
Orginally Written by Aditya Shastri
Updated on Feb 12, 2026
Share on:
The business model of Jollibee centers on a unique fusion strategy, blending Western fast food formats with Filipino flavors while maintaining affordable pricing. This localization-first approach helped Jollibee dominate its home market with 50% share against McDonald's 29%, and now fuels aggressive global expansion across 33 countries.
By combining company-owned stores in strategic markets with an asset-light franchising model, targeted acquisitions of complementary brands, and deep cultural resonance through emotional marketing, the business model of Jollibee transforms nostalgic comfort food into a $4.71 billion revenue engine.
The brand's secret: understanding that customers don't just buy fried chicken, they buy joy, community, and a taste of home.
About Jollibee

Jollibee was founded in 1975 by Tony Tan Caktiong in Quezon City, Philippines. Starting as a Magnolia ice cream parlor, it pivoted to fast food by 1978 after customers demanded hot meals, becoming the nation's beloved burger chain.
The one great idea that propelled Jollibee to global success was localizing fast food for Filipino tastes. Sweet spaghetti with hotdogs, Chickenjoy fried chicken, and garlic rice created dishes McDonald's couldn't match when it entered the Philippines in 1981.
Today, Jollibee operates 10,304 stores across 33 countries, generating ₱289.27 billion ($5.20B USD) in revenue. With 3,445 Philippines locations and rapid US expansion (first franchise August 2025), it plans a US IPO by 2027.
Jollibee cares deeply about joy, community, and Filipino hospitality. Their "Kwentong Jollibee" campaigns celebrate family moments. Customers experience consistent quality and warmth, whether in Manila or Manhattan. Its success lies in authentic Filipino flavors, operational excellence, and emotional brand storytelling that resonates globally while staying true to local roots.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Founded | 1975 (Ice cream parlor) → 1978 (Fast food) |
| Founder | Tony Tan Caktiong |
| Headquarters | Pasig, Metro Manila, Philippines |
| Store Network | 10,304 stores (3,445 Philippines, 6,859 International) |
| Countries | 33 countries globally |
| Revenue | ₱289.27 billion (~$5.20 billion USD, TTM June 2025) |
| Market Share | ~50% (Philippines chicken-and-burger segment) |
| Key Products | Chickenjoy, Jolly Spaghetti, Yumburger, Palabok |
| Brand Portfolio | Jollibee, Chowking, Greenwich, Red Ribbon, Mang Inasal, Smashburger, CBTL, Highlands Coffee, Tim Ho Wan, Compose Coffee |
| Stock Exchange | Philippine Stock Exchange (PSE: JFC) |


Learn Digital Marketing for FREE


How Does Jollibee Make Money?
Understanding Jollibee's revenue approach requires examining its diversified streams that balance Philippine dominance with aggressive international growth.
Product Sales (Primary Revenue Stream - ~70%): Revenue from company-owned and franchised stores selling fried chicken, burgers, spaghetti, and other menu items drives the majority of income. The flagship Jollibee brand contributes approximately 50% of total group revenue, with strong performance in both domestic (₱244.1 billion Philippine business SWS in 2024) and international markets (growing 29.5% in Q1 2025).
Franchise Fees (~20%): Jollibee's extensive franchising network generates substantial income through initial franchise fees and ongoing royalty payments. After operating 107 company-owned restaurants in North America, Jollibee launched US franchising in March 2025. The first US franchise in Queens, New York reports $17,000 in average daily sales ($6.2 million annualized). With 47 multi-unit development agreements signed and 30 more in pipeline, franchise revenue is accelerating.
Licensing Revenue (~5%): The Jollibee brand licenses its intellectual property for various consumer products and merchandise, generating additional income streams beyond restaurant operations.
Delivery Services (~5%): Revenue from both third-party platforms (GrabFood, DoorDash) and Jollibee's proprietary mobile app. The company launched a redesigned delivery app in September 2025 to reduce 20-30% commission costs from aggregators while building direct customer relationships and first-party data.
Multi-Brand Portfolio: Acquired brands contribute significantly, Compose Coffee (acquired August 2024 for $340 million) added 2,629 stores; CBTL (1,232 stores), Smashburger, Tim Ho Wan, Highlands Coffee (865 stores), Milksha (336 stores), and Mang Inasal all generate independent revenue streams.
