
Orginally Written by Aditya Shastri
Updated on Dec 12, 2025
Share on:
Reliance Industries' business model is built on its diversified portfolio, including petrochemicals, refining, telecom, and retail. This strategy allows them to offer a broad range of products and services while maintaining strong market leadership. Reliance achieves this by integrating technology, optimising supply chains, and leveraging economies of scale.
By continually innovating and expanding across sectors, Reliance drives growth and global competitiveness. In this blog, we decode Reliance Industries’ revenue model and strategy, shedding light on how it has achieved market dominance and consistent growth.
Curious about how Reliance’s diversified model powers its global success? Read on to learn more!
About Reliance Industries

Founded by Dhirubhai Ambani in 1966, Reliance Industries Limited (RIL) is one of India’s largest conglomerates with a diverse business presence across petrochemicals, refining, telecommunications, and retail. The company’s unique value proposition lies in its integrated business model, utilising synergies across different sectors to fuel growth and innovation.
RIL has posted a revenue of ₹8.39 trillion in FY 2023 and employs over 2,50,000 people globally, securing its position as a market leader. Reliance’s customer-first approach, commitment to sustainability, and focus on continuous innovation have helped it expand and lead across various industries.
With a deep-rooted philosophy of empowering people and businesses, RIL’s diversified model is the key to its long-term success and leadership across sectors.
Summary table
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Founded | 1966 |
| Founder | Dhirubhai Ambani |
| Headquarters | Mumbai, India |
| Industry | Conglomerate (Petrochemicals, Refining, Retail, Telecom) |
| Revenue (2023) | ₹8.39 trillion |
| Presence | Global, 50+ countries |
| Employees | 2,50,000+ |
| Popular for | Telecom (Jio), Retail (Reliance Retail), Petrochemicals & Refining |


