
Orginally Written by Aditya Shastri
Updated on Feb 18, 2026
Share on:
Intel, once the uncontested leader of microprocessors, now stands at a critical inflection point in 2025. Legacy strengths like brand and scale persist but so do serious execution, financial, and competitive challenges.
In this in-depth SWOT analysis of Intel, we uncover where Intel is strong, where it’s vulnerable, where it can grow, and what external threats it must counter. For entrepreneurs, tech strategists, and students, this is your lens into how a tech giant reinvents itself under pressure.
Before diving into the article, we would like to inform you that the research and initial analysis for this piece were conducted by Tanaya Shirke. She is a current student in IIDE's Online Digital Marketing Course, May Batch 2025.
If you find this helpful, feel free to reach out to Tanaya Shirke to send quick note of appreciation for her fantastic research, she will appreciate the kudos!
About Intel
Intel Corporation was founded in 1968 by Robert Noyce and Gordon Moore, headquartered in Santa Clara, California. Over decades, Intel became synonymous with the PC era, with its iconic “Intel Inside” campaign embedding it into global consumer consciousness.
Today, Intel’s portfolio includes CPUs, GPUs, accelerators, memory, and foundry services. In 2025, under new CEO Lip-Bu Tan, the company is executing its IDM 2.0 strategy, combining internal and external manufacturing to compete in the AI and data-centric era.
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Official Name | Intel Corporation |
| Founded | 1968 |
| Founders | Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore |
| Headquarters | Santa Clara, California, USA |
| Core Industries |
Semiconductors, CPUs, Foundry, AI Accelerators |
| Geographic Reach | Global |
| Latest Performance |
Stock recovery in 2025 but credit downgraded by Fitch |
| Employees |
~108,900 (with 24,000 layoffs planned in 2025) |
| Major Competitors |
AMD, NVIDIA, TSMC, Samsung, Qualcomm |
Why Intel's SWOT Analysis Matters Now?
- The semiconductor race is heating up, driven by AI and next-gen computing.
- Consumer behavior is shifting from PCs to AI and data center workloads.
- Global politics and subsidies are reshaping manufacturing and trade routes.
- Intel is betting big on its IDM 2.0 strategy, but execution is everything.
So, this SWOT analysis helps us see where Intel still has an edge and where it’s losing ground.


Learn Digital Marketing for FREE


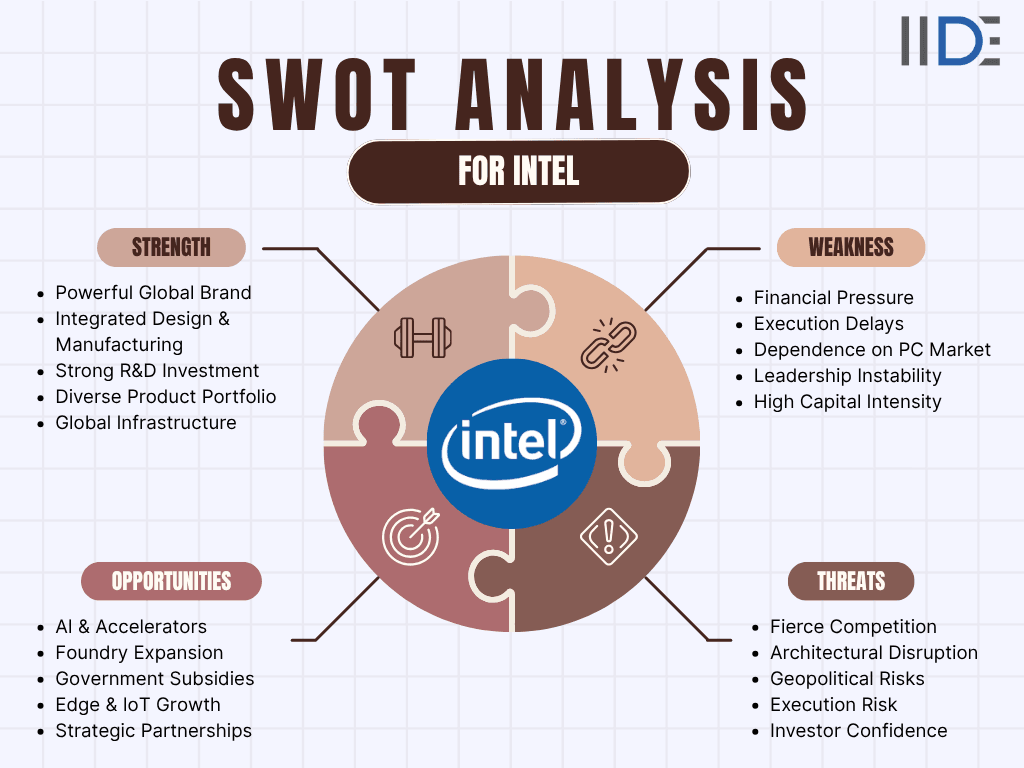
SWOT Analysis of Intel (2025)
The SWOT analysis of Intel (2025) reveals a company at a pivotal moment. Its biggest strengths lie in its trusted global brand, deep R&D capabilities, and integrated manufacturing model (IDM 2.0), which together form a powerful foundation for innovation. However, Intel continues to face weaknesses like execution delays, financial strain, and reliance on a shrinking PC market. Opportunities abound in AI, foundry services, sustainability, and edge computing but rising threats from AMD, NVIDIA, and new chip architectures demand faster, more agile transformation to secure Intel’s future.
