About PayPal

Source: Google
Founded by Peter Thiel, Max Levchin, and Luke Nosek in 1998, PayPal has grown into one of the world’s foremost online payment platforms. Headquartered in San Jose, California, the company operates in over 200 markets worldwide.
The company’s mission is to make financial services accessible to everyone and empower people and businesses to join and thrive in the global economy. Key milestones of PayPal include its acquisition by eBay in 2002, its spin-off as an independent company in 2015, and its ongoing expansion into new markets and services.
But how does PayPal’s business work?
It’s simple – by offering a trusted platform for seamless transactions while continuously adapting to the evolving financial landscape. Whether it’s through merchant services, peer-to-peer payments, or innovative financial products, PayPal remains at the forefront of the digital payment revolution.
As digital transformation is increasingly reshaping the digital payments industry, PayPal is increasingly integrating digital marketing strategies into its business model. This evolution is creating many great opportunities for aspirants who want to work in this industry as digital marketing professionals. Many aspirants who want to work in such companies start looking for a digital marketing course in India to master this field and make a successful career in this dynamic industry.
Latest Statistics
- PayPal’s revenue for FY 2023 was $29 billion, reflecting an 8% increase from the previous year. [Source: PayPal Annual Report 2023]
- PayPal has 426 million active user accounts as of 2023. [Source: PayPal Q4 2023 Earnings Call]
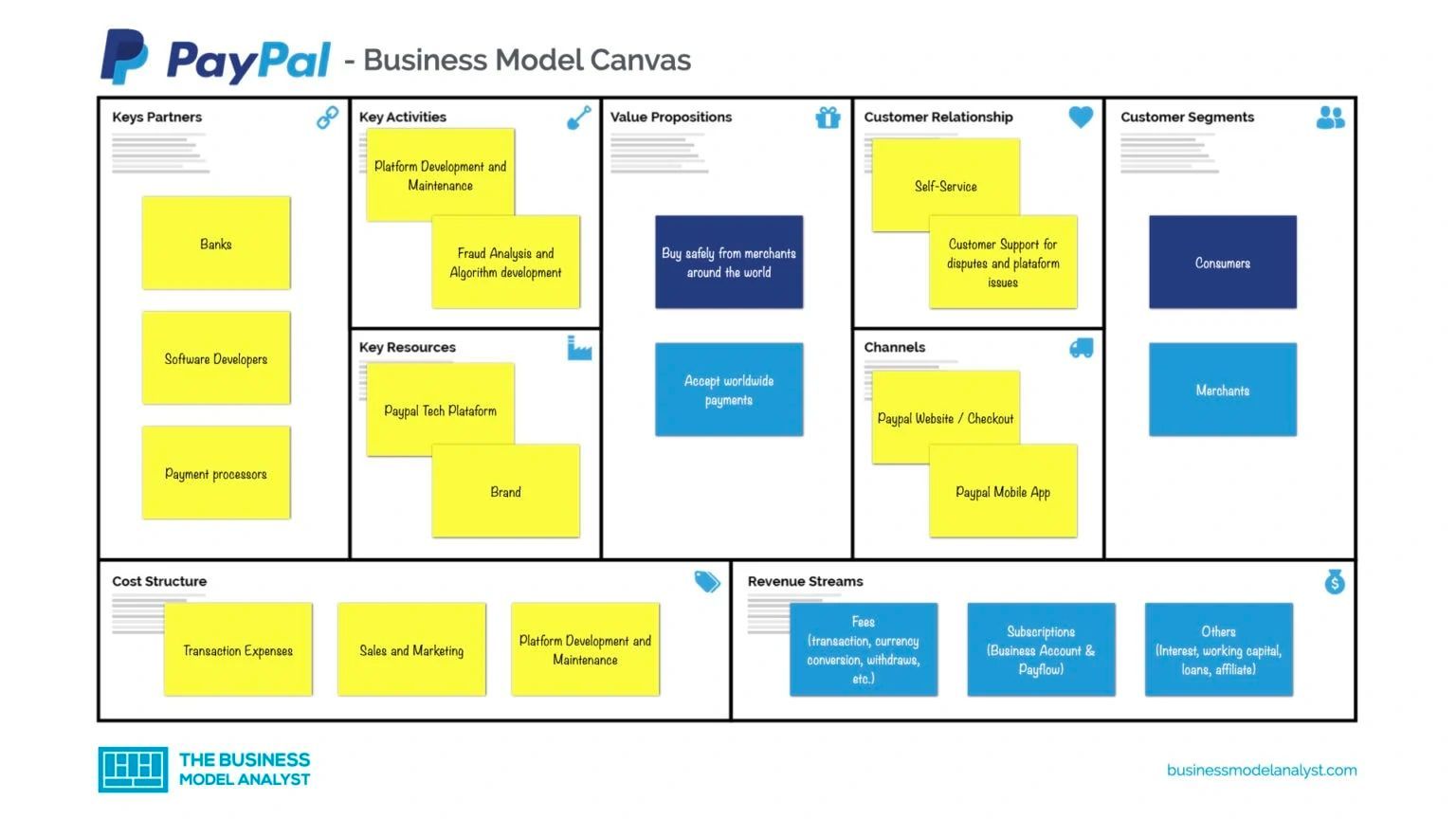
Business Model of PayPal
PayPal’s business model revolves around facilitating digital payments for both personal and business purposes. It operates as a payment gateway, processing transactions for e-commerce sites, auction platforms, and financial institutions.
So, how does PayPal make money? PayPal generates revenue primarily through transaction fees, interest on customer funds, and value-added services like credit and loans.
The business model of PayPal relies heavily on network effects – the more people and businesses use the platform, the more valuable it becomes. PayPal’s revenue streams come from a diverse set of sources, including fees charged to merchants, currency conversion fees, and interest earned on funds held in customer accounts. Additionally, PayPal’s business units, such as Venmo and Braintree, cater to different segments of the market, expanding its reach and influence.
Source: businessmodelanalyst.com
In essence, PayPal’s business model is built around providing convenient and secure digital payment solutions while tapping into diverse revenue streams that drive growth and sustainability.
