
Orginally Written by Aditya Shastri
Updated on Dec 11, 2025
Share on:
Zara's business model revolves around a unique blend of fast fashion, sustainability, and cutting-edge technology. The brand is committed to offering stylish, affordable clothing through a seamless in-store and online experience.
By focusing on agile supply chains and customer insights, Zara maintains strong profit margins and delivers constant growth in an ever-evolving market.
About Zara
Zara, founded by Amancio Ortega in 1975, revolutionized fashion with its fast-paced production model and commitment to offering the latest styles at affordable prices. As part of Inditex, Zara has grown to become one of the world’s largest fashion retailers, with over 5,500 stores globally, spanning from Spain to the Americas, Europe, and beyond.
Zara’s success is driven by its customer-centric approach, using real-time data from stores to anticipate and respond to consumer demand swiftly. The brand is popular for its efficient supply chain, with a quick turnaround from design to retail, allowing it to keep up with rapidly changing fashion trends. Zara also prioritizes sustainability, incorporating eco-friendly materials and reducing waste through innovative practices.
With a robust online presence and strategically placed physical stores, Zara offers an omnichannel shopping experience that strengthens its position in the competitive fashion industry.
The key to Zara's success lies in its ability to adapt quickly to market trends while maintaining high-quality production standards.
Feature Details Table:
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Founded | 1975 |
| Founder | Amancio Ortega |
| Headquarters | Arteixo, Spain |
| Industry | Fashion Retail |
| Revenue (2023) | €38.6 Billion |
| Presence | Global, 5,563 stores |
| Employees | 174 nationalities |
| Popular for | Fast fashion, sustainability |
How does Zara make money?
Revenue Stream Breakdown:
- Zara’s primary revenue stream comes from product sales across its global retail network, both in-store and online.
- The company also generates income through franchise agreements, especially in regions where it does not directly manage stores.
Revenue Contribution:
- Product sales: 70%
- Franchise fees: 20%
- Online sales: 10%
Pricing Strategy:
- Zara uses a value-based pricing model, offering trendy, high-quality fashion at accessible prices, catering to a broad customer demographic.
- This strategy helps Zara maintain competitive pricing while ensuring strong margins.
Zara Business Model Canvas
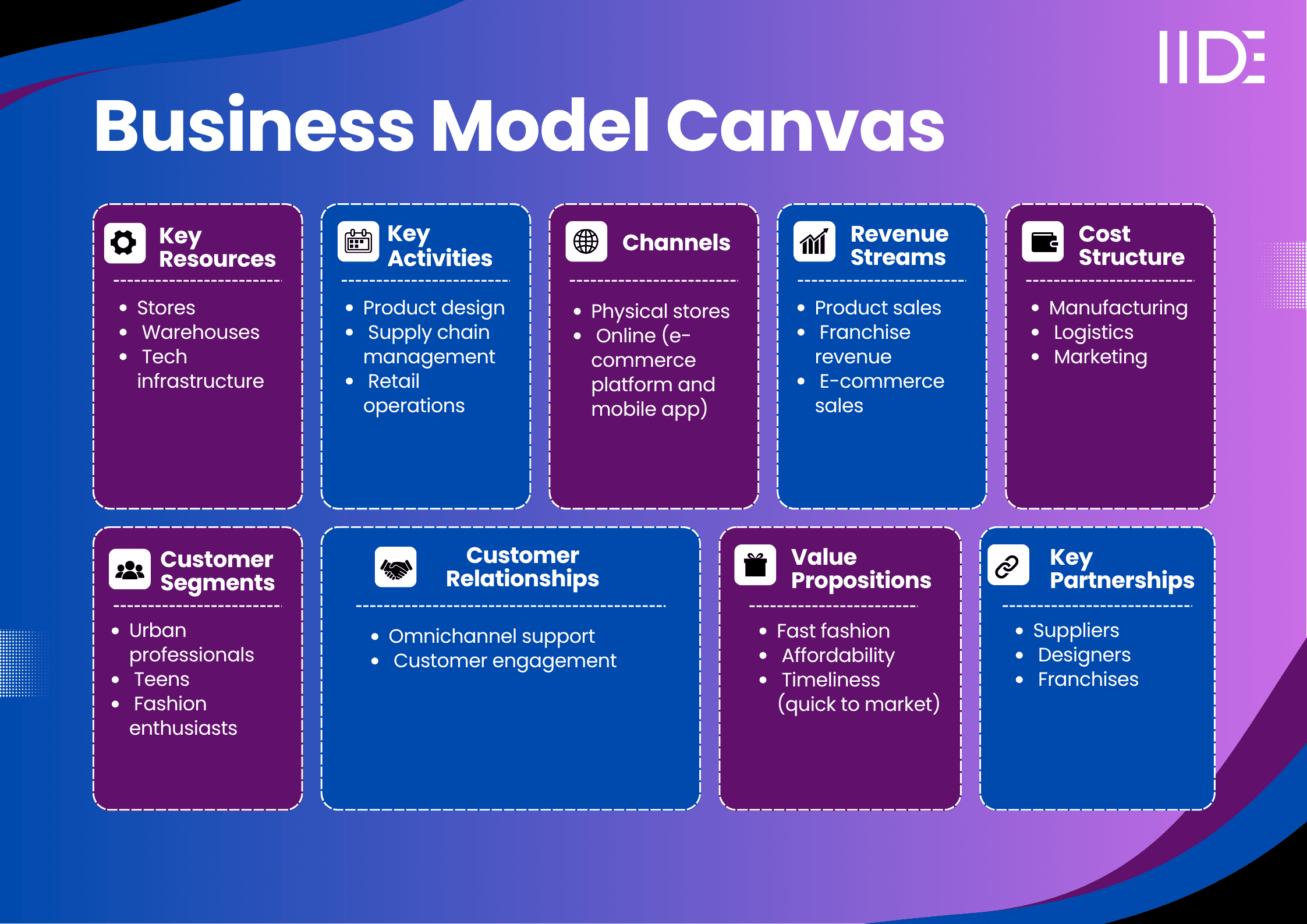
Zara’s Value Proposition
Zara offers a unique value proposition by combining the latest fashion trends with quick turnaround times at affordable prices.
Unlike many competitors, Zara’s strength lies in its ability to design, manufacture, and deliver new collections in a matter of weeks, which means it can respond rapidly to changing customer preferences.
This fast-fashion model allows Zara to keep its offerings fresh and relevant.
The brand also ensures a premium customer experience by integrating its online and in-store operations, offering seamless shopping experiences across channels.
For eco-conscious consumers, Zara’s commitment to sustainability, through initiatives like the use of organic fabrics and sustainable packaging, adds an emotional value.
Functional benefits include a wide range of styles that cater to different demographics, from high-quality everyday wear to more luxurious pieces.
Zara’s competitive edge is its ability to adapt to fashion demands swiftly while maintaining a high standard of quality, providing significant value to its customers.
Zara’s Revenue Model
Zara’s revenue model is primarily driven by product sales across its retail network, both physical and online, with a significant contribution from franchise partnerships.
The brand operates with a low-cost pricing strategy, aiming to provide high-fashion products at affordable prices.