Here’s a deep dive into the SWOT Analysis -
1. Strengths of Intel in 2025
Intel remains one of the most influential names in global tech. Even in a hyper-competitive chip market, its innovation, scale, and brand legacy keep it at the center of the semiconductor story.
1. Globally Trusted Brand
- Intel is still the most recognized semiconductor brand worldwide, with over 90% awareness among PC users.
- The legendary “Intel Inside” campaign built unmatched consumer trust and OEM loyalty with brands like Dell, HP, and Lenovo.
- Ranked among the Top 20 global tech brands, Intel’s name continues to carry influence in enterprise and government sectors.
2. Massive R&D and Innovation Power
- With $17.5 billion+ in annual R&D spend, Intel remains an innovation powerhouse.
- Advancements in 18A and 14A nodes, 3D packaging, and Gaudi AI chips keep it relevant in the AI and data-center boom.
- Flagship launches like Granite Rapids Xeon underline its continued technical leadership.
3. Integrated Design & Manufacturing (IDM 2.0)
- Intel’s IDM 2.0 strategy blends in-house fabs with external foundries, offering agility and supply-chain control.
- Government incentives such as the U.S. CHIPS Act back its fab expansions in Arizona and Ireland.
- This structure helps Intel weather global chip shortages and even attract new foundry customers like AMD and Qualcomm.
4. Diversified Product Portfolio
- Intel’s reach spans client computing, data centers, AI, IoT, and networking reducing reliance on PCs.
- The Data Center & AI Group posted 12% YoY growth in early 2025.
- Emerging lines like Arc GPUs and Gaudi AI processors push Intel deeper into high-growth markets.
5. Scale and Strategic Partnerships
- Operating in 70+ countries with 100k+ employees, Intel has unmatched manufacturing scale.
- Partnerships from NVIDIA’s $5B investment to Amazon’s custom AI chips expand its ecosystem and future relevance.
Summary: Intel’s biggest strengths lie in its brand trust, innovation depth, and manufacturing control. These pillars still make it a key driver of the semiconductor industry’s future in 2025.
2. Weaknesses of Intel in 2025
Even a global leader like Intel isn’t immune to challenges. In 2025, Intel’s biggest roadblocks stem from execution missteps, legacy dependence, and the sheer speed at which the industry is evolving.
1. Execution & Manufacturing Delays
- Intel has repeatedly faced production delays on key nodes, most notably its 10 nm and 7 nm transitions.
- Competitors like TSMC and AMD have capitalized, launching faster chips and capturing enterprise demand.
- These setbacks have hurt Intel’s perception as an innovation leader.
2. Financial Pressure & Credit Downgrade
- Despite revenue of $53.1 billion in 2024, profitability remains under pressure.
- In August 2025, Fitch downgraded Intel’s credit rating, citing weak demand and execution risk.
- High capital intensity from fab expansions and debt-servicing costs have reduced cash flexibility.
3. Dependence on a Declining PC Market
- Around 50 % of Intel’s revenue still comes from PCs, a category slowing as consumers shift to AI-driven and mobile devices.
- Gen Z and younger consumers increasingly prioritize portability and energy-efficient computing over traditional desktops.
4. Organizational Instability
- New CEO Lip-Bu Tan’s restructuring includes ~24 000 layoffs, causing uncertainty and morale challenges.
