
Orginally Written by Aditya Shastri
Updated on Dec 11, 2025
Share on:
Starbucks' business model is built on premium beverage experiences, customer‑centric innovation, and global scale. This strategy enables superior customer loyalty while maintaining profitability and a competitive edge. Starbucks achieves this through tech‑enabled loyalty programs, strategic store redesigns, and streamlined operations. It uses economies of scale, data analytics, and store optimisation to boost efficiency. But what’s the secret behind its brand resurgence? Discover Starbucks’ strategy for global success.
About Starbucks

Founded in 1971 by Jerry Baldwin, Zev Siegl, and Gordon Bowker in Seattle, Starbucks began as a single coffee bean retailer before evolving into a global coffeehouse brand. Its core unique selling proposition lies in the "third‑place" experience, a welcoming environment between home and work that fosters community and consistency.
As of fiscal 2024, Starbucks generated $36.18 billion in revenue, operating over 40,000 stores across 87 countries, with approximately 361,000 employees globally.
Starbucks is committed to ethical sourcing (99% C.A.F.E. verified coffee) and sustainability, with a goal to halve water and carbon footprints by 2030.
Customers enjoy personalised mobile ordering, rewards, and consistent global quality. The brand's ethos emphasises community, sustainability, and premium consistency. The secret to Starbucks’ success: balancing innovation and service with scale and strong global brand equity.
Summary table
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Founded | 1971 |
| Founder | Jerry Baldwin, Zev Siegl, Gordon Bowker |
| Headquarters | Seattle, Washington, USA |
| Industry | Coffeehouse / Food & Beverage |
| Revenue 2024 | $36.18 B |
| Presence | 40,000+ stores in 87 countries |
| Employees | ~361,000 |
| Popular for | Premium coffee, loyalty, café experience |