Its omnichannel approach ensures a broad customer base while maintaining high margins.
Zara’s franchise agreements and international expansion help diversify its revenue streams, particularly in emerging markets.
Zara’s Cost Structure
Zara's primary expenses stem from manufacturing, logistics, and marketing.
The brand's quick-turnaround production model requires significant investment in supply chain management and inventory control.
Zara focuses on minimizing costs by leveraging bulk production, maintaining a global distribution network, and outsourcing certain operations.
It uses automation to streamline operations and control inventory efficiently.
Despite these high costs, Zara ensures healthy margins through its pricing strategy and rapid turnover of products, which maintains profitability.
Zara’s Customer Segment
Zara operates on a B2C model, primarily targeting fashion-conscious consumers aged 18-45, with a focus on urban professionals and teenagers.
The brand attracts customers looking for trendy, high-quality fashion at affordable prices.
Zara’s customer base spans multiple demographics, with a strong presence in Europe, the Americas, and Asia.
It appeals to both high-income and middle-income segments by offering a broad range of styles, from casual wear to semi-formal and formal attire.
Zara also targets eco-conscious consumers through sustainable collections.
Zara’s Distribution Channels
Zara operates through an integrated omnichannel strategy, seamlessly blending physical retail stores and online platforms.
With over 5,500 stores worldwide, the brand maintains a strong brick-and-mortar presence in key global shopping hubs.
Its eCommerce platform allows customers to shop online, with the option of home delivery or in-store pickup.
Zara utilizes third-party marketplaces for additional reach, while also leveraging innovative tech like RFID for real-time inventory management.
This integrated model ensures convenience for customers and efficient stock management.
Zara’s Key Partnerships
Zara’s key partnerships include relationships with suppliers, designers, and franchisees, enabling the brand to quickly adapt to market trends.
Its close collaboration with suppliers ensures that production is flexible and can quickly respond to demand shifts.
Zara also partners with tech companies for eCommerce and logistics solutions, enhancing its omnichannel capabilities.
Additionally, Zara works with sustainability-focused NGOs and initiatives to reduce its environmental footprint, aligning with its commitment to responsible business practices.
SWOT Analysis of Zara
| Strengths | Weaknesses | Opportunities | Threats |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fast fashion model | High production costs | Expanding into emerging markets | Intense competition |
| Strong brand recognition | Dependency on suppliers | Digital transformation in retail | Supply chain disruptions |
| Efficient supply chain | Limited product variety | Increasing demand for sustainable fashion | Economic downturns |
| Omnichannel integration | Store dependency | Innovation in customer experience | Geopolitical instability |
Zara’s Competitor Comparison
| Aspect | Zara | H&M | Uniqlo |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pricing | Affordable, value-based | Affordable, value-based | Mid-range, value-oriented |
| Customer Experience | Omnichannel, quick fashion cycle | Wide range, quality-conscious | Minimalist, functional designs |
| Channel Strategy | Integrated online and physical | Strong online presence, physical stores | Focus on physical retail with online growth |
| Market Focus | Fashion-forward, urban consumers | Broad market appeal, family-focused | Casualwear and functional attire |
| Innovation | Real-time inventory management | Focus on sustainability | Technology-driven, HeatTech fabric |
| Sustainability | Strong commitment to sustainable practices | Increasing focus on eco-friendly products | Significant emphasis on sustainable production |