- These internal shifts may distract from long-term innovation goals.
5. Slower AI Market Penetration
- While NVIDIA dominates AI hardware, Intel is still catching up with its Gaudi AI chips and accelerator lines.
- Limited early-stage adoption and marketing awareness have kept Intel from fully leveraging the AI gold rush.
Summary: Intel’s weaknesses center on speed, structure, and focus. Its scale is an advantage, but agility remains its biggest missing piece.
Read Intel’s marketing strategy that focuses on powerful advertising campaigns that highlight innovation, performance, and trust.
3. Opportunities for Intel in 2025
Intel sits at the intersection of several booming global trends AI, sustainability, and Gen Z-driven tech innovation. These shifts open new doors for growth if Intel executes strategically.
1. The AI & Accelerator Revolution
- The global AI semiconductor market is projected to exceed $120 billion by 2030.
- Intel’s Gaudi 3 AI accelerators and Granite Rapids Xeon processors position it to capture enterprise AI workloads.
- Expanding AI partnerships with AWS, Google Cloud, and emerging startups can accelerate adoption.
2. Foundry Expansion & Global Manufacturing Push
- Intel’s IDM 2.0 strategy opens foundry services to external clients, including AMD and Qualcomm.
- Global governments from the U.S. to the EU are offering billions in subsidies under CHIPS Acts, giving Intel a competitive cost edge.
- This opportunity aligns perfectly with Intel’s manufacturing heritage and scale.
3. Sustainability & Green Chip Innovation
- Eco-friendly production is now a consumer and investor priority.
- Intel’s 2030 RISE goals aim for net-zero emissions and water-positive fabs.
- Gen Z, which heavily supports sustainable tech brands, could become a strong driver of Intel’s next-gen brand loyalty.
4. Gen Z Market & Edge Computing Growth
- Gen Z’s mobile-first lifestyle is accelerating edge computing, AR/VR, and wearable AI demand.
- Intel’s low-power processors and Nervana/Movidius AI platforms can lead this transition.
- Collaborations with startups and consumer-tech brands can help Intel stay relevant to younger, innovation-focused consumers.
5. Strategic Partnerships & M&A
- Intel’s $5 billion collaboration with NVIDIA (2025) strengthens cross-industry innovation and credibility.
- Acquiring AI-software startups or energy-efficient chip designers could diversify its ecosystem.
- These moves reinforce Intel’s core strengths: scale, R&D, and global reach to seize future demand.
Summary: Intel’s future growth depends on capitalizing on AI, sustainability, and Gen Z-driven tech shifts in all areas where its brand and R&D power can shine.
4. Threats to Intel in 2025
Intel’s challenges aren’t just internal, the industry around it is changing faster than ever. From new chip architectures to global politics, these external forces could shape Intel’s next decade.
1. Fierce Industry Competition
- Rivals AMD, NVIDIA, TSMC, and Samsung are advancing rapidly with cutting-edge architectures.
- NVIDIA dominates AI GPUs, while TSMC leads manufacturing efficiency both directly threaten Intel’s market share.
2. Technological Disruption (ARM & RISC-V)
- ARM-based chips power almost all mobile devices and are gaining traction in data centers.
- Open-source RISC-V processors are emerging as low-cost, flexible alternatives particularly attractive to startups.
3. Geopolitical & Supply Chain Risks
- Ongoing U.S. - China trade tensions and export restrictions on advanced semiconductors could limit Intel’s reach.
- Regional instability also affects raw-material availability and manufacturing timelines.
4. Economic & Credit Instability
- The 2025 Fitch downgrade highlights investor concern over Intel’s debt exposure and delayed profitability.
- Global inflation and fluctuating demand can pressure capital-heavy industries like semiconductors.
5. Evolving Consumer Preferences
- Gen Z consumers expect energy-efficient, AI-driven, and eco-friendly devices.
- If Intel fails to reposition its brand as sustainable and youth-relevant, it risks losing the next generation of customers.
Summary: Intel faces a future shaped by ruthless competition, new architectures, and shifting consumer values but with the right agility, it can turn these threats into innovation opportunities.
IIDE Student Takeaway & Conclusion
Key Takeaway
Intel’s 2025 story is one of legacy versus agility. The SWOT analysis shows a brand built on unmatched innovation, R&D power, and trust yet challenged by execution gaps, slower AI adoption, and fierce global competition.