Pricing Strategy: Jollibee employs a value-based, low-cost pricing strategy. Meals remain affordable to middle and lower-income consumers while maintaining quality perception. This volume-driven approach builds market share and customer loyalty. Average US store generates $14,500 in daily sales ($5.3 million annually), with average unit volume at $4.4 million, demonstrating strong pricing power despite competitive positioning.
Buyers Persona:

M. Ramesh
Visakhapatnam
Occupation: Junior lecturer
Age: 24 years
Motivation
Interest & Hobbies
Pain Points
Social Media Presence
Jollibee Business Model Canvas:
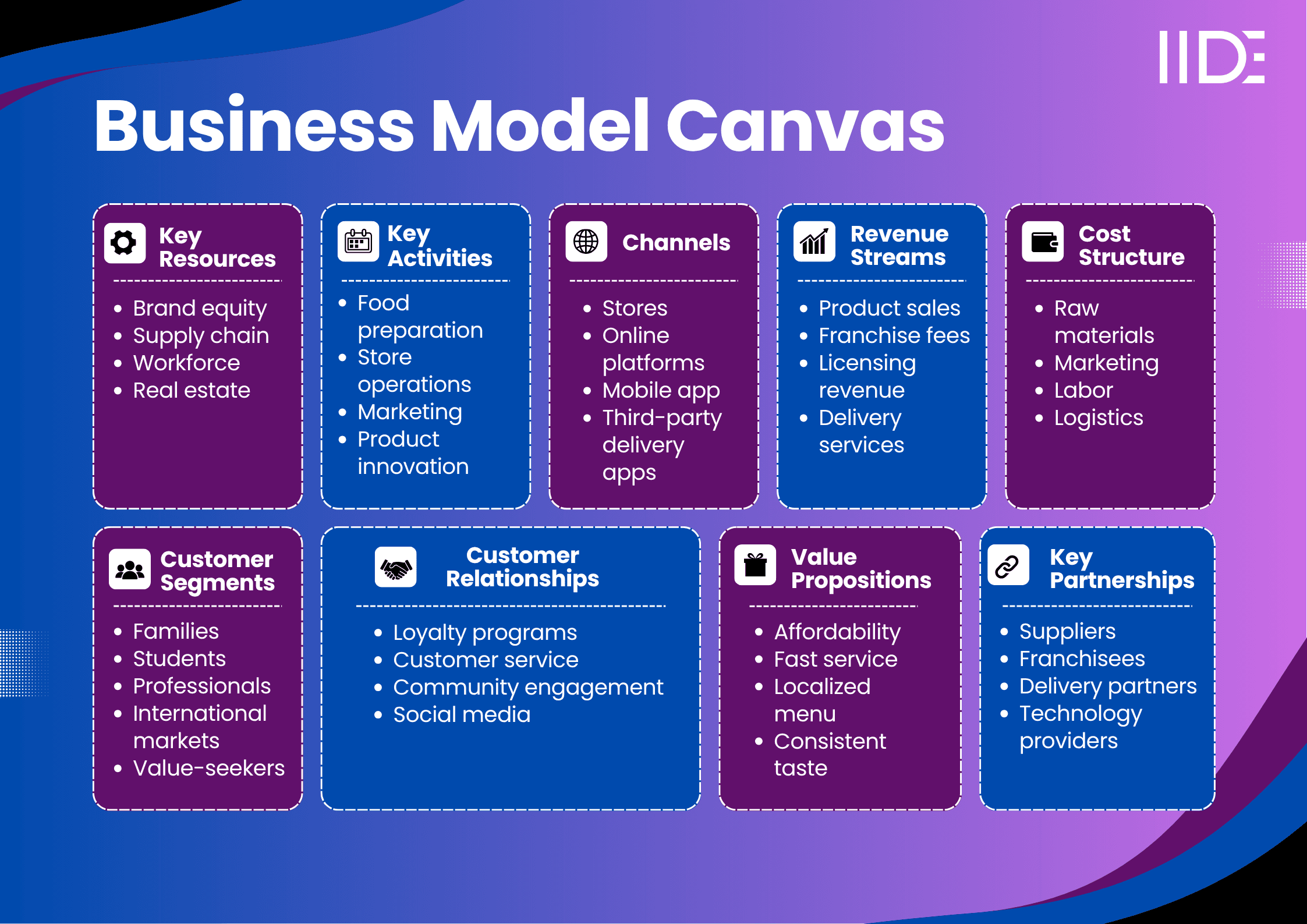
Value Proposition of Jollibee
The value proposition of Jollibee addresses multiple customer needs simultaneously, creating a unique market position.