Learn Digital Marketing for FREE


What’s New with Zara?
In 2025, Zara continued to innovate by expanding its digital presence, introducing an AI-powered personalisation engine that tailors product recommendations to individual customer preferences.
The brand also increased its sustainability efforts, introducing eco-friendly materials and packaging, and launching new circular economy initiatives.
Zara has focused on reducing carbon emissions and improving its waste management systems as part of its commitment to sustainability.
Furthermore, Zara has embraced automation and AI in its logistics and supply chain operations, ensuring better inventory control and faster order fulfilment.
Business model of IKEA highlights how inventory control and global logistics support scalability similar to Zara’s fast-fashion operational efficiency.
Key Takeaways for Students / Marketers & Conclusion
Key Takeaways:
Scalable Business Model: Zara’s success is rooted in its ability to scale rapidly through a flexible supply chain, omnichannel sales, and an adaptive business model.
Technology Integration: The brand demonstrates how integrating technology, like RFID and AI, can optimize operations and customer experience.
Sustainability as Strategy: Zara’s focus on sustainability shows how large retailers can balance business growth with environmental responsibility.
Omnichannel Advantage: Zara’s seamless blend of online and in-store experiences highlights the importance of an integrated sales environment in today’s retail landscape.
Innovation in Design & Production: Zara’s quick response to fashion trends, paired with its sustainable production practices, positions it as a leader in the fast-fashion sector.
Marketing strategy of Uniqlo provides a contrast in how minimalist branding and innovation shape success in the fashion retail space.
Conclusion:
Zara’s business model continues to evolve with the ever-changing retail landscape, combining agility, technology, and sustainability.
Its ability to adapt quickly to market demands, its omnichannel approach, and its focus on customer experience have cemented Zara as a leader in the global fashion industry.
As the brand moves toward 2025, its commitment to innovation, sustainability, and operational excellence will drive its future growth and success.
Will Zara’s model shape the future of fast fashion as we know it?
Want to Know Why 2,50,000+ Students Trust Us?
Dive into the numbers that make us the #1 choice for career success

MBA - Level
Best For
Fresh Graduates
Mode of Learning
On Campus (Mumbai & Delhi)
Starts from
Mar 23, 2026
Duration
11 Months
Live & Online
Best For
Working Professionals
Mode of Learning
Online
Starts from
Mar 6, 2026
Duration
4-6 Months

Online
Best For
AI Enthusiasts
Mode of Learning
Online
Duration
5 Months

Offline
Best For
12th Passouts
Mode of Learning
On Campus (Mumbai)
Duration
3 Years
Recent Post
Aditya Shastri leads the Business Development segment at IIDE and is a seasoned Content Marketing expert. With over a decade of experience, Aditya has trained more than 20,000 students and professionals in digital marketing, collaborating with prestigious institutions and corporations such as Jet Airways, Godrej Professionals, Pfizer, Mahindra Group, Publicis Worldwide, and many others. His ability to simplify complex marketing concepts, combined with his engaging teaching style, has earned him widespread admiration from students and professionals alike.
Aditya has spearheaded IIDE’s B2B growth, forging partnerships with over 40 higher education institutions across India to upskill students in digital marketing and business skills. As a visiting faculty member at top institutions like IIT Bhilai, Mithibai College, Amity University, and SRCC, he continues to influence the next generation of marketers.
Apart from his marketing expertise, Aditya is also a spiritual speaker, often traveling internationally to share insights on spirituality. His unique blend of digital marketing proficiency and spiritual wisdom makes him a highly respected figure in both fields.