Learn Digital Marketing for FREE


How does Starbucks make money?
Revenue Stream Breakdown:
- Product Sales (e.g., physical goods, beverages):
Starbucks generates a significant portion of its revenue from company-operated stores where customers purchase beverages and food.
Contribution: 82.6% of net revenue ($7.81B of $9.456B in Q3 FY25).
- Franchise Fees (e.g., royalties):
Revenue from licensed stores, including franchise fees and royalties, forms a secondary revenue stream for Starbucks.
Contribution: ~11.7% of total revenue.
- Channel-Development (includes packaged goods & partnerships):
- Starbucks also earns revenue from packaged goods sold through retail partners and its brand partnerships.
Contribution: 5.7% ($0.54B).
Revenue Contribution:
- Product Sales: Make up the largest share, accounting for 82.6% of Starbucks' revenue, primarily from beverages and food sold at company-operated stores.
- Franchise Fees: Contribute around 11.7%, generated from licensed stores, including franchise royalties and fees.
- Channel-Development: Contributes 5.7%, consisting of packaged goods and various business partnerships.
Pricing Strategy:
Starbucks follows a value-based premium pricing strategy. Its strong brand identity, premium quality, and the experience provided to customers enable the company to charge higher prices compared to competitors. This approach supports healthy profit margins despite market pressures like inflation and competition.
Starbucks’ premium pricing is central to its market positioning as a high-end, experience-driven brand, allowing the company to maintain profitability and consistent growth even in a competitive environment.
Starbucks' Business Model Canvas
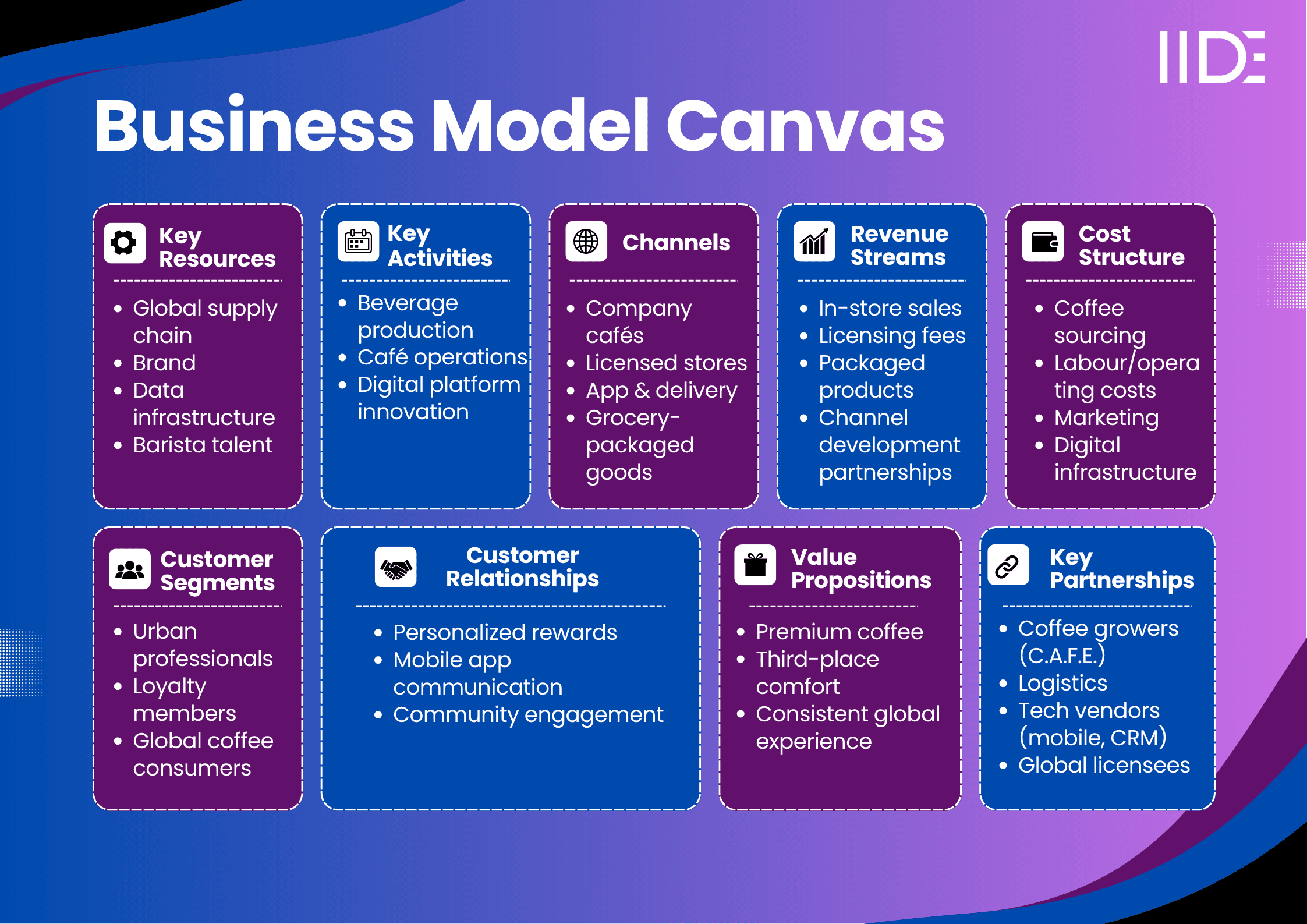
Starbucks Value Proposition
Starbucks delivers a distinct blend of premium beverages and a welcoming café atmosphere that serves as a trusted third‑place destination. Unlike other coffee brands, Starbucks offers consistent quality and a personalised experience powered by its robust digital loyalty platform and data-driven personalisation. It solves key customer pain points—providing convenience through fast mobile ordering and delivery, consistency in taste and service worldwide, and an aspirational ambience.
Emotionally, Starbucks fosters community pride through its ethical sourcing and sustainability efforts, enabling customers to feel connected to positive social impact. Their advanced loyalty platform empowers confidence in personalised rewards and seamless experiences.
Functionally, Starbucks offers fast service, efficient delivery, and durable product consistency across regions. Its competitive advantage lies in integrating advanced customer data analytics with real-world café experience—something competitors can struggle to replicate. This hybrid strength in digital-first personalisation and in-store community ambience sets Starbucks apart.
Starbucks Revenue Model
Starbucks generates the majority of revenue (~82.6%) from company-operated stores selling beverages and food. Licensed stores contribute ~11.7% through franchise and royalty fees.
The Channel Development segment—packaged goods and partnerships accounts for ~5.7%.
Most revenue is generated in physical cafés, with digital channels (mobile app and delivery) driving ~30% of transactions.
After launching the “Back to Starbucks” turnaround in 2025, Starbucks reported a 4% net revenue increase in Q3 FY25 to $9.456 B despite same-store sales declines.
Starbucks Cost Structure
Major expenses include coffee procurement, store operating labour, utilities, digital platform development, and marketing.
To manage costs, Starbucks employs economies of scale in sourcing, invests in automation (e.g., mobile-order systems), and uses bulk production and logistics efficiencies.
The “Back to Starbucks” initiative reinvested over $500 M into store labour and operations, temporarily reducing operating margin from ~21% to ~13.3% in North America during Q3 FY25.
Customer Segment
Starbucks operates a primarily B2C model targeting urban and suburban consumers aged 18–50 with middle-to-high incomes.
These digital‑savvy, brand‑aware customers seek convenience, consistency, and ethical sourcing.
Early adopters and health-conscious consumers gravitate toward innovations like protein foams and coconut‑water beverages.
Customers choose Starbucks for its premium experience, loyalty perks, and service speed, even as competitors emerge, its personalised digital engagement and community atmosphere maintain strong loyalty.
Distribution Channels
Starbucks distributes via company-operated cafés, licensed and franchised stores, and through Channel Development via packaged offerings in retail.
Its digital presence includes a mobile app, delivery, and rewards-driven eCommerce. Starbucks follows an omnichannel strategy, integrating in-store, mobile, and retail channels.
Additional touchpoints include the app, influencer campaigns, and personalised marketing via mobile and social media.
Renovated stores and tech upgrades (e.g. app-driven ordering, pick-up lines) improve efficiency and customer connection.
Key Partnerships
Starbucks partners with sustainable coffee growers under its C.A.F.E. program, third-party logistics firms, tech providers for mobile and CRM infrastructure, licensed store operators globally, and NGOs focused on climate resilience and farmer productivity.
These collaborations bolster operational efficiency, ensure ethical sourcing, and support community and environmental goals—fostering supply chain resilience and brand integrity.
SWOT Analysis of Starbucks
| Strengths | Weaknesses | Opportunities | Threats |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brand Loyalty | Margin Pressure | Health‑focused menu | Enabled Competitors |
| Digital Personalization | Store Sales Decline | Partnerships in China | Union Tensions |
| Sustainability Ethos | Cost Structure | Store Remodels | Inflation & Macro Risk |
Competitor Comparison
| Brand | Pricing | Customer Exp. | Channels | Market Focus | Innovation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Starbucks | Premium | Cozy café feel | Omni‑channel | Global urban | Digital loyalty, sustainability |
| McDonald’s Coffee | Value | Fast convenience | Drive‑thru, retail | Mass market | Global scale, speed |
| Dunkin’ | Affordable | Quick service | Drive‑thru, app | U.S. focus | Simplicity, speed |
What’s New With Starbucks?
Starbucks’ 2025 turnaround includes a digital loyalty revamp, AI-driven personalisation, new product innovations (e.g., protein cold foam, coconut-water drinks), a global store remodel program (“Green Apron Service”), and phasing out pickup-only formats in favour of community café spaces. Sustainability remains central, phasing out disposable cups in Korea by 2025 and targeting a 50% reduction in water and carbon footprint by 2030.
Want to Know Why 5,00,000+ Students Trust Us?
Dive into the numbers that make us the #1 choice for career success

