuring drivers remain satisfied and incentivised to offer their services
- Technology & Research & Development: Continuous investment in app development and autonomous vehicle technology
- Marketing and Customer Acquisition: Significant spending on digital marketing to acquire new users
- Logistics & Operations: The cost of running a global service infrastructure
Uber uses cost-saving strategies such as automating processes and outsourcing certain services. The brand's ability to keep operating costs low while scaling rapidly has allowed it to maintain competitive margins despite heavy investments in technology and expansion.
Uber Customer Segments
Uber’s primary customer segments include:
- Consumers (B2C): Primarily urban dwellers and tech-savvy users who prefer the convenience of on-demand services. This group spans various age groups and income levels
- Businesses (B2B): Companies using Uber for Business, which allows businesses to arrange transportation for employees
- Freight Providers: Businesses requiring transportation of goods via Uber Freight, catering to a niche logistics market
Customers are motivated by the ease of use, competitive pricing, and fast services, while businesses value the flexibility and efficiency Uber offers.
Uber Key Partnerships
Uber partners with a range of companies to operate efficiently, including:
- Drivers: Independent contractors who provide the ride-hailing services
- Restaurants: Partners in the Uber Eats ecosystem, providing food for delivery
- Freight Companies: Logistics providers using Uber Freight to connect truckers with shipping needs
- Tech Partners: Collaborations with mapping, AI, and payment processing platforms
These partnerships help Uber optimise its service delivery, improve its technological infrastructure, and ensure smooth operations.
DHL’s SWOT analysis provides an interesting comparison of how a logistics giant manages global supply chains, a factor relevant to Uber’s expansion into delivery and logistics services.
SWOT Analysis of Uber
| Strengths | Weaknesses | Opportunities | Threats |
|---|---|---|---|
| Market Leader, Strong Brand, Global Reach | Regulatory Challenges, High Operational Costs | Autonomous Vehicles, Expansion into New Markets | Intense Competition, Regulatory Hurdles |
Uber Competitor Comparison
| Aspect | Uber | Lyft | DoorDash |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pricing | Dynamic, Value-based | Competitive, slightly lower | Service fees based on orders |
| Customer Experience | Efficient, app-driven | Simplified, user-friendly | Fast, food-focused |
| Channel Strategy | eCommerce, Mobile App | eCommerce, Mobile App | eCommerce, Mobile App |
| Market Focus | Global, Tech-Savvy | Primarily U.S. | U.S., Food Delivery |
| Innovation | Autonomous Vehicles, AI | AI, Competitive Pricing | AI-based Delivery, Quick Service |
Key Takeaways for Students / Marketers
- Scalability: Uber's model is highly scalable due to its tech-driven, asset-light business model
- Customer Focus: Uber's focus on customer convenience, flexibility, and innovation is key to its success
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaborations with drivers, restaurants, and tech partners strengthen Uber's operations globally
- Adaptability: Uber continuously innovates, focusing on autonomous vehicles and expanding into new sectors like freight
Conclusion
Uber's business model emphasises leveraging technology for operational efficiency and global reach. With continuous innovation, it is poised to further disrupt multiple industries, maintaining its competitive edge. Will Uber's integration of autonomous vehicles reshape the future of transportation?
Want to Know Why 2,50,000+ Students Trust Us?
Dive into the numbers that make us the #1 choice for career success

MBA - Level
Best For
Fresh Graduates
Mode of Learning
On Campus (Mumbai & Delhi)
Starts from
Mar 23, 2026
Duration
11 Months
Live & Online
Best For
Working Professionals
Mode of Learning
Online
Starts from
Mar 6, 2026
Duration
4-6 Months

Online
Best For
AI Enthusiasts
Mode of Learning
Online
Duration
5 Months

Offline
Best For
12th Passouts
Mode of Learning
On Campus (Mumbai)
Duration
3 Years
Recent Post
Uber’s main products include UberX, UberPOOL, UberBLACK, UberEATS, UberFREIGHT, and Jump.
Uber’s top competitors include Lyft, Didi Chuxing, Ola, Grab, and Bolt.
Uber uses AI, machine learning, and advanced algorithms for route optimisation, dynamic pricing, and personalised recommendations.
UberEATS is a food delivery service that connects customers with local restaurants for convenient meal delivery.
Uber holds approximately 68% of the US ride-hailing market.
Uber’s CSR initiatives include transitioning to electric vehicles, enhancing safety features, and supporting community health and disaster response.
Uber operates a two-sided marketplace connecting drivers and riders, using advanced technology for efficient service delivery.
Aditya Shastri leads the Business Development segment at IIDE and is a seasoned Content Marketing expert. With over a decade of experience, Aditya has trained more than 20,000 students and professionals in digital marketing, collaborating with prestigious institutions and corporations such as Jet Airways, Godrej Professionals, Pfizer, Mahindra Group, Publicis Worldwide, and many others. His ability to simplify complex marketing concepts, combined with his engaging teaching style, has earned him widespread admiration from students and professionals alike.
Aditya has spearheaded IIDE’s B2B growth, forging partnerships with over 40 higher education institutions across India to upskill students in digital marketing and business skills. As a visiting faculty member at top institutions like IIT Bhilai, Mithibai College, Amity University, and SRCC, he continues to influence the next generation of marketers.
Apart from his marketing expertise, Aditya is also a spiritual speaker, often traveling internationally to share insights on spirituality. His unique blend of digital marketing proficiency and spiritual wisdom makes him a highly respected figure in both fields.