Functional Benefits: Jollibee delivers quick-service food with consistent quality across all locations. The menu offers familiar Western fast-food formats (burgers, fried chicken, spaghetti) with Filipino flavor profiles, sweeter spaghetti sauce, perfectly seasoned chicken, unique burger combinations. Generous portions at affordable prices make meals accessible to families and budget-conscious consumers. The hand-breaded, marinated Chickenjoy takes hours to prepare, delivering restaurant-quality taste despite fast-food speeds.
Emotional Benefits: For Filipino customers, Jollibee represents national pride, a homegrown brand that defeated McDonald's on home turf. The value proposition of Jollibee extends beyond food to encompass nostalgia, family memories, and cultural identity. The brand's "Kwentong Jollibee" video series showcases authentic stories about reunions, sacrifice, and love, creating deep emotional resonance. International diaspora communities find comfort and connection to home through Jollibee meals.
Unique Differentiators: Unlike competitors offering standardized global menus, Jollibee succeeds through localization. The brand understands that Filipino consumers prefer bold, sweet, and savory combinations over bland Western flavors. Menu items like Jolly Spaghetti (sweet sauce with sliced hotdogs), Palabok (Filipino noodles), and Chickenjoy (with signature gravy) deliver authentic Filipino-fusion cuisine. USA Today named Jollibee's fried chicken "Best Fast Food Fried Chicken" in 2024 and 2025, validating that this unique positioning resonates beyond ethnic markets.
Convenience: Multiple ordering channels, dine-in, drive-thru, delivery apps, and Jollibee's mobile app with AI-powered personalized recommendations (launched 2025), meet customers wherever they are.
Jollibee Revenue Model
The business model of Jollibee generates revenue through multiple complementary streams that balance stability with growth.
Primary Revenue Sources:
1. Restaurant Sales (Company-Owned Stores) - ~60% of revenue: Direct sales from 3,445 Philippine locations and 1,828 international company-owned stores. Philippine business generated ₱224.2 billion in nine-month 2025 revenue with 5.5% same-store sales growth. International company-owned locations show stronger growth, 32.4% increase in Q1-Q3 2025. North American stores average $14,500 daily sales ($5.3 million annually), significantly above industry standards.
2. Franchise Revenue - ~20% of total revenue: Initial franchise fees plus ongoing royalties (typically 5-6% of gross sales) and required marketing contributions. With the March 2025 US franchise launch, this stream is expanding rapidly. The first Queens franchise generates $17,000 daily ($6.2 million annually). With 47 signed multi-unit development agreements and 30 more in pipeline, franchise revenue will accelerate 2026-2028.
3. Multi-Brand Portfolio Revenue - ~15%: Acquired brands operate semi-independently:
- Compose Coffee: 2,629 stores in South Korea, contributed 22.6% growth to coffee/tea segment
- CBTL (Coffee Bean & Tea Leaf): 1,232 stores, 16% SWS growth in 2024
- Highlands Coffee: 865 stores (mainly Vietnam), 13% SWS growth
- Smashburger: 369 North American locations
- Tim Ho Wan: Michelin-starred dim sum chain
- Mang Inasal: Philippine barbecue chicken, 86 stores opened in 2011 alone
- Chowking, Greenwich, Red Ribbon: Philippine heritage brands
4. Delivery Platform Revenue - ~5%: Income from delivery services through both third-party aggregators and Jollibee's proprietary app. The September 2025 app redesign aims to shift volume from 20-30% commission aggregators to direct orders, improving margins while building customer data assets.
5. Licensing and Other Income - ~5%: Brand licensing for consumer products, real estate income, investment returns, and royalties from international licensees.