Learn Digital Marketing for FREE


How Does Reliance Industries Make Money?
Revenue Stream Breakdown:
Product Sales: Reliance generates significant income from petrochemical products, refined fuels, and textiles. These products serve both domestic and international markets, contributing heavily to its revenue.
Subscription Fees: Reliance Jio, a leading telecommunications provider in India, brings in substantial recurring revenue from mobile and broadband subscriptions.
Franchise Fees: Reliance Retail operates numerous outlets under its brands, contributing revenue through franchise agreements.
Advertising Revenue: Reliance’s media division, particularly through Jio and its broadcast content, generates advertising revenue from TV ads, online content, and sponsored promotions.
Services: Reliance provides services such as broadband, telecom, and cloud offerings. These services contribute to its recurring revenue model.
Licensing/Royalties: Revenue from telecom spectrum sales and intellectual property rights, such as licensing deals, contributes to Reliance’s income stream.
Other Revenue Streams: Income from one-time events, asset sales, or special projects also form part of its diversified revenue generation.
Revenue Contribution:
Telecom (Jio): Approximately 35% of total revenue, driven by the broad adoption of mobile, broadband, and digital services in India.
Petrochemicals: Around 30% of total revenue is generated through the sale of petrochemical products, refined fuels, and textiles.
Retail: Contributes approximately 25% of total revenue, driven by Reliance Retail's dominance in the Indian retail sector.
Others (Media & Licensing): Contributes around 10% of total revenue from advertising and licensing income.
Pricing Strategy:
Value-Based Pricing: Used for telecom services through Jio, where the pricing is set according to the perceived value of mobile data, internet services, and broadband offerings.
Competitive Pricing: Applied to petroleum products and petrochemicals, where Reliance competes on price while maintaining quality and operational efficiency.Premium Pricing: Used for select luxury goods offered under Reliance Retail, targeting higher-income customers who value premium quality products and services.
This pricing model allows Reliance to attract a broad consumer base, from mass-market users for telecom and petroleum products to high-end buyers for luxury goods. The diverse pricing strategy strengthens its market positioning across various sectors, ensuring substantial revenue across its portfolio.
Reliance Industries Business Model Canvas
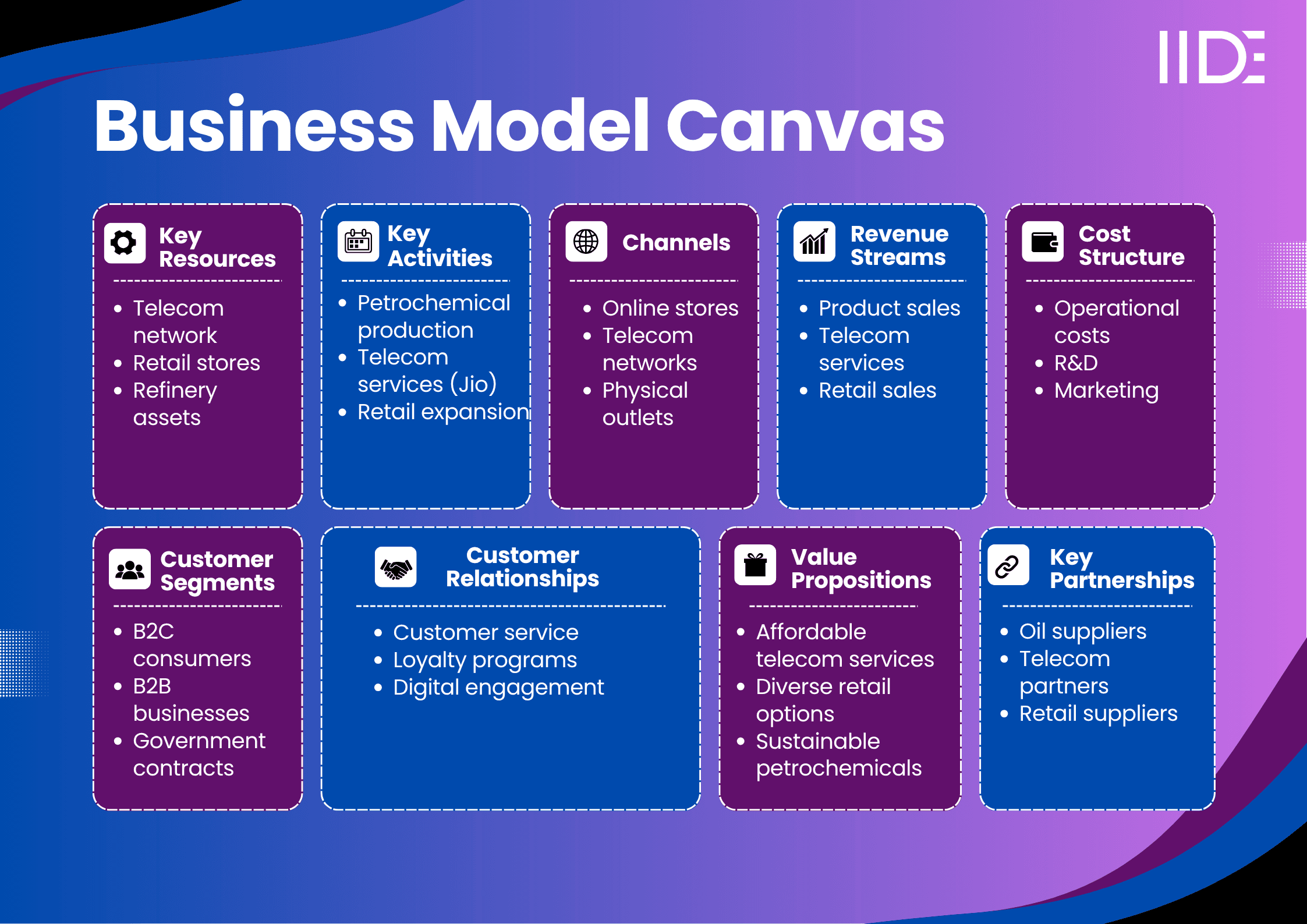
Reliance Industries Value Proposition
Reliance Industries uniquely integrates diverse sectors, from petrochemicals and telecom to retail, creating synergies that fuel growth.
By providing affordable, high-quality telecom services through Jio, Reliance revolutionised communication in India.
The retail division offers a wide range of products, from groceries to electronics, supported by both physical and online shopping experiences.
Reliance’s commitment to sustainability in petrochemical and retail operations addresses eco-conscious consumer needs.
It creates an emotional bond by offering innovation, customer-first solutions, and sustainable practices.
Customers benefit from functional advantages like speed, convenience, and quality.
Reliance’s competitive edge lies in its diversified and integrated business model, which competitors struggle to replicate.
Reliance Industries Revenue Model
Reliance Industries generates revenue through various sectors. The largest contributions come from product sales in petrochemicals (30%) and telecom services through Jio (35%).
Retail sales, both physical and e-commerce, account for about 25%, while media, advertising, and licensing contribute the remaining 10%.
This diverse approach ensures consistent revenue growth across multiple markets, balancing product sales and subscription-based models.
Reliance Industries Cost Structure
Reliance's major expenses include high costs for manufacturing, logistics, R&D, marketing, and telecom infrastructure.
Significant investments in refining, retail expansion, and technology lead to high capital expenditure.
To manage costs, Reliance focuses on bulk production, automation, and outsourcing non-core services.
These strategies help maintain healthy profit margins while driving growth in all sectors.
Reliance Industries Customer Segment
Reliance operates on a B2C and B2B model, serving a wide customer base. Its core B2C segment includes urban middle to high-income consumers, tech-savvy individuals, and eco-conscious buyers.
Reliance targets consumers of all ages who seek affordable telecom services, diverse retail options, and sustainable products.
The B2B segment includes businesses needing petrochemical products and telecom infrastructure, while government contracts further expand its reach.
Reliance Industries Distribution Channels
Reliance uses both physical and digital channels for distribution. Its telecom services, including Jio, are available through a vast retail network and digital platforms.
Reliance Retail operates both online via JioMart and through physical stores across India.
The brand also follows an omnichannel approach, seamlessly integrating online and offline experiences for convenience, with additional services like app-based shopping and customer support.
Reliance Industries Key Partnerships
Reliance collaborates with several key partners, including raw material suppliers for petrochemical production, telecom infrastructure providers for network development, and technology partners for digital services.
It works with retail suppliers and franchisees to expand its retail footprint.
Reliance also engages in sustainability partnerships with NGOs and government entities to ensure eco-friendly practices and promote green technologies across its operations.
SWOT Analysis of Reliance Industries
| Strengths | Weaknesses | Opportunities | Threats |
|---|---|---|---|
| Market leader in multiple sectors | High debt levels | Expanding telecom and retail globally | Intense competition in telecom and retail |
| Strong technological infrastructure | Dependence on oil prices | Growth in digital services | Regulatory challenges in energy sectors |
| Diversified revenue streams | Operational complexities | Sustainable energy investments | Fluctuating global market conditions |
Competitor Comparison:
| Parameter | Reliance Industries | Tata Group | Adani Group |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pricing | Competitive | Premium | Competitive |
| Customer Experience | Affordable, Tech-driven | Premium, Service-oriented | Value-focused |
| Channel Strategy | Omnichannel, Retail, E-commerce | Hybrid, Physical and Digital | Physical & Digital |
| Market Focus | Global | Global | Domestic & Regional |
| Innovation | Telecom, Retail Tech | IT, Automotive | Energy, Infrastructure |
Want to Know Why 5,00,000+ Students Trust Us?
Dive into the numbers that make us the #1 choice for career success

