
Updated on Nov 13, 2025
Share on:
HDFC Bank is one of India’s largest and most comprehensive banking corporations, offering a wide range of financial services. As a leading player in the private banking sector, HDFC stands out as a well-organised and customer-focused institution, winning over clients with its top-notch service quality and robust digital banking platform.
For market leaders like HDFC Bank, a strong online presence plays a crucial role in maintaining their leadership position. In today’s digital-first world, digital marketing is more important than ever - businesses need to be visible online to stay ahead.
In this case study, we’ll conduct a SWOT analysis of HDFC Bank to get a clearer picture of its position in the banking sector. Before you dive in, a shoutout to Harshada Joshi, a current student of IIDE’s ACDMS, May Batch 2025, who did all the research and initial analysis for this piece. If you found this article useful, don’t hesitate to drop Harshada a quick note of appreciation.
About HDFC Bank
HDFC Bank is one of India’s leading private sector banks, recognized for its strong financial performance, robust digital infrastructure, and customer-centric approach. The bank traces its origins to Housing Development Finance Corporation Limited (HDFC), established in 1977. As part of India’s banking sector liberalization, HDFC received in-principle approval from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in 1994 to set up a private sector bank. HDFC Bank commenced operations as a scheduled commercial bank in January 1995.
Over the years, the bank has built an extensive domestic network, comprising over 9,499 branches and 21,251 ATMs across 4,153 cities and towns as of June 30, 2025. More than half of these branches are strategically located in semi-urban and rural areas, reinforcing the bank’s commitment to financial inclusion and deeper market penetration.
HDFC Bank also maintains a growing international presence, with branches in Hong Kong, Bahrain, and Dubai, alongside an IFSC Banking Unit (IBU) at GIFT City, Gujarat. The bank’s representative offices in Kenya, Abu Dhabi, Dubai, London, and Singapore primarily cater to the Non-Resident Indian (NRI) segment, offering a range of cross-border financial solutions.
With a focus on innovation, operational excellence, and sustainable growth, HDFC Bank continues to play a pivotal role in shaping India’s banking landscape and expanding its global footprint.
| Metric | Details |
|---|---|
| Chairman | Atanu Chakraborty |
| Year Founded | Mon Aug 01 1994 00:00:00 GMT+0530 (India Standard Time) |
| Headquarters | Mumbai, Maharashtra, India |
| Number of Employees | 214,521 (as of March 31, 2025) |
| Company Type | Public |
| Market Capitalization | $170.11 billion (as of October 7, 2025) |
| Annual Revenue (FY25) | ₹2.73 trillion (approx. $32.7 billion USD) |
| Net Profit (FY25) | ₹188.3 billion (approx. $2.3 billion USD) |