Revenue Split by Geography (2024):
- Philippines: ~57% of revenue (₱244.1 billion SWS)
- International: ~43% of revenue, growing faster (32.4% in 2024 vs 10.1% domestic)
2024 Financial Performance:
- System-wide sales: ₱390.3 billion (13% YoY growth)
- Revenue: ₱269.94 billion ($4.71 billion USD)
- Net Income: ₱10.3 billion (first time exceeding ₱10 billion)
- Operating profit: ₱14.4 billion
2025 Projections (Management Guidance):
- System-wide sales growth: 8-12%
- Same-store sales growth: 4-6%
- Store network growth: 4-8%
- Operating profit growth: 10-15%
- Capital expenditure: ₱18-21 billion
- New stores: 700-800 (gross openings)
The revenue model demonstrates strong unit economics with consistent growth, transitioning from pure company-ownership to asset-light franchising internationally while maintaining dominance in high-margin Philippine operations.
Jollibee Cost Structure
Understanding Jollibee's operational costs requires examining how the company manages expenses while maintaining affordability and quality.
Major Operating Expenses:
1. Cost of Sales (50-55% of revenue): Food ingredients, packaging, and direct production costs constitute the largest expense. Jollibee maintains consistency through proprietary marinades and preparation processes. Chickenjoy requires hours of marination and hand-breading, labor-intensive but essential for quality. Commodity price fluctuations (chicken, flour, oil) directly impact margins. Philippine inflation reached 6% in 2023, forcing selective price increases.
2. Labor Costs (20-25% of revenue): Employee salaries, benefits, and training across 10,304+ stores globally. Jollibee maintains service quality through comprehensive training programs while managing labor inflation. Quick-service model minimizes per-transaction labor costs compared to full-service restaurants.
3. Occupancy and Real Estate (8-12% of revenue): Rent for leased locations, maintenance, utilities, and property expenses. Jollibee adapts to diverse real estate formats, urban inlines (Times Square), freestanding drive-thrus, mall locations, and strip-center endcaps. This flexibility reduces dependence on premium locations while maintaining accessibility.
4. Marketing and Advertising (5-7% of revenue): Traditional advertising, digital marketing, influencer campaigns, and the renowned "Kwentong Jollibee" emotional video series. Social media engagement, celebrity partnerships (Brent Manalo, Mika Salamanca for 2025 app launch), and limited-time offers drive traffic cost-effectively. Jollibee won 18 awards at the 2025 Marketing Excellence Awards for innovative campaigns.
5. Depreciation and Capital Expenditures: Store build-outs, equipment, technology infrastructure, and facility maintenance. 2025 budgets ₱18-21 billion for capital expenditure supporting 700-800 new store openings and digital infrastructure.
6. General and Administrative (6-8% of revenue): Corporate overhead, management salaries, IT systems, franchise support teams, and professional services.
Cost-Saving Strategies:
Franchising Model: Shifting from 100% company-owned North American stores to franchising transfers capital expenditure, operational risks, and labor management to franchisees while Jollibee collects royalties. This asset-light expansion accelerates growth without proportional cost increases.
Vertical Integration: Strategic partnerships with suppliers and some captive production (commissaries in Philippines) reduce procurement costs and ensure quality consistency. Philippine commissary sites achieved 32% energy reduction, 33% water reduction, and 44% waste decrease per metric ton versus 2020 baselines.
Operational Efficiency: Standardized processes, proven recipes, and systematic training minimize waste and maximize throughput. Smaller-footprint stores achieve higher sales per square meter than competitors.
Technology Investment: The 2025 mobile app redesign reduces third-party delivery commissions (20-30%) by driving direct orders. AI-powered personalization increases average order values. Digital ordering, automated inventory, and kitchen display systems improve efficiency.
Supply Chain Optimization: Logistics partnerships, bulk purchasing through multi-brand portfolio, and strategic vendor relationships control costs. Compose Coffee acquisition (2,629 stores) increases purchasing power for coffee segment.
Multi-Brand Leverage: Shared infrastructure, administrative systems, and supply chain relationships across Jollibee, Chowking, Greenwich, Red Ribbon, Mang Inasal, CBTL, and other brands distribute fixed costs.
Despite cost pressures, Jollibee maintains healthy margins through volume sales, operational discipline, and strategic pricing, with gross profit margins expanding 30 basis points and operating margins improving 10 basis points in Q1 2025.
Jollibee Customer Segment
Jollibee targets multiple customer segments with tailored approaches.