Below is the list of components that form a part of PayPal’s Business Model.
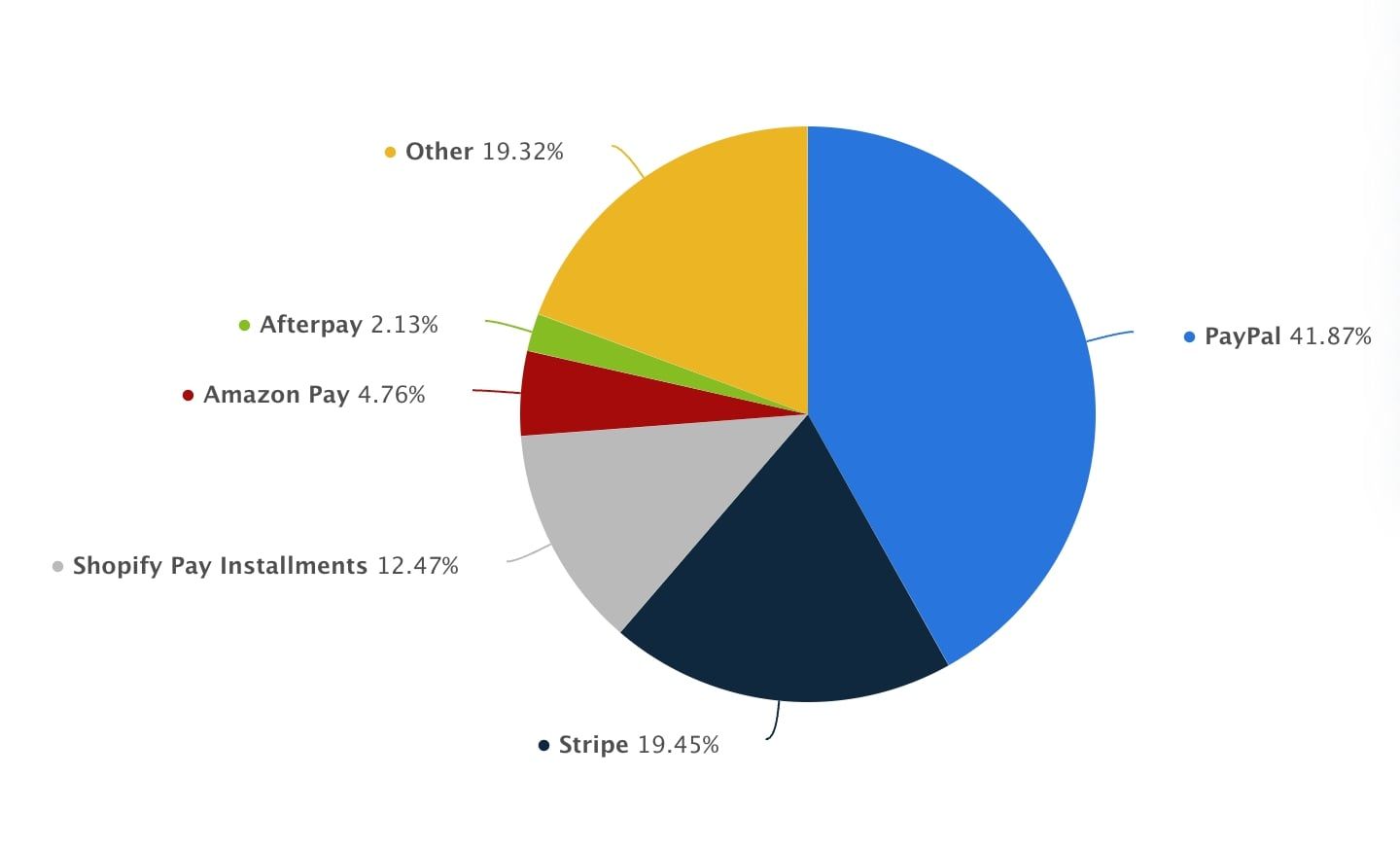
Business Model of PayPal: Brand’s Market Share and Analysis
PayPal’s business plan strategically positions the company to maintain a significant share of the global online payment market, with 426 million active user accounts worldwide. The company’s market analysis reveals strong growth in mobile payments and increasing adoption of digital wallets. PayPal’s comprehensive suite of services and global reach position it as a leader in the digital payment space. According to Statista, PayPal leads the global payments market with a 42% share.
Source: Google
Curious to learn how these elements contribute to a company’s business model? Check out our courses on digital marketing online to understand this from a marketer’s perspective.
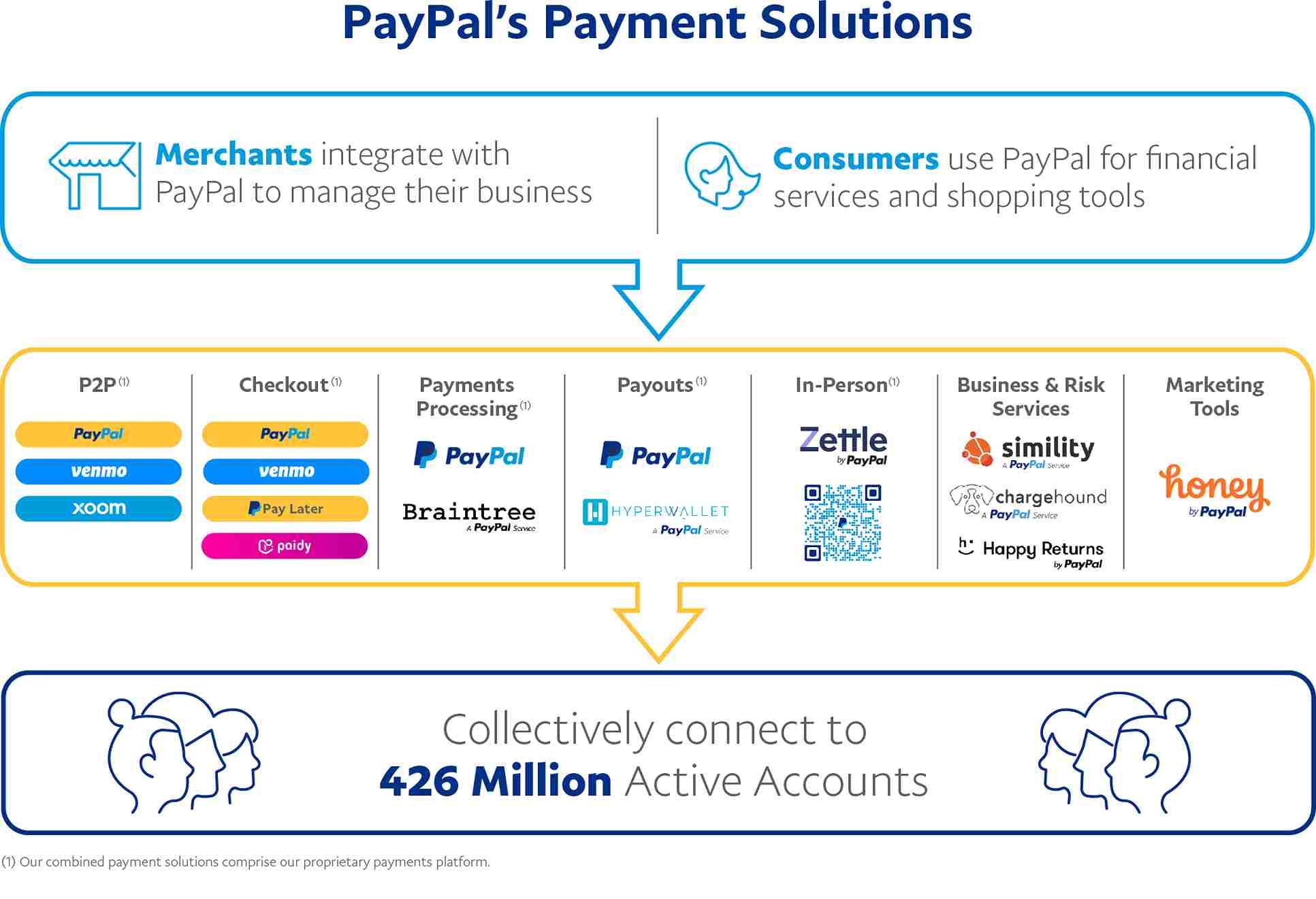
Business Model of PayPal: Product Offerings
PayPal offers a variety of products, including PayPal, PayPal Credit, Venmo, Braintree, and Xoom. These services cater to individual consumers and businesses, providing solutions for online payments, credit services, peer-to-peer transactions, and international money transfers. The diversity of these offerings plays a crucial role in PayPal’s revenue streams, while its integration with e-commerce platforms enhances its appeal to online merchants.
Source: Google
Curious to learn about how companies like PayPal leverage their business model to design marketing campaigns that bring in revenue? Then, study digital marketing online and learn how to apply strategies in real-life scenarios.
Target Audience of PayPal
PayPal’s target audience encompasses individual consumers, small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs), and large enterprises. Consumers use PayPal for secure online payments and money transfers, while businesses leverage its payment solutions to facilitate transactions and manage cash flow. PayPal’s business model also targets developers with APIs and tools for integrating payment solutions into apps and websites.
If you are interested in personal branding, then check out our free LinkedIn Essentials Masterclass and learn to build a powerful personal brand on the platform.
Business Model of PayPal: Funding and Investors
PayPal’s initial funding came from various venture capital firms, including Sequoia Capital. The company’s IPO in 2002 raised $70 million, and it later re-entered the public market in 2015 after its spin-off from eBay. PayPal continues to attract institutional investors, mutual funds, and individual shareholders due to its strong financial performance and growth prospects. A key factor in this success is PayPal’s revenue streams and its diverse business units, which contribute to its robust financial health and appeal to investors.