MBA - Level
Best For
Fresh Graduates
Mode of Learning
On Campus (Mumbai & Delhi)
Starts from
Mar 23, 2026
Duration
11 Months
Live & Online
Best For
Working Professionals
Mode of Learning
Online
Starts from
Mar 23, 2026
Duration
4-6 Months

Online
Best For
AI Enthusiasts
Mode of Learning
Online
Duration
5 Months

Offline
Best For
12th Passouts
Mode of Learning
On Campus (Mumbai)
Duration
3 Years
Recent Post
Aditya Shastri leads the Business Development segment at IIDE and is a seasoned Content Marketing expert. With over a decade of experience, Aditya has trained more than 20,000 students and professionals in digital marketing, collaborating with prestigious institutions and corporations such as Jet Airways, Godrej Professionals, Pfizer, Mahindra Group, Publicis Worldwide, and many others. His ability to simplify complex marketing concepts, combined with his engaging teaching style, has earned him widespread admiration from students and professionals alike.
Aditya has spearheaded IIDE’s B2B growth, forging partnerships with over 40 higher education institutions across India to upskill students in digital marketing and business skills. As a visiting faculty member at top institutions like IIT Bhilai, Mithibai College, Amity University, and SRCC, he continues to influence the next generation of marketers.
Apart from his marketing expertise, Aditya is also a spiritual speaker, often traveling internationally to share insights on spirituality. His unique blend of digital marketing proficiency and spiritual wisdom makes him a highly respected figure in both fields.