Primary Customer Segments:
1. Filipino Families (Core Domestic Market):
- Demographics: Ages 18-55, middle to lower-middle income families
- Location: Philippines (especially Metro Manila, provincial cities)
- Psychographics: Value-conscious, family-oriented, community-focused
- Motivation: Affordable meals for family gatherings, celebrations, everyday dining
- Behavior: Frequent visitors (weekly or bi-weekly), high brand loyalty, multi-generational customer base
2. Filipino Diaspora (International Growth Driver):
- Demographics: Filipino immigrants and descendants globally
- Location: USA (particularly California, New York, Texas, Nevada, Florida), Canada, Middle East, Europe
- Psychographics: Nostalgic, community-connected, cultural identity conscious
- Motivation: Connection to homeland, comfort food, cultural pride
- Behavior: Willing to travel distances for Jollibee, creates viral "first Jollibee visit" moments, high social media engagement
3. Value-Conscious Fast Food Consumers:
- Demographics: Ages 18-45, students, young professionals, lower to middle income
- Location: All markets (Philippines and international)
- Psychographics: Price-sensitive but quality-conscious, convenience-oriented
- Motivation: Affordable, filling meals without compromising taste
- Behavior: Frequent quick-service restaurant users, comparison shoppers, promotion-responsive
4. Food Explorers and Mainstream Americans:
- Demographics: Ages 25-50, diverse ethnic backgrounds, middle income
- Location: US urban markets (New York, Los Angeles, Texas, Florida)
- Psychographics: Adventurous eaters, social media active, experience-seekers
- Motivation: Trying unique international flavors, Instagram-worthy food experiences
- Behavior: First-time visitors driven by curiosity or USA Today "Best Fried Chicken" recognition, potential for repeat if product delivers
5. Digital-First Young Consumers:
- Demographics: Ages 18-35, digitally native, urban
- Location: Major cities globally
- Psychographics: Tech-savvy, mobile-dependent, influenced by social media
- Motivation: Convenience, app exclusives, personalized recommendations
- Behavior: Orders through mobile app, engages with limited-time offers, responds to influencer marketing
Business Model Orientation: Primarily B2C (Business-to-Consumer) with direct sales to individual customers and families. Limited B2B through catering services and bulk orders.
Market Positioning by Segment:
- Philippines: Market leader with ~50% share (vs McDonald's 29%), positioned as national champion
- North America: Premium-casual fast food competing with Chick-fil-A, Raising Cane's on quality; with KFC, Popeyes on chicken; positioned as "differentiated Filipino-fusion experience"
- Asia (China, Vietnam, Singapore): Regional player growing through localized menus and strategic acquisitions
- Middle East: Targeting Filipino OFW (Overseas Filipino Worker) communities while building mainstream appeal
Jollibee succeeds by serving core Filipino customers with unwavering loyalty while gradually expanding to mainstream markets through quality product, word-of-mouth, and strategic patience.
Distribution Channels of Jollibee
Jollibee reaches customers through an omnichannel approach combining physical and digital touchpoints.
Physical Retail Channels:
Company-Owned Stores: 3,445 locations in Philippines and select international markets (107 in North America before franchising launch). These flagship locations maintain brand standards, test new products, and demonstrate operational excellence. Formats include:
- Urban inline locations (Times Square, New York)
- Freestanding drive-thru units (suburban USA)
- Mall food court locations (Philippine shopping centers)
- Strip-center endcaps (neighborhood convenience)
Franchise Locations: Rapidly expanding post-March 2025 US franchise launch. First US franchise in Queens, New York opened August 2025, generating $17,000 daily sales. 47 multi-unit development agreements signed for California, New Jersey, New York, and Texas. International franchising established in Middle East, Southeast Asia, and other markets. Franchisees invest capital, manage operations, and pay royalties while Jollibee provides brand, systems, training, and support.
Multi-Brand Outlets: Portfolio brands operate independently:
- Compose Coffee: 2,629 stores (South Korea)
- CBTL: 1,232 stores globally
- Highlands Coffee: 865 stores (primarily Vietnam)
- Smashburger: 369 stores (North America)
- Mang Inasal, Chowking, Greenwich, Red Ribbon (Philippines)
- Tim Ho Wan (Asia Pacific)
Digital and Delivery Channels:
Jollibee Mobile App: Redesigned September 2025 with celebrity ambassadors Brent Manalo and Mika Salamanca. Features include:
- AI-powered personalized meal recommendations
- Direct ordering (avoiding 20-30% third-party commissions)
- Exclusive app-only promotions and limited-time offers
- Loyalty program enrollment (1 million members by end-2025)
- Mobile payment integration
Third-Party Delivery Platforms: Partnerships with GrabFood (Southeast Asia), DoorDash, Uber Eats (North America) expand reach beyond physical locations. While commission-heavy (20-30%), these platforms provide customer acquisition and convenience.