Learn Digital Marketing for FREE


SWOT Analysis of HDFC
SWOT analysis is a practical way to assess a company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Let’s explore each aspect to understand what makes HDFC Bank tick and the challenges ahead.
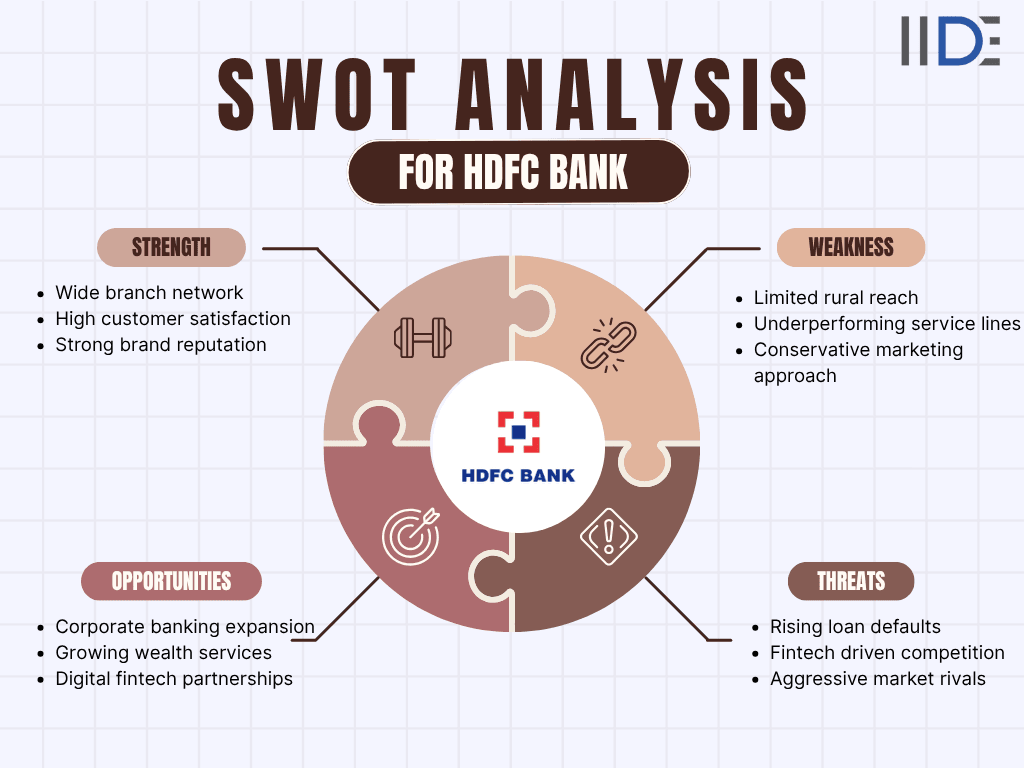
1. Strengths of HDFC
HDFC Bank’s success is powered by its internal strengths - qualities it manages and leverages effectively. Here are the key ones:
- Extensive Branch & ATM Network: As of June 2025, HDFC Bank has 9,499 branches and 21,251 ATMs across 4,153 cities, with over half in semi-urban and rural areas, boosting reach and accessibility.
- Strong Customer Satisfaction: HDFC Bank consistently ranks high in customer satisfaction, thanks to its digital initiatives that make banking faster, smoother, and more personalized.
- High Employee Retention: HDFC Bank has successfully reduced employee turnover, with attrition dropping to 22.6% in FY25, reflecting its strong focus on engagement and workplace satisfaction.
- Strong Brand Recognition: HDFC Bank enjoys a trusted reputation and continues to be recognized for excellence. In 2025, it won three major awards at the Global Private Banking Innovation Awards, including Best Domestic Private Bank-India, Best Private Bank for Insurance, and Best Wealth Management for $100k–$250k AUM.
2. Weaknesses Of HDFC
Weaknesses are flaws that detract from one’s strengths. These are areas that the business may need to improve to remain competitive:
- Limited Rural Presence: HDFC Bank’s reach in rural areas is still limited compared to competitors, leaving untapped growth opportunities in these markets.
- Underperforming Products: Some areas, like wealth management and insurance, haven’t reached their full potential, limiting HDFC Bank’s growth and diversification.
- Conservative Marketing: HDFC Bank focuses on brand trust over aggressive marketing, which can limit its reach to new customers.
- Stock Price Volatility: HDFC Bank’s shares can fluctuate frequently, which may affect investor confidence.
Discover the marketing strategy of HDFC Bank and see how it continues to stay ahead in a competitive banking landscape.
3. Opportunities of HDFC
Opportunities are external factors a company can leverage for growth and innovation. For HDFC Bank, they offer ways to expand reach, improve services, and strengthen its leadership in India’s banking sector.
- Strong Growth Potential: HDFC Bank’s superior asset quality compared to public sector banks positions it for sustained profit growth.
- Expansion in Corporate Banking: The growing SME sector gives the bank an opportunity to expand corporate services and attract more business clients.
- Wealth Management & Insurance Growth: With strong performance from subsidiaries like HDFC ERGO and HDFC Asset Management, the bank can offer tailored wealth and insurance solutions to affluent customers.
- Digital Banking & Fintech Collaboration: By embracing digital innovation and partnering with fintech companies, HDFC Bank can enhance services, improve efficiency, and attract tech-savvy customers.
- Global Expansion: The bank’s solid financial standing allows it to explore international markets through strategic alliances and acquisitions, diversifying revenue streams.
- Sustainable Banking Initiatives: Growing demand for eco-friendly financial products provides HDFC Bank an opportunity to introduce green loans and sustainable investment options.
4. Threats of HDFC
External elements over which the bank has no control are referred to as threats. The company needs to develop contingency plans for coping with them if they arise.
- Rising NPAs: Loan defaults have slightly increased, which could impact financial stability.
- Competition from New-Age Banks: Digital-first banks and fintechs are attracting tech-savvy customers.
- Pressure from ICICI Bank: Aggressive expansion by competitors is challenging HDFC’s market share.
- Modernizing Public Banks: Public sector banks are upgrading technology, intensifying competition.
- Foreign Investment Rules: Eased regulations could bring more foreign players into the Indian banking sector.
IIDE Student Takeaway, Recommendations and Conclusion
Student Takeaways
- A SWOT analysis gives a clear, structured understanding of what drives HDFC Bank’s performance and where it needs improvement.
- HDFC Bank’s biggest strengths come from its large physical network, strong brand image, high customer satisfaction, and stable workforce.
- Weaknesses like limited rural penetration, inconsistent performance in certain product lines, and conservative marketing show that even top banks have gaps to address.
- Opportunities such as expanding corporate banking, strengthening digital partnerships, entering global markets, and adopting sustainable banking can drive future growth.
- Threats like rising NPAs, new digital competitors, aggressive rivals like ICICI Bank, and foreign players entering the market show how dynamic and competitive the banking landscape is.
Recommendations
- Strengthen rural presence by increasing branches, agent networks, and micro-loan offerings in underserved regions.
- Revamp underperforming divisions such as wealth management and insurance through targeted strategies, improved customer segmentation, and stronger cross-selling.
- Adopt bolder marketing strategies to reach younger audiences and stand out in a competitive market.
- Collaborate with fintech innovators to enhance digital services, reduce operational costs, and offer faster, more intuitive customer experiences.
- Improve risk management systems to keep NPAs under control and maintain investor confidence.
- Explore global alliances for diversified growth, especially in markets with high Indian diaspora presence.
- Increase focus on sustainability by offering green loans and environment-friendly investment products.
Conclusion
The SWOT analysis of HDFC Bank shows that it remains one of India’s strongest and most trusted private banks, backed by a large network, innovative digital initiatives, and a powerful brand presence. At the same time, areas like rural penetration, product performance, and sharper marketing need attention to sustain long-term leadership.
With expanding opportunities in corporate banking, digital innovation, global markets, and sustainable finance, HDFC Bank is well positioned to grow further. However, to maintain its competitive edge, it must address rising NPAs, navigate pressure from digital-first competitors, and stay agile in a rapidly evolving banking landscape.
Want to Know Why 2,50,000+ Students Trust Us?
Dive into the numbers that make us the #1 choice for career success