MBA - Level
Best For
Fresh Graduates
Mode of Learning
On Campus (Mumbai & Delhi)
Starts from
Mar 23, 2026
Duration
11 Months
Live & Online
Best For
Working Professionals
Mode of Learning
Online
Starts from
Mar 6, 2026
Duration
4-6 Months

Online
Best For
AI Enthusiasts
Mode of Learning
Online
Duration
5 Months

Offline
Best For
12th Passouts
Mode of Learning
On Campus (Mumbai)
Duration
3 Years
Recent Post
Aditya Shastri leads the Business Development segment at IIDE and is a seasoned Content Marketing expert. With over a decade of experience, Aditya has trained more than 20,000 students and professionals in digital marketing, collaborating with prestigious institutions and corporations such as Jet Airways, Godrej Professionals, Pfizer, Mahindra Group, Publicis Worldwide, and many others. His ability to simplify complex marketing concepts, combined with his engaging teaching style, has earned him widespread admiration from students and professionals alike.
Aditya has spearheaded IIDE’s B2B growth, forging partnerships with over 40 higher education institutions across India to upskill students in digital marketing and business skills. As a visiting faculty member at top institutions like IIT Bhilai, Mithibai College, Amity University, and SRCC, he continues to influence the next generation of marketers.
Apart from his marketing expertise, Aditya is also a spiritual speaker, often traveling internationally to share insights on spirituality. His unique blend of digital marketing proficiency and spiritual wisdom makes him a highly respected figure in both fields.