E-Commerce Website: Online ordering for delivery or pickup through jollibee.com and regional variants.
Innovation Channels:
Click-and-Collect: Customers order online, pick up in-store, reducing wait times and labor costs.
Drive-Thru: Standard in suburban US locations, increasingly common in Philippines, enables quick service for on-the-go customers.
Catering Services: Bulk orders for parties, events, corporate functions extend brand reach beyond individual transactions.
Social Commerce: Direct purchasing through social media platforms (Facebook, Instagram) where Jollibee maintains exceptionally active presence.
Omnichannel Strategy: Jollibee meets customers wherever they are, physical stores for experience and community, delivery for convenience, mobile app for personalization and efficiency. Real-time inventory integration ensures consistent availability across channels. The 2025 digital push aims to shift volume from commission-heavy aggregators to owned platforms, improving margins while building direct customer relationships and valuable first-party data for targeted marketing.
Omnichannel Strategy: Jollibee reaches customers through an omnichannel approach combining physical and digital touchpoints.
Jollibee Key Partnerships
Strategic partnerships enable Jollibee's global expansion and operational excellence.
Supplier Partnerships:
Food Suppliers: Long-term relationships with chicken, beef, produce, and dry goods suppliers ensure consistent quality and competitive pricing. Proprietary marinades and breading for Chickenjoy require specific ingredients sourced from trusted vendors. Multi-year contracts provide volume guarantees and price stability.
Commissaries and Processing Partners: Philippine commissary sites handle bulk food preparation, marination, and pre-processing before distribution to stores. These facilities achieved significant sustainability improvements, 32% energy reduction, 33% water reduction, 44% waste decrease per metric ton versus 2020.
Packaging Suppliers: Custom packaging maintaining brand identity while supporting sustainability initiatives. Transition to eco-friendly materials reduces plastic waste (2025 sustainability initiative).
Logistics and Distribution Partners:
Transportation Companies: Cold-chain logistics partners ensure fresh ingredients reach stores across Philippines archipelago and international markets. Blockchain technology exploration (2025) aims to improve supply chain transparency and traceability.
Warehousing Solutions: Regional distribution centers strategically positioned to serve store clusters efficiently.
Last-Mile Delivery: Integration with GrabFood, DoorDash, Uber Eats provides delivery infrastructure without capital investment in fleet.
Technology and Digital Partners:
Mobile Platform Developers: Partners built the September 2025 app redesign featuring AI-powered personalization engine.
Payment Processors: Integration with GCash (Philippines' leading mobile wallet, Jollibee won Third Place Excellence Growth Potential Award at GCash Digital Excellence Awards 2023), credit cards, and digital payment platforms.
CRM and Marketing Technology: Customer data platforms, email marketing systems, and analytics tools support personalized marketing and loyalty programs.
Franchise Partners:
Multi-Unit Developers: Experienced restaurant operators signing development agreements for 5-20+ stores. These franchisees bring capital, local market knowledge, and operational expertise. Current pipeline includes 47 signed agreements plus 30 commitments for US expansion.
Master Franchisees: Regional franchise rights holders in Middle East, Southeast Asia managing sub-franchisee networks and maintaining brand standards.
Financial and Advisory Partners:
Investment Banks and Advisors: International and local advisors working on planned US IPO of international business (late 2027). Goldman Sachs and others supporting corporate structure, valuation, and investor relations.
Private Equity: Historical partnerships like Titan Dining Partners (Tim Ho Wan acquisition) and ongoing relationships for acquisition financing.
Acquisition Targets Turned Partners:
Compose Coffee: $340 million acquisition (August 2024) added 2,629 stores and coffee expertise. Titan Dining II LP and Elevation Equity Partners Korea Limited retained minority stakes (5% and 25%).
Sustainability and Community Partners:
Environmental Organizations: Partnerships support eco-friendly packaging development, plastic waste reduction, and sustainable ingredient sourcing.
NGOs and Local Governments: Collaborate on community programs like Jollibee Group Foundation's Farmer Entrepreneurship Program (earned 2024 Entrepreneurship Development Programme Award, Social Welfare Award).