MBA - Level
Best For
Fresh Graduates
Mode of Learning
On Campus (Mumbai & Delhi)
Starts from
Jan 5, 2026
Duration
11 Months
Live & Online
Best For
Working Professionals
Mode of Learning
Online
Starts from
Dec 19, 2025
Duration
4-6 Months

Online
Best For
AI Enthusiasts
Mode of Learning
Online
Duration
5 Months

Offline
Best For
12th Passouts
Mode of Learning
On Campus (Mumbai)
Duration
3 Years
Recent Post
HDFC Bank is known for its strong financial performance, excellent customer service, low NPA ratios, and robust digital platforms. Its consistent awards and high customer satisfaction also reinforce its leadership position.
HDFC Bank offers mobile banking, net banking, AI-driven support, contactless payments, instant loans, and seamless onboarding through digital KYC, making services faster and more convenient.
The bank focuses on trust, customer experience, and long-term relationships. It uses a mix of digital campaigns, financial literacy initiatives, brand partnerships, and product-led communication to build credibility.
HDFC Bank is known for strong asset quality, steady profitability, and responsible risk management. This financial stability helps the bank maintain investor confidence and long-term growth.
As of 2025, the CEO of HDFC Bank is Sashidhar Jagdishan, who has been leading the bank since 2020.
The bank’s vision is to create a world-class Indian bank focused on operational excellence, customer-centric services, and sustained financial performance.
Aditya Shastri leads the Business Development segment at IIDE and is a seasoned Content Marketing expert. With over a decade of experience, Aditya has trained more than 20,000 students and professionals in digital marketing, collaborating with prestigious institutions and corporations such as Jet Airways, Godrej Professionals, Pfizer, Mahindra Group, Publicis Worldwide, and many others. His ability to simplify complex marketing concepts, combined with his engaging teaching style, has earned him widespread admiration from students and professionals alike.
Aditya has spearheaded IIDE’s B2B growth, forging partnerships with over 40 higher education institutions across India to upskill students in digital marketing and business skills. As a visiting faculty member at top institutions like IIT Bhilai, Mithibai College, Amity University, and SRCC, he continues to influence the next generation of marketers.
Apart from his marketing expertise, Aditya is also a spiritual speaker, often traveling internationally to share insights on spirituality. His unique blend of digital marketing proficiency and spiritual wisdom makes him a highly respected figure in both fields.