These days, businesses all across India, especially in Mumbai and Delhi, are increasingly interested in finding out how funding is allocated to marketing within a company’s business model and the specifics of digital marketing investment. This rising curiosity has led them to search for keywords (words used to search for information over the internet) like ‘digital marketing courses in Mumbai’ and ‘digital marketing courses in Delhi’.
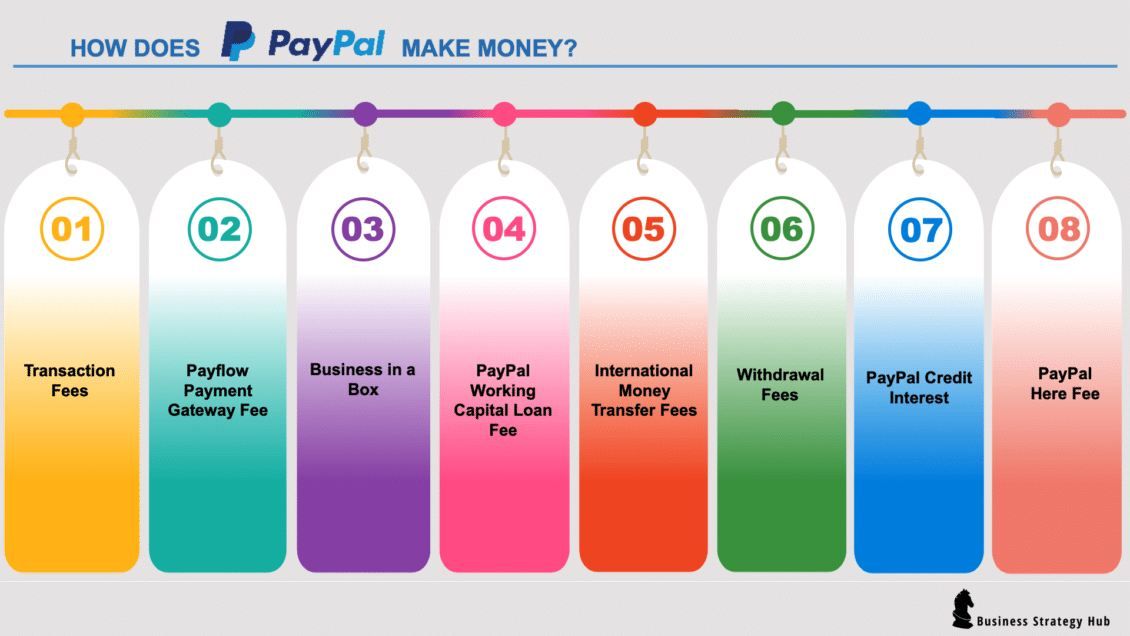
PayPal’s Revenue Model
PayPal’s revenue model is diverse, including transaction fees, cross-border fees, and interest on credit products. The company generates income from merchant services, including transaction processing fees and currency conversion fees. PayPal’s recent ventures into cryptocurrency transactions and buy-now-pay-later (BNPL) services further diversify its revenue streams.
Source: bstrategyhub.com
PayPal’s revenue model is also enhanced by its subscription services and value-added offerings. By providing premium features to businesses and consumers alike, PayPal captures multiple streams of revenue. PayPal’s business plan focuses on leveraging its global reach, customer trust, and technological innovation to maintain a competitive edge in the fintech industry.
Marketing Strategy
PayPal’s marketing strategy focuses on building trust and brand recognition. Digital marketing, social media, and strategic partnerships are key components of PayPal’s business plan to reach its audience. PayPal also invests in targeted advertising campaigns and collaborates with major retailers and financial institutions to enhance its market presence.
If you are eager to learn how marketing can influence and strengthen the business model of PayPal or any other company, join our free digital marketing masterclass and gain insights from both marketing and business perspectives!

Value Proposition
PayPal’s value proposition lies in providing a secure, convenient, and reliable platform for online payments. The company’s extensive network and innovative services ensure seamless transactions for consumers and businesses. PayPal’s commitment to security and user experience strengthens its position as a trusted payment provider.
Operational Model
PayPal operates a scalable and efficient operational model and it is supported by advanced technology and a global network of financial partners, which is a key aspect of PayPal’s business model. The company’s operations are driven by data analytics, machine learning, and robust fraud detection systems, ensuring secure and efficient transaction processing.
Business Model of PayPal: Strategic Alliances and Partnerships
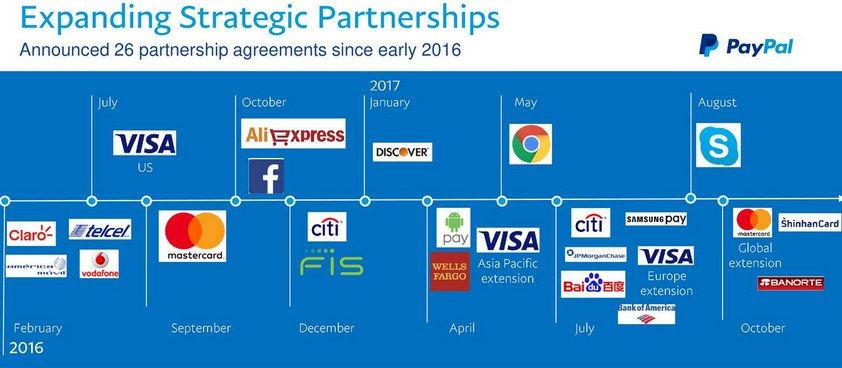
Source: Google
PayPal’s business plan includes forming strategic alliances with various e-commerce platforms, financial institutions, and technology companies. Partnerships with companies like eBay, Shopify, and Visa enhance PayPal’s capabilities and market reach. These collaborations also foster innovation and integration across different payment solutions.
Business Model of PayPal: Technological Innovations
PayPal invests heavily in technological innovation, focusing on enhancing security, expanding digital payment options, and developing new financial services. Innovations like One Touch payments, PayPal Here, and PayPal.me not only demonstrate the company’s dedication to staying at the forefront of digital payment technology but also play a crucial role in diversifying PayPal’s revenue streams.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
PayPal’s CSR initiatives are always aligned with PayPal’s business plan and it focuses on financial inclusion, sustainability, and community support. The company’s goal is to provide access to financial services for underserved populations and support various environmental and social causes. PayPal’s efforts in promoting digital literacy and entrepreneurship further underscore its commitment to positive social impact.

Source: Google
Do you find this article insightful? Check out our digital marketing blogs now!
Top Competitors of PayPal
PayPal is not the only business that operates in the digital payments industry. There are many other players in the market with the potential to compete with PayPal’s business model and potentially force them to make adjustments to it.
Here are some of the top competitors that rival PayPal’s business model:
- Square (Block, Inc.): A leading competitor in digital payments, Square offers point-of-sale systems and financial services for small businesses. Square’s Cash App also competes with PayPal in peer-to-peer payments.
- Stripe: Known for its developer-friendly payment processing platform, Stripe competes with PayPal’s business model in the e-commerce and online business sectors.
- Adyen: A global payment company that provides end-to-end payment solutions for businesses. Adyen’s strong presence in Europe and its comprehensive services make it a key competitor of PayPal.
- Apple Pay: Competes with PayPal’s business model in mobile payments and digital wallets. Apple Pay’s integration with iOS devices provides a seamless payment experience for Apple users.
- Amazon Pay: Amazon’s payment service rivals PayPal’s business model in the e-commerce space, offering a convenient payment option for Amazon customers and merchants.
These days, many businesses in Bangalore are facing intense marketing competition, but there’s a way to overcome it! Enrolling in a digital marketing course in Bangalore will equip you with the skills and knowledge to tackle these challenges effectively.
Learn From Asia’s #1
Digital Marketing Institute
AI-Based Curriculum
Dive in to the future with the latest AI tools
Placement at top brands and agencies

