Reforestation Partners: Planted 21,500 mangrove propagules with local government units and employee volunteers supporting coastal restoration.
These partnerships optimize Jollibee's supply chain, reduce capital requirements through franchising, accelerate technology adoption, and enhance community impact, all essential components of the Jollibee business model enabling global scale while maintaining operational excellence.
SWOT Analysis of Jollibee
| Strengths | Weaknesses | Opportunities | Threats |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strong brand loyalty | Philippine market reliance | Global market expansion | Intense global competition |
| Localized menu differentiation | Unhealthy menu perception | Delivery platform growth | Rising raw material costs |
| Emotional customer connection | Multi‑brand complexity | Asian cuisine demand | Health trend shifts |
| Multi‑brand portfolio | Supply chain issues | Digital personalization | Currency fluctuations |
Jollibee Competitor Comparison
| Factor | Jollibee | McDonald's | KFC (Yum Brands) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Global Store Count | 10,304 (as of Sept 2025) | ~40,000 | ~30,000 |
| Market Cap | $3.9 billion | ~$210 billion | $37 billion (Yum Brands) |
| Primary Focus | Filipino-fusion fast food, fried chicken | Burgers, fries, global consistency | Fried chicken, global scale |
| Pricing Strategy | Value-based, affordable for middle/lower income | Mid-tier, premium in some markets | Mid-tier competitive |
| Menu Approach | Highly localized (sweet spaghetti, Filipino flavors) | Standardized globally with regional additions | Standardized chicken, regional customization |
| Customer Experience | Emotional connection, community-focused, Filipino hospitality | Fast, efficient, predictable experience | Casual dining, family-oriented |
| Distribution Model | Hybrid: Company-owned (strategic markets) + franchising (expansion) | Primarily franchised (~95%) | Primarily franchised |
| Growth Strategy | Targeted international expansion, diaspora-first then mainstream | Maintaining dominance, menu innovation, digital | Opening new franchise every 2 hours (Yum) |
| Technology/Digital | 2025 app redesign, AI personalization, building loyalty base | Advanced mobile ordering, delivery integration, digital kiosks | Mobile ordering, delivery partnerships |
| Brand Strength | Dominant in Philippines (50% share), cult following diaspora, emerging mainstream US | Globally recognized, decades of brand equity | Strong global recognition, established category leader |
| Competitive Advantage | Unique Filipino flavors, cultural authenticity, USA Today "Best Fried Chicken" | Scale, brand recognition, supply chain efficiency | Original Recipe secret blend, fried chicken expertise |
| Market Position | Growing challenger, regional leader Philippines | Global market leader | Global chicken category leader |
Want to Know Why 5,00,000+ Students Trust Us?
Dive into the numbers that make us the #1 choice for career success

MBA - Level
Best For
Fresh Graduates
Mode of Learning
On Campus (Mumbai & Delhi)
Starts from
Mar 23, 2026
Duration
11 Months
Live & Online
Best For
Working Professionals
Mode of Learning
Online
Starts from
Mar 6, 2026
Duration
4-6 Months

Online
Best For
AI Enthusiasts
Mode of Learning
Online
Duration
5 Months

Offline
Best For
12th Passouts
Mode of Learning
On Campus (Mumbai)
Duration
3 Years
Recent Post
Aditya Shastri leads the Business Development segment at IIDE and is a seasoned Content Marketing expert. With over a decade of experience, Aditya has trained more than 20,000 students and professionals in digital marketing, collaborating with prestigious institutions and corporations such as Jet Airways, Godrej Professionals, Pfizer, Mahindra Group, Publicis Worldwide, and many others. His ability to simplify complex marketing concepts, combined with his engaging teaching style, has earned him widespread admiration from students and professionals alike.
Aditya has spearheaded IIDE’s B2B growth, forging partnerships with over 40 higher education institutions across India to upskill students in digital marketing and business skills. As a visiting faculty member at top institutions like IIT Bhilai, Mithibai College, Amity University, and SRCC, he continues to influence the next generation of marketers.
Apart from his marketing expertise, Aditya is also a spiritual speaker, often traveling internationally to share insights on spirituality. His unique blend of digital marketing proficiency and spiritual wisdom makes him a highly respected figure in both fields.