About Lowes
Lowe’s is an American home improvement retailer that was founded in 1921 by Lucius Smith Lowe. It is the world’s second-largest hardware chain. In North America, Lowe’s and its subsidiaries operate 2,197 home improvement and hardware stores.
Lowe’s sold mostly to contractors in its early years, and its locations were designed to seem like modest neighbourhood hardware stores. When Robert Strickland took over as chairman of the firm in 1978, he devised a marketing strategy aimed towards do-it-yourselfers.
Appliances, home décor, and garden items were added to the company’s product line, which had previously only included enormous tool and building supply inventories. From 2003 through 2010, Lowe’s received eight consecutive Energy Star honours, including four Energy Star Partner of the Year accolades for educating customers about the benefits of energy conservation.
Quick Stats on Lowe’s
| Founder |
Lucius Smith Lowe |
| Year Founded |
1921 |
| Origin |
Mooresville, North Carolina, US |
| No. of Employees |
300,000 |
| Company Type |
Public |
| Market Cap |
$162.57 Billion (2021) |
| Annual Revenue |
$72.148 Billion (2020) |
| Net Income |
$4.281 Billion (2020) |
Products of Lowes
- Home improvement
- Hardware
- Appliance items
Competitors of Lowes
- The Home Depot
- Target
- Walmart
- Best Buy
- Costco
Now that we have understood the company’s business and functions, let’s look into the SWOT Analysis of Lowe’s.
SWOT Analysis of Lowes
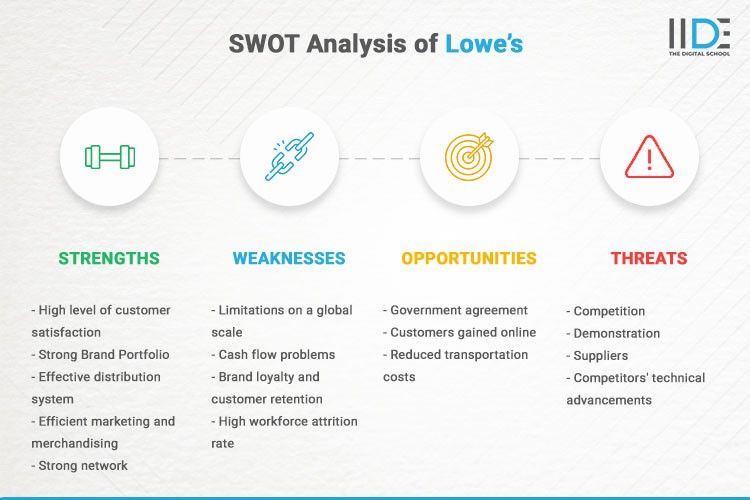
1. Strength of Lowe’s
As one of the industry’s leading corporations, Lowes has a significant advantage that helps it prosper in the marketplace. The following are Lowe’s strengths:
- High level of customer satisfaction: Owing to its devoted customer relationship, the firm has achieved a high level of customer happiness among current customers and strong brand equity among future consumers. They prioritise their customers’ wants and strive to meet them.
- Strong Brand Portfolio: Lowes, the retailing powerhouse, has focused on developing a strong brand portfolio. Lowes’ SWOT analysis just highlights this point. If the company wishes to grow into other product categories, this brand portfolio may be incredibly beneficial.
- Strong and effective distribution system: Lowe’s maintains 14 regional distribution networks in operation. For timber, building supplies, and other long-length products, they operate 15 truckload depots. Lowe’s can now effectively transport 75% of its products to its outlets and acquire large-scale purchases at a discount and pass the savings on to its consumers.
- Efficient marketing and merchandising: Lowe’s shops offer diverse sections to meet the requirements of different customers. Two examples are drive-through timber yards and outdoor garden centres.
- Strong network: Lowes has established a solid distribution network over the years that can reach the majority of its targeted market. Lowe’s Companies serve more than 14 million consumers.
2. Weakness of Lowe’s
The following are Lowe’s weaknesses that must be resolved for them to maintain their position in the industry.
- Limitations on a global scale: Lowe’s owns stores in the United States, Canada, and Mexico. While many of its merchandise may be sent anywhere in the globe, the lack of physical outlets in other countries may affect gross sales.
- Cash flow problems: Lowes has cash flow issues due to a lack of effective financial planning, which has resulted in situations where there isn’t enough cash flow as required, resulting in needless unexpected borrowing.
- Brand loyalty and customer retention: Recalls of products like the LED clip-on desk lights offered only at Lowe’s harm customer retention and loyalty.
- High workforce attrition rate: In the workforce, there is a high rate of attrition. In comparison to similar businesses in the industry, there is a high incidence of employee attrition. Lowes has a higher turnover rate and must spend significantly more on staff training and development than its competitors.
3. Opportunities for Lowe’s
Some of the opportunities for Lowe’s are mentioned below:
- Government agreement leads to new market opportunities: Lowes has been allowed to enter a new emerging market thanks to the adoption of a new technological standard and a government free trade agreement.
- Customers gained through the internet channel: The firm has put a lot of money into the internet platform in the last few years. Lowes has gained access to a new sales channel as a result of its investment. In the next few years, the firm can capitalise on this potential by better understanding its customers and addressing their requirements using advanced analytics.
- Reduced transportation costs: Lower shipping costs can lower the cost of Lowe’s products, giving the firm the option of either increasing profitability or passing on the savings to customers to win market share.
4. Threats to Lowe’s
Although Lowe’s is the industry’s topmost brand, numerous possible challenges might put the company at a disadvantage. The following are the threats mentioned in Lowe’s Companies’ SWOT Analysis:
- Competition: Lowe’s is the world’s second-biggest home improvement retailer. Retailers such as Wal-Mart and Home Depot are among its biggest competitors. Lowe’s must maintain competitive pricing and in-stock goods to sustain great financial success.
- Demonstration: Clients aren’t able to touch or feel the item, they might get confused and would prefer buying from elsewhere. Humane contact is a significant key in this industry, and the unavailability of doing so is a major danger because other firms provide it.
- Suppliers: As the number of suppliers has decreased over time, suppliers’ negotiating strength has grown. This might lead to a rise in Lowes’ input expenses.
- Competitors’ technical advancements: New technological advancements by a few competitors within the sector represent a danger to Lowes since customers are drawn to the new technology may be lost to competitors, reducing Lowes’ total market share.