Its biggest tension lies in maintaining brand leadership while modernizing for an AI-driven, Gen Z-influenced market that values speed, sustainability, and relevance.
IIDE Student Recommendations
As an IIDE student, I’d recommend Intel to:
- Leverage its brand credibility and IDM 2.0 model to build stronger global collaborations in AI, 5G, and edge computing.
- Adopt agile marketing: Reposition Intel as a “future-focused AI brand,” not just a PC chip maker, using youth-driven campaigns and partnerships.
- Invest in sustainable tech storytelling, highlighting its green fabs and net-zero goals to appeal to Gen Z and eco-conscious investors.
- Build emotional engagement through influencer and educational content that makes complex innovation relatable to consumers.
Future Outlook
Intel stands at a decisive crossroads. Its scale, trust, and technology still make it a global powerhouse but its survival depends on how fast it transforms. If Intel can marry its engineering strength with sharper marketing, faster execution, and youth relevance, it can reclaim leadership in the AI era. The next few years will define whether Intel’s legacy evolves into a comeback story or a lesson in how giants must learn to move faster in a changing world.
Conclusion
Intel stands at a pivotal juncture in 2025, leveraging its trusted brand, extensive R&D, and integrated manufacturing capabilities to maintain its influence in the semiconductor industry. However, execution delays, high competition, and reliance on traditional markets pose significant challenges.
The company's future growth hinges on capitalizing on emerging opportunities such as AI, autonomous vehicles, and edge computing, while swiftly addressing its internal weaknesses. By adapting to industry disruptions and accelerating innovation, Intel can transition from a legacy leader to a pioneer in next-generation technology, ensuring long-term relevance and competitiveness in a rapidly evolving landscape.
Want to Know Why 2,50,000+ Students Trust Us?
Dive into the numbers that make us the #1 choice for career success

MBA - Level
Best For
Fresh Graduates
Mode of Learning
On Campus (Mumbai & Delhi)
Starts from
Mar 23, 2026
Duration
11 Months
Live & Online
Best For
Working Professionals
Mode of Learning
Online
Starts from
Mar 23, 2026
Duration
4-6 Months

Online
Best For
AI Enthusiasts
Mode of Learning
Online
Duration
5 Months

Offline
Best For
12th Passouts
Mode of Learning
On Campus (Mumbai)
Duration
3 Years
Recent Post
Intel designs and manufactures CPUs, GPUs, AI accelerators, memory, and foundry services primarily for computing and data centers.
Intel remains one of the most recognized and trusted semiconductor brands worldwide, built on decades of innovation and partnerships.
Intel’s strengths include integrated manufacturing (IDM 2.0), massive R&D investments, a diversified product portfolio, and strategic partnerships.
Challenges include execution delays, financial pressures with credit downgrades, dependence on the shrinking PC market, and organizational restructuring impacts.
Top competitors are AMD, NVIDIA, TSMC, Samsung, and emerging architecture firms challenging x86 dominance like ARM and RISC-V.
Intel is accelerating AI chip development with Gaudi accelerators and strategic partnerships but trails NVIDIA in early AI hardware adoption.
Intel commits to net-zero emissions and eco-friendly fabs with ‘RISE’ 2030 goals to appeal to environmentally conscious consumers and investors.
In 2025, under CEO Lip-Bu Tan, Intel has restructured including major layoffs (~24,000 employees) and refocused on core businesses to enhance agility and execution.
Aditya Shastri leads the Business Development segment at IIDE and is a seasoned Content Marketing expert. With over a decade of experience, Aditya has trained more than 20,000 students and professionals in digital marketing, collaborating with prestigious institutions and corporations such as Jet Airways, Godrej Professionals, Pfizer, Mahindra Group, Publicis Worldwide, and many others. His ability to simplify complex marketing concepts, combined with his engaging teaching style, has earned him widespread admiration from students and professionals alike.
Aditya has spearheaded IIDE’s B2B growth, forging partnerships with over 40 higher education institutions across India to upskill students in digital marketing and business skills. As a visiting faculty member at top institutions like IIT Bhilai, Mithibai College, Amity University, and SRCC, he continues to influence the next generation of marketers.
Apart from his marketing expertise, Aditya is also a spiritual speaker, often traveling internationally to share insights on spirituality. His unique blend of digital marketing proficiency and spiritual wisdom makes him a highly respected figure